Related Research Articles

Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery and liberate slaves around the world.

Salem is a city in northern Columbiana County, Ohio, United States. At the 2020 census, the city's population was 11,915. Extending into southern Mahoning County, it is the principal city of the Salem micropolitan area, which includes all of Columbiana County. It lies about 18 miles (29 km) southwest of Youngstown, 28 miles (45 km) east of Canton, and 60 miles (97 km) southeast of Cleveland.

Mount Pleasant is a village in southern Jefferson County, Ohio, United States. The population was 394 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Weirton–Steubenville metropolitan area. Founded in 1803 by anti-slavery Quakers, the village was an early center of abolitionist activity and a well-known haven for fugitive slaves on the Underground Railroad.

William Lloyd Garrison was an American abolitionist, journalist, social reformer and antisemite. He is best known for his widely read anti-slavery newspaper The Liberator, which Garrison founded in 1831 and published in Boston until slavery in the United States was abolished by the Thirteenth Amendment in 1865.

Benjamin Lundy was an American Quaker abolitionist from New Jersey of the United States who established several anti-slavery newspapers and traveled widely. He lectured and published seeking to limit slavery's expansion and tried to find a place outside the United States to establish a colony in which freed slaves might relocate.
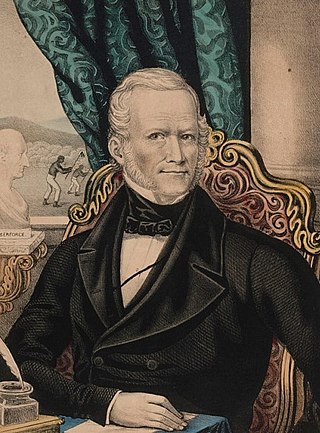
James Gillespie Birney was an American abolitionist, politician, and attorney born in Danville, Kentucky. He changed from being a planter and slave owner to abolitionism, publishing the abolitionist weekly The Philanthropist. He twice served as the presidential nominee for the anti-slavery Liberty Party.

The Liberator (1831–1865) was a weekly abolitionist newspaper, printed and published in Boston by William Lloyd Garrison and, through 1839, by Isaac Knapp. Religious rather than political, it appealed to the moral conscience of its readers, urging them to demand immediate freeing of the slaves ("immediatism"). It also promoted women's rights, an issue that split the American abolitionist movement. Despite its modest circulation of 3,000, it had prominent and influential readers, including all the abolitionist leaders, among them Frederick Douglass, Beriah Green, Arthur and Lewis Tappan, and Alfred Niger. It frequently printed or reprinted letters, reports, sermons, and news stories relating to American slavery, becoming a sort of community bulletin board for the new abolitionist movement that Garrison helped foster.

Christian views on slavery are varied regionally, historically and spiritually. Slavery in various forms has been a part of the social environment for much of Christianity's history, spanning well over eighteen centuries. Saint Augustine described slavery as being against God's intention and resulting from sin. In the eighteenth century the abolition movement took shape among Christians across the globe.
The bugle is a brass musical instrument.
The Genius of Universal Emancipation was an abolitionist newspaper founded by Benjamin Lundy in 1821, in Mount Pleasant, Ohio.

Elizabeth Margaret Chandler was an American poet and writer from Pennsylvania and Michigan. She became the first female writer in the United States to make the abolition of slavery her principal theme.
Elihu Embree was an abolitionist in Jonesborough, Tennessee, and publisher of Manumission Intelligencier. Founded in 1819, it was the first newspaper in the United States devoted exclusively to the cause of abolishing slavery.
The Manumission Intelligencier was an abolitionist newspaper founded by Elihu Embree, a Quaker, in 1819. It was later renamed The Emancipator.
The Emancipator (1833–1850) was an American abolitionist newspaper, at first published in New York City and later in Boston. It was founded as the official newspaper of the American Anti-Slavery Society (AASS). From 1840 to 1850, it was published by the Liberty Party; the publication changed names several times as it merged with other abolitionist newspapers in Boston.

Barclay Coppock, also spelled "Coppac", "Coppic", and "Coppoc", was a follower of John Brown and a Union Army soldier in the American Civil War. Along with his brother Edwin Coppock, he participated in Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry.

In the United States, abolitionism, the movement that sought to end slavery in the country, was active from the colonial era until the American Civil War, the end of which brought about the abolition of American slavery, except as punishment for a crime, through the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.
Jane Elizabeth Jones was an American suffragist and abolitionist and member of the early women's rights movement.
The Ohio Women's Convention at Salem in 1850 met on April 19–20, 1850 in Salem, Ohio, a center for reform activity. It was the third in a series of women's rights conventions that began with the Seneca Falls Convention of 1848. It was the first of these conventions to be organized on a statewide basis. About five hundred people attended. All of the convention's officers were women. Men were not allowed to vote, sit on the platform or speak during the convention. The convention sent a memorial to the convention that was preparing a new Ohio state constitution, asking it to provide for women's right to vote.

The Union Literary Institute, located in rural Randolph County, Indiana, at 8605 East County Road 600 South, Union City, Indiana, was a historic school founded in 1846 primarily for blacks by abolitionist Quakers and free blacks in three local communities. Only white students were allowed to attend the public schools in the state. The term "literary institute" at the time meant a non-religious school.

Marius Robinson (1806–1878) was an American minister, abolitionist, and newspaper editor of the antislavery newspaper The Philanthropist and The Anti-Slavery Bugle. He helped establish a school for African Americans in Cincinnati, Ohio while attending Lane Seminary. Responding to backlash from the city's residents, he continued to teach and was one of the Lane Rebels who would not be pressured to give up improving the lives of African Americans. He was an anti-slavery lecturer. He worked together with his wife Emily Rakestraw Robinson, to better the lives of African Americans.
References
- ↑ "About Anti-slavery bugle. (New-Lisbon, Ohio) 1845-1861". African American Newspapers. Library of Congress. Retrieved 11 December 2012.