
Androsterone, or 3α-hydroxy-5α-androstan-17-one, is an endogenous steroid hormone, neurosteroid, and putative pheromone. It is a weak androgen with a potency that is approximately 1/7 that of testosterone. Androsterone is a metabolite of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). In addition, it can be converted back into DHT via 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, bypassing conventional intermediates such as androstanedione and testosterone, and as such, can be considered to be a metabolic intermediate in its own right.
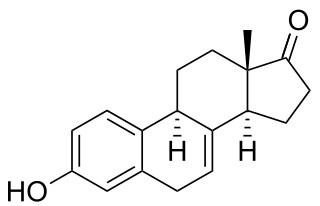
Equilin is a naturally occurring estrogen sex hormone found in horses as well as a medication. It is one of the estrogens present in the estrogen mixtures known as conjugated estrogens and esterified estrogens. CEEs is the most commonly used form of estrogen in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for menopausal symptoms in the United States. Estrone sulfate is the major estrogen in CEEs while equilin sulfate is the second major estrogen in the formulation, present as about 25% of the total.

Deoxyadenosine monophosphate (dAMP), also known as deoxyadenylic acid or deoxyadenylate in its conjugate acid and conjugate base forms, respectively, is a derivative of the common nucleic acid AMP, or adenosine monophosphate, in which the -OH (hydroxyl) group on the 2' carbon on the nucleotide's pentose has been reduced to just a hydrogen atom. Deoxyadenosine monophosphate is abbreviated dAMP. It is a monomer used in DNA.
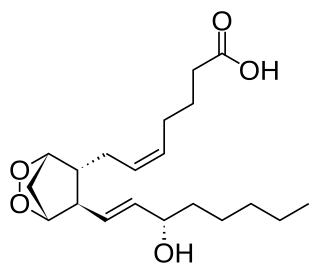
Prostaglandin H2 is a type of prostaglandin and a precursor for many other biologically significant molecules. It is synthesized from arachidonic acid in a reaction catalyzed by a cyclooxygenase enzyme. The conversion from Arachidonic acid to Prostaglandin H2 is a two step process. First, COX-1 catalyzes the addition of two free oxygens to form the 1,2-Dioxane bridge and a peroxide functional group to form Prostaglandin G2. Second, COX-2 reduces the peroxide functional group to a Secondary alcohol, forming Prostaglandin H2. Other peroxidases like Hydroquinone have been observed to reduce PGG2 to PGH2. PGH2 is unstable at room temperature, with a half life of 90-100 seconds, so it is often converted into a different prostaglandin.

3α-Androstanediol glucuronide (3α-ADG) is a metabolite formed from human androgens; compounds involved in the development and maintenance of sexual characteristics. It is formed by the glucuronidation of both dihydrotestosterone and testosterone, and has been proposed as means of measuring androgenic activity.

An estrogen conjugate is a conjugate of an endogenous estrogen. They occur naturally in the body as metabolites of estrogens and can be reconverted back into estrogens. They serve as a circulating reservoir for estrogen, particularly in the case of orally administered pharmaceutical estradiol. Estrogen conjugates include sulfate and/or glucuronide conjugates of estradiol, estrone, and estriol:

Estriol glucuronide (E3G), or oestriol glucuronide, also known as estriol monoglucuronide, as well as estriol 16α-β-D-glucosiduronic acid, is a natural, steroidal estrogen and the glucuronic acid conjugate of estriol. It occurs in high concentrations in the urine of pregnant women as a reversibly formed metabolite of estriol. Estriol glucuronide is a prodrug of estriol, and was the major component of Progynon and Emmenin, estrogenic products manufactured from the urine of pregnant women that were introduced in the 1920s and 1930s and were the first orally active estrogens. Emmenin was succeeded by Premarin, which is sourced from the urine of pregnant mares and was introduced in 1941. Premarin replaced Emmenin due to the fact that it was easier and less expensive to produce.

Estradiol glucuronide, or estradiol 17β-D-glucuronide, is a conjugated metabolite of estradiol. It is formed from estradiol in the liver by UDP-glucuronyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys. It has much higher water solubility than does estradiol. Glucuronides are the most abundant estrogen conjugates.
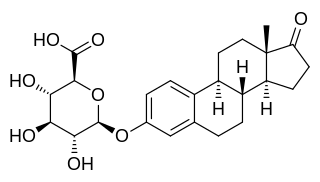
Estrone glucuronide, or estrone-3-D-glucuronide, is a conjugated metabolite of estrone. It is formed from estrone in the liver by UDP-glucuronyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys. It has much higher water solubility than does estrone. Glucuronides are the most abundant estrogen conjugates and estrone glucuronide is the dominant metabolite of estradiol.

