
First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person with either a minor or serious illness or injury, with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, or to promote recovery. It includes initial intervention in a serious condition prior to professional medical help being available, such as performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) while waiting for an ambulance, as well as the complete treatment of minor conditions, such as applying a plaster to a cut. First aid is generally performed by someone with basic medical training. Mental health first aid is an extension of the concept of first aid to cover mental health, while psychological first aid is used as early treatment of people who are at risk for developing PTSD. Conflict First Aid, focused on preservation and recovery of an individual's social or relationship well-being, is being piloted in Canada.

A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers (Pentadactyly).

A diving suit is a garment or device designed to protect a diver from the underwater environment. A diving suit may also incorporate a breathing gas supply. but in most cases the term applies only to the environmental protective covering worn by the diver. The breathing gas supply is usually referred to separately. There is no generic term for the combination of suit and breathing apparatus alone. It is generally referred to as diving equipment or dive gear along with any other equipment necessary for the dive.

The capitate bone is a bone in the human wrist found in the center of the carpal bone region, located at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone and forms the third carpometacarpal joint. The capitate bone is the largest of the carpal bones in the human hand. It presents, above, a rounded portion or head, which is received into the concavity formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones; a constricted portion or neck; and below this, the body. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "third distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.

A finger cot is a medical device used to cover one or more fingers in situations where a full glove seems unnecessary. Like medical and rubber gloves, finger cots may be made from a variety of water-tight materials including latex, nitrile rubber, and vinyl.

Dupuytren's contracture is a condition in which one or more fingers become progressively bent in a flexed position. It is named after Guillaume Dupuytren, who first described the underlying mechanism of action, followed by the first successful operation in 1831 and publication of the results in The Lancet in 1834. It usually begins as small, hard nodules just under the skin of the palm, then worsens over time until the fingers can no longer be fully straightened. While typically not painful, some aching or itching may be present. The ring finger followed by the little and middle fingers are most commonly affected. It can affect one or both hands. The condition can interfere with activities such as preparing food, writing, putting your hand in a tight pocket, putting on gloves, or shaking hands.
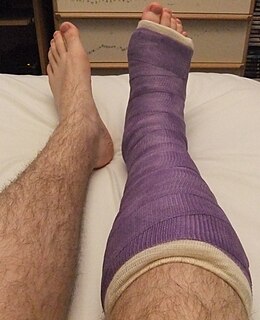
An orthopedic cast, or simply cast, is a shell, frequently made from plaster or fiberglass, that encases a limb to stabilize and hold anatomical structures—most often a broken bone, in place until healing is confirmed. It is similar in function to a splint.

A boxer's fracture is the break of the 5th metacarpal bones of the hand near the knuckle. Occasionally it is used to refer to fractures of the 4th metacarpal as well. Symptoms include pain and a depressed knuckle.
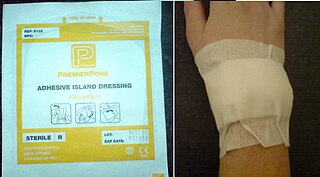
A dressing is a sterile pad or compress applied to a wound to promote healing and protect the wound from further harm. A dressing is designed to be in direct contact with the wound, as distinguished from a bandage, which is most often used to hold a dressing in place. Many modern dressings are self-adhesive.

Surgical tape or medical tape is a type of pressure-sensitive adhesive tape used in medicine and first aid to hold a bandage or other dressing onto a wound. These tapes usually have a hypoallergenic adhesive which is designed to hold firmly onto skin, dressing materials, and underlying layers of tape, but to remove easily without damaging the skin. They allow air to reach the skin ("breathable"). Some breathable tapes such as kinesiology tape, and other elastic bandages with adhesive are made of cotton. Surgical tape is often white because it contains zinc oxide, which is added to help prevent infections. Tapes made of porous material, such as 3M Micropore, are widely used.
The history of wound care spans from prehistory to modern medicine. Wounds naturally heal by themselves, but hunter-gatherers would have noticed several factors and certain herbal remedies would speed up or assist the process, especially if it was grievous. In ancient history, this was followed by the realisation of the necessity of hygiene and the halting of bleeding, where wound dressing techniques and surgery developed. Eventually the germ theory of disease also assisted in improving wound care.

Negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT), also known as a vacuum assisted closure (VAC), is a therapeutic technique using a suction pump, tubing and a dressing to remove excess exudate and promote healing in acute or chronic wounds and second- and third-degree burns. The therapy involves the controlled application of subatmospheric pressure to the local wound environment using a sealed wound dressing connected to a vacuum pump. The use of this technique in wound management started in the 1990s and this technique is often recommended for treatment of a range of wounds including dehisced surgical wounds, closed surgical wounds, open abdominal wounds, open fractures, pressure injuries or pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, venous insufficiency ulcers, some types of skin grafts, burns, sternal wounds. It may also be considered after a clean surgery in a person who is obese.

Buddy wrapping, also called neighbour strapping or buddy taping, is the act of bandaging a damaged or particularly a fractured finger or toe together with a healthy one. The bandage or medical tape is usually stiff, not allowing the digits to move; the healthy digit acts as a splint, keeping the damaged one in a natural position for healing. Rest plays a major role in the healing process. Buddy wrapping may also be used for sprains, dislocations, and other injuries.

In medicine, an avulsion is an injury in which a body structure is torn off by either trauma or surgery. The term most commonly refers to a surface trauma where all layers of the skin have been torn away, exposing the underlying structures. This is similar to an abrasion but more severe, as body parts such as an eyelid or an ear can be partially or fully detached from the body.

A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking.

An ulna fracture is a break in the ulna bone, one of the two bones in the forearm. It is often associated with a fracture of the other forearm bone, the radius.

Athletic taping is the process of applying tape directly to the skin or over pre-wrap in order to maintain a stable position of bones and muscles during athletic activity. It is a procedure that uses athletic tape, attached to the skin, to physically hold muscles or bones at a certain position. This reduces pain and aids recovery. Taping is usually used to help recover from overuse and other injuries.

Pressure-sensitive tape, known also in various countries as PSA tape, adhesive tape, self-stick tape, sticky tape, Sellotape, or just tape, is an adhesive tape that will stick with application of pressure, without the need for a solvent or heat for activation. It can be used in the home, office, industry, and institutions for a wide variety of purposes.

A broken toe is a type of bone fracture. Symptoms include pain when the toe is touched near the break point, or compressed along its length. There may be bruising, swelling, stiffness, or displacement of the broken bone ends from their normal position.
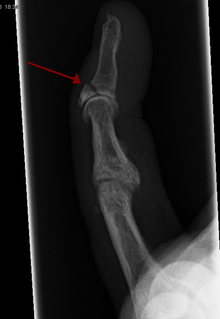
A broken finger or finger fracture is a common type of bone fracture, affecting a finger. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, tenderness, bruising, deformity and reduced ability to move the finger. Although most finger fractures are easy to treat, failing to deal with a fracture appropriately may result in long-term pain and disability.



















