Diagnosis
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (February 2024) |
| Sulfhemoglobinemia | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Hematology |
| Symptoms | Cyanosis, urinary tract infection and chronic constipation |
| Complications | Hypoxemia, methemoglobinemia, and hypoxia |
| Duration | 100-120 days (lifespan of red blood cells) |
| Causes | Sulfur medications such as phenacetin, metoclopramide, dapsone, phenzopyridine, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; hydrogen-sulfide-producing intestinal bacteria, such as Morganella morganii |
| Risk factors | Pulmonary arteriovenous malformation |
| Prevention | Avoidance of sulfur-containing compounds including drugs |
| Treatment | Blood transfusions |
Sulfhemoglobinemia is a rare condition in which there is excess sulfhemoglobin (SulfHb) in the blood. The pigment is a greenish derivative of hemoglobin which cannot be converted back to normal, functional hemoglobin. It causes cyanosis even at low blood levels.
It is a rare blood condition in which the β-pyrrole ring of the hemoglobin molecule has the ability to bind irreversibly to any substance containing a sulfur atom. [1] [2] When hydrogen sulfide (H2S) (or sulfide ions) and ferrous ions combine in the heme of hemoglobin, the blood is thus incapable of transporting oxygen to the tissues.
Symptoms include a blueish or greenish coloration of the blood (cyanosis), skin, and mucous membranes, even though a blood count test may not show any abnormalities in the blood. This discoloration is caused by greater than 5 grams per cent of deoxyhemoglobin, or 1.5 grams per cent of methemoglobin, or 0.5 grams per cent of sulfhemoglobin, all serious medical abnormalities.[ citation needed ]
Sulfhemoglobinemia is usually drug induced, with drugs associated with it including sulphonamides, such as sulfasalazine or sumatriptan. Another possible cause is occupational exposure to sulfur compounds.[ citation needed ]
It can also be caused by phenazopyridine. [3]
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (February 2024) |
The condition generally resolves itself with erythrocyte (red blood cell) turnover, although blood transfusions can be necessary in extreme cases.[ citation needed ]
On June 8, 2007, Canadian anesthesiologists Dr. Stephan Schwarz, Dr. Giuseppe Del Vicario, and Dr. Alana Flexman presented an unusual case in The Lancet . [4] A 42-year-old male patient was brought into Vancouver's St. Paul's Hospital after falling asleep in a kneeling position, which caused compartment syndrome and a buildup of pressure in his legs. When doctors drew the man's blood prior to performing the surgery to relieve the pressure from the man's legs, they noted his blood was green. A sample of the blood was immediately sent to a lab. In this case, sulfhemoglobinemia was possibly caused by the patient taking higher-than-prescribed doses of sumatriptan. [5] [6]

Amyl nitrite is a chemical compound with the formula C5H11ONO. A variety of isomers are known, but they all feature an amyl group attached to the nitrite functional group. The alkyl group is unreactive and the chemical and biological properties are mainly due to the nitrite group. Like other alkyl nitrites, amyl nitrite is bioactive in mammals, being a vasodilator, which is the basis of its use as a prescription medicine. As an inhalant, it also has a psychoactive effect, which has led to its recreational use, with its smell being described as that of old socks or dirty feet. It was first documented in 1844 and came into medical use in 1867.

Hypoxia is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply at the tissue level. Hypoxia may be classified as either generalized, affecting the whole body, or local, affecting a region of the body. Although hypoxia is often a pathological condition, variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise.

Hemoglobin is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transport of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin in the blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs to the other tissues of the body, where it releases the oxygen to enable aerobic respiration which powers the animal's metabolism. A healthy human has 12 to 20 grams of hemoglobin in every 100 mL of blood. Hemoglobin is a metalloprotein, a chromoprotein, and globulin.

Red blood cells (RBCs), scientific name erythrocytes (from Greek erythros 'red' and kytos 'hollow vessel', with -cyte translated as 'cell' in modern usage), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells) or haematids, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. Erythrocytes take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries.

Hemoglobinopathy is the medical term for a group of inherited blood disorders and diseases that primarily affect red blood cells. They are single-gene disorders and, in most cases, they are inherited as autosomal co-dominant traits.

Anemia or anaemia is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin or hemoglobin abnormalities. The name is derived from Ancient Greek ἀν- (an-) 'not', and αἷμα (haima) 'blood'. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe.

Methemoglobinemia, or methaemoglobinaemia, is a condition of elevated methemoglobin in the blood. Symptoms may include headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, nausea, poor muscle coordination, and blue-colored skin (cyanosis). Complications may include seizures and heart arrhythmias.

Cyanosis is the change of body tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the body tissues covered with thin skin, including the mucous membranes, lips, nail beds, and ear lobes. Some medications may cause discoloration such as medications containing amiodarone or silver. Furthermore, mongolian spots, large birthmarks, and the consumption of food products with blue or purple dyes can also result in the bluish skin tissue discoloration and may be mistaken for cyanosis. Appropriate physical examination and history taking is a crucial part to diagnose cyanosis. Management of cyanosis involves treating the main cause, as cyanosis isn’t a disease, it is a symptom.
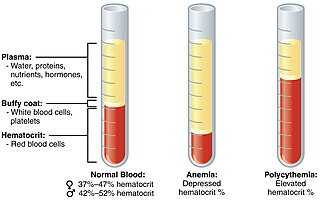
Polycythemia is a laboratory finding in which the hematocrit and/or hemoglobin concentration are increased in the blood. Polycythemia is sometimes called erythrocytosis, and there is significant overlap in the two findings, but the terms are not the same: polycythemia describes any increase in hematocrit and/or hemoglobin, while erythrocytosis describes an increase specifically in the number of red blood cells in the blood.
Sumatriptan, sold under the brand name Imitrex among others, is a medication used to treat migraine headaches and cluster headaches. It is taken orally, intranasally, or by subcutaneous injection. Therapeutic effects generally occur within three hours.