Estriol sulfate, or estriol 3-sulfate, is a conjugated metabolite of estriol that is present in high quantities during pregnancy. It is formed from estriol in the liver and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys. It has much higher water solubility than does estriol. Estriol sulfate is the second most prevalent conjugated metabolite of estriol during pregnancy; 35 to 46% is estriol glucuronide and 15 to 22% is estriol 3-sulfate, while the double conjugate estriol sulfate glucuronide also occurs. Estriol sulfate was a component, along with estriol glucuronide, of the early pharmaceutical estrogens Progynon and Emmenin.

Estriol sulfate glucuronide, or estriol 3-sulfate 16α-glucuronide, is an endogenous, naturally occurring diconjugated metabolite of estriol. It is generated in the liver from estriol sulfate by UDP-glucuronyltransferase and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys. It occurs in high concentrations during pregnancy along with estriol sulfate and estriol glucuronide, and was a component of the early pharmaceutical estrogens Progynon and Emmenin.

Androsterone glucuronide (ADT-G) is a major circulating and urinary metabolite of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It accounts for 93% of total androgen glucuronides in women. ADT-G is formed from androsterone by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, with the major enzymes being UGT2B15 and UGT2B17. It is a marker of acne in women while androstanediol glucuronide is a marker of hirsutism in women.
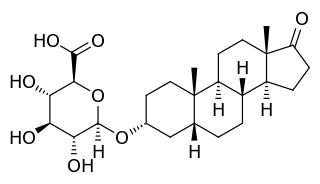
Etiocholanolone glucuronide (ETIO-G) is an endogenous, naturally occurring metabolite of testosterone. It is formed in the liver from etiocholanolone by UDP-glucuronyltransferases. ETIO-G has much higher water solubility than etiocholanolone and is eventually excreted in the urine via the kidneys. Along with androsterone glucuronide, it is one of the major inactive metabolites of testosterone.

Testosterone glucuronide is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and minor urinary metabolite of testosterone.
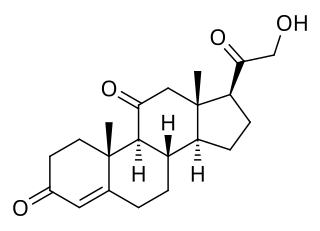
11-Dehydrocorticosterone (11-DHC), also known as 11-oxocorticosterone or 17-deoxycortisone, as well as 21-hydroxypregn-4-ene-3,11,20-trione, is a naturally occurring, endogenous corticosteroid related to cortisone and corticosterone. It is a potent mineralocorticoid, with generally greater such activity than that of corticosterone.

Androsterone sulfate, also known as 3α-hydroxy-5α-androstan-17-one 3α-sulfate, is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and one of the major urinary metabolites of androgens. It is a steroid sulfate which is formed from sulfation of androsterone by the steroid sulfotransferase SULT2A1 and can be desulfated back into androsterone by steroid sulfatase.

Estrone sulfate (E1S) is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is used in menopausal hormone therapy among other indications. As the sodium salt, it is the major estrogen component of conjugated estrogens (Premarin) and esterified estrogens. In addition, E1S is used on its own as the piperazine salt estropipate. The compound also occurs as a major and important metabolite of estradiol and estrone. E1S is most commonly taken by mouth, but in the form of Premarin can also be taken by parenteral routes such as transdermal, vaginal, and injection.

Estradiol 3-glucuronide (E2-3G), also known as 17β-estradiol 3-(β-D-glucuronide), is a naturally occurring and endogenous estrogen conjugate. It is specifically the C3 glucuronide conjugate of estradiol, the major estrogen in the body. It is formed from estradiol in the liver by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in urine and bile. Similarly to estrogen sulfates like estrone sulfate, estrogen glucuronides have much higher water solubility than do unconjugated estrogens like estradiol.
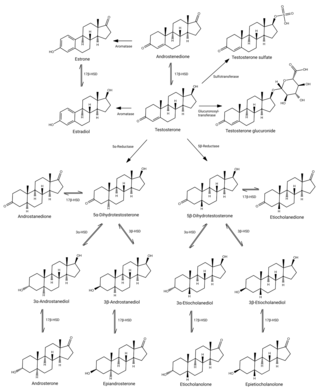
An androgen conjugate is a conjugate of an androgen, such as testosterone. They occur naturally in the body as metabolites of androgens. Androgen conjugates include sulfate esters and glucuronide conjugates and are formed by sulfotransferase and glucuronosyltransferase enzymes, respectively. In contrast to androgens, conjugates of androgens do not bind to the androgen receptor and are hormonally inactive. However, androgen conjugates can be converted back into active androgens through enzymes like steroid sulfatase.

Estradiol 3-glucuronide 17β-sulfate (E2-3G-17S) is an endogenous estrogen conjugate and metabolite of estradiol. It is related to estradiol 3-sulfate and estradiol 17β-glucuronide. Estradiol 3-glucuronide 17β-sulfate has 0.0001% of the relative binding affinity of estradiol for the ERα, one of the two estrogen receptors (ERs). It shows less than one million-fold lower potency in activating the estrogen receptors relative to estradiol in vitro.



















