A dining car or a restaurant car (English), also a diner, is a railroad passenger car that serves meals in the manner of a full-service, sit-down restaurant.

The Southwest Chief is a long-distance passenger train operated by Amtrak on a 2,265-mile (3,645 km) route between Chicago and Los Angeles through the Midwest and Southwest via Kansas City, Albuquerque, and Flagstaff mostly on the BNSF's Southern Transcon, but branches off between Albuquerque and Kansas City via the Topeka, La Junta, Raton, and Glorieta Subdivision. Amtrak bills the route as one of its most scenic, with views of the Painted Desert and the Red Cliffs of Sedona, as well as the plains of Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, and Colorado.

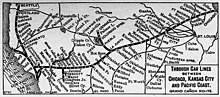
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States between 1859 and 1996.

The City of Los Angeles was a streamlined passenger train between Chicago, Illinois, and Los Angeles, California via Omaha, Nebraska, and Ogden, Utah. Between Omaha and Los Angeles it ran on the Union Pacific Railroad; east of Omaha it ran on the Chicago and North Western Railway until October 1955 and on the Milwaukee Road thereafter. The train had number 103 westbound and number 104 eastbound.

A dome car is a type of railway passenger car that has a glass dome on the top of the car where passengers can ride and see in all directions around the train. It also can include features of a coach, lounge car, dining car, sleeping car or observation. Beginning in 1945, dome cars were primarily used in the United States and Canada, though a small number were constructed in Europe for Trans Europ Express service.

The Union Pacific Railroad's M-10002 was a diesel-electric streamliner train built in 1936 by Pullman-Standard, with prime movers from the Winton Engine division of General Motors Corporation and General Electric generator, control equipment and traction motors. It was the UP's third streamliner, and the last turret-cab streamliner.

The El Capitan was a streamlined passenger train operated by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway between Chicago, Illinois, and Los Angeles, California. It operated from 1938 to 1971; Amtrak retained the name until 1973. The El Capitan was the only all-coach or "chair car" to operate on the Santa Fe main line between Chicago and Los Angeles on the same fast schedule as the railroad's premier all-Pullman Super Chief. It was also the first train to receive the pioneering Hi-Level equipment with which it would become synonymous.

The Chief was an American long-distance named passenger train of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway that ran between Chicago, Illinois and Los Angeles, California. The Santa Fe initiated the Chief in 1926 to supplement the California Limited. In 1936 the Super Chief was introduced, after the Super Chief was relaunched in 1948 with daily departures from LA and Chicago it gradually eclipsed the Chief as the standard bearer of the Santa Fe because of its timetable oriented to the Raton Pass transit. For some the Chief and San Francisco Chief as deluxe integrated trains with both Pullman sleepers and fully reclining coach seating with all facilities; lounges and pleasure domes, available to all passengers were at least equal flagships better suited to the business and executive market. From the mid 1960s the super Chief was only a small entirely separate section of the El Capitan seated vista train, the El Capitan passengers having no access to the Super Chiefs expensive eateries and bars which selling point was exclusion and service. The Chief was discontinued in 1968 due to high operating costs, competition from airlines, and the loss of Postal Office contracts.

The Coast Daylight, originally known as the Daylight Limited, was a passenger train on the Southern Pacific Railroad (SP) between Los Angeles and San Francisco, California, via SP's Coast Line. It was advertised as the "most beautiful passenger train in the world," carrying a particular red, orange, and black color scheme. The train operated from 1937 until 1974, being retained by Amtrak in 1971. Amtrak merged it with the Coast Starlight in 1974.

The California Limited was one of the named passenger trains of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. It carried train Nos. 3 & 4 and ran between Chicago, Illinois, and Los Angeles, California.

The Grand Canyon Limited was one of the named passenger trains of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. It was train Nos. 23 & 24 between Chicago, Illinois, and Los Angeles, California.

The San Francisco Chief was a streamlined passenger train on the Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe Railway between Chicago and the San Francisco Bay Area. It ran from 1954 until 1971. The San Francisco Chief was the last new streamliner introduced by the Santa Fe, its first full train between Chicago and the Bay, the only Chicago–Bay Area train running over just one railroad, and at 2,555 miles (4,112 km) the longest run in the country on one railroad. The San Francisco Chief was one of many trains discontinued when Amtrak began operations in 1971.

The Santa Fe de Luxe was the first extra-fare named passenger train on the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.

The Golden State was a named passenger train between Chicago and Los Angeles from 1902–1968 on the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad and the Southern Pacific Company (SP) and predecessors. It was named for California, the “Golden State”.

The Capitol Limited was an American passenger train run by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, originally between New York City and Grand Central Station in Chicago, via Washington Union Station in Washington, D.C., Camden Station in Baltimore, and Pittsburgh. For almost 48 years, it was the B&O's flagship passenger train, noted for personalized service and innovation. At the time of its discontinuation on May 1, 1971, when Amtrak took over most rail passenger service in the U.S., the Capitol Limited operated between Washington and Chicago.

The City of San Francisco was a streamlined through passenger train which ran from 1936 to 1971 on the Overland Route between Chicago, Illinois and Oakland, California, with a ferry connection on to San Francisco. It was owned and operated jointly by the Chicago and North Western Railway (1936–55), Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (1955–71), the Union Pacific Railroad, and the Southern Pacific Railroad. It provided premium extra fare service from Chicago to San Francisco when introduced in 1936 with a running time of 39 hours and 45 minutes each way.

The Scott Special, also known as the Coyote Special, the Death Valley Coyote or the Death Valley Scotty Special, was a one-time, record-breaking passenger train operated by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway from Los Angeles, California, to Chicago, Illinois, at the request of Walter E. Scott, known as "Death Valley Scotty". At the time of its transit in 1905, the Scott Special made the 2,265-mile (3,645 km) trip between the two cities at the fastest speed recorded to date; in doing so, it established the Santa Fe as the leader in high-speed travel between Chicago and the West Coast. The Scott Special made the trip in 44 hours and 54 minutes breaking the previous records, set in 1900 by the Peacock Special, by 13 hours and 2 minutes, and in 1903 by the Lowe Special, by 7 hours and 55 minutes. Santa Fe's regular passenger service from Los Angeles to Chicago at the time was handled on a 2½-day schedule by the California Limited. It was not until the 1936 introduction of the Super Chief that Santa Fe trains would regularly exceed the speeds seen on the Scott Special.

The Museum of the American Railroad, formerly known as the Age of Steam Railroad Museum, is a railroad museum in Frisco, Texas. The museum has more than 70 pieces of steam, diesel, passenger, and freight railroad equipment sitting on 15 acres making it one of the largest historic rail collections in the US. Guests may walk through some of the equipment on guided tours.

The Texas Chief was a passenger train operated by the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway between Chicago, Illinois and Galveston, Texas. It was the first Santa Fe "Chief" outside the Chicago–Los Angeles routes. The Santa Fe conveyed the Texas Chief to Amtrak in 1971, which renamed it the Lone Star in 1974. The train was discontinued in 1979.

The Hi-Level was a type of bilevel intercity railroad passenger car used in the United States. Car types included coaches, dining cars, and lounge cars; a sleeping car variant was considered but never produced. Most passenger spaces were on the upper level, which featured a row of windows on both sides. Boarding was on the lower level; passengers climbed up a center stairwell to reach the upper level. Vestibules on the upper level permitted passengers to walk between cars; some coaches had an additional stairwell at one end to allow access to single-level equipment.