Triptans are a family of tryptamine-based drugs used as abortive medication in the treatment of migraines and cluster headaches. This drug class was first commercially introduced in the 1990s. While effective at treating individual headaches, they do not provide preventive treatment and are not considered a cure. They are not effective for the treatment of tension–type headache, except in persons who also experience migraines. Triptans do not relieve other kinds of pain.

Methemoglobin (British: methaemoglobin, shortened MetHb) (pronounced "met-hemoglobin") is a hemoglobin in the form of metalloprotein, in which the iron in the heme group is in the Fe3+ (ferric) state, not the Fe2+ (ferrous) of normal hemoglobin. Sometimes, it is also referred to as ferrihemoglobin. Methemoglobin cannot bind oxygen, which means it cannot carry oxygen to tissues. It is bluish chocolate-brown in color. In human blood a trace amount of methemoglobin is normally produced spontaneously, but when present in excess the blood becomes abnormally dark bluish brown. The NADH-dependent enzyme methemoglobin reductase (a type of diaphorase) is responsible for converting methemoglobin back to hemoglobin.
Phenazopyridine is a medication which, when excreted by the kidneys into the urine, has a local analgesic effect on the urinary tract. It is often used to help with the pain, irritation, or urgency caused by urinary tract infections, surgery, or injury to the urinary tract.
Hemoglobin C is an abnormal hemoglobin in which glutamic acid residue at the 6th position of the β-globin chain is replaced with a lysine residue due to a point mutation in the HBB gene. People with one copy of the gene for hemoglobin C do not experience symptoms, but can pass the abnormal gene on to their children. Those with two copies of the gene are said to have hemoglobin C disease and can experience mild anemia. It is possible for a person to have both the gene for hemoglobin S and the gene for hemoglobin C; this state is called hemoglobin SC disease, and is generally more severe than hemoglobin C disease, but milder than sickle cell anemia.

Hypochromic anemia is a generic term for any type of anemia in which the red blood cells are paler than normal. A normal red blood cell has a biconcave disk shape and will have an area of pallor in its center when viewed microscopically. In hypochromic cells, this area of central pallor is increased. This decrease in redness is due to a disproportionate reduction of red cell hemoglobin in proportion to the volume of the cell. Clinically the color can be evaluated by the mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) or mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). The MCHC is considered the better parameter of the two as it adjusts for effect the size of the cell has on its amount of hemoglobin. Hypochromia is clinically defined as below the normal MCH reference range of 27–33 picograms/cell in adults or below the normal MCHC reference range of 33–36 g/dL in adults.

Hemoglobinemia is a medical condition in which there is an excess of hemoglobin in the blood plasma. This is an effect of intravascular hemolysis, in which hemoglobin separates from red blood cells, a form of anemia.

Oxygen saturation is the fraction of oxygen-saturated haemoglobin relative to total haemoglobin in the blood. The human body requires and regulates a very precise and specific balance of oxygen in the blood. Normal arterial blood oxygen saturation levels in humans are 96–100 percent. If the level is below 90 percent, it is considered low and called hypoxemia. Arterial blood oxygen levels below 80 percent may compromise organ function, such as the brain and heart, and should be promptly addressed. Continued low oxygen levels may lead to respiratory or cardiac arrest. Oxygen therapy may be used to assist in raising blood oxygen levels. Oxygenation occurs when oxygen molecules enter the tissues of the body. For example, blood is oxygenated in the lungs, where oxygen molecules travel from the air and into the blood. Oxygenation is commonly used to refer to medical oxygen saturation.
Hemoglobin O (HbO) is a rare type of hemoglobin in which there is a substitution of glutamic acid by lysine as in hemoglobin C, but at different positions. Since the amino acid substitution can occur at different positions of the β-globin chain of the protein, there are several variants. In hemoglobin O-Arab (HbO-Arab) substitution occurs at position 121, while in hemoglobin O-Padova (HbO-Padova) it is at 11 position, and in hemoglobin O Indonesia (HbOIna) it is at 116.
Hemolytic jaundice, also known as prehepatic jaundice, is a type of jaundice arising from hemolysis or excessive destruction of red blood cells, when the byproduct bilirubin is not excreted by the hepatic cells quickly enough. Unless the patient is concurrently affected by hepatic dysfunctions or is experiencing hepatocellular damage, the liver does not contribute to this type of jaundice.

Hemoglobin M disease is a rare form of hemoglobinopathy, characterized by the presence of hemoglobin M (HbM) and elevated methemoglobin (metHb) level in blood. HbM is an altered form of hemoglobin (Hb) due to point mutation occurring in globin-encoding genes, mostly involving tyrosine substitution for proximal (F8) or distal (E7) histidine residues. HbM variants are inherited as autosomal dominant disorders and have altered oxygen affinity. The pathophysiology of hemoglobin M disease involves heme iron autoxidation promoted by heme pocket structural alteration.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)