
Tarbosaurus is a genus of tyrannosaurine theropod dinosaur that lived in Asia about 72 million years ago to 68 million years ago, during the Maastrichtian age at the end of the Late Cretaceous period, considered to contain a single known species: Tarbosaurus bataar. Fossils have been recovered from the Nemegt Formation of Mongolia, with more fragmentary remains found further afield in the Subashi Formation of China.

George Edward Challenger is a fictional character in a series of fantasy and science fiction stories by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. Unlike Doyle's self-controlled, analytical character, Sherlock Holmes, Professor Challenger is an aggressive, hot-tempered, dominating figure.

The Lost World is a science fiction novel by British writer Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, published by Hodder & Stoughton in 1912, concerning an expedition to a plateau in the Amazon basin of South America where prehistoric animals still survive. It was originally published serially in the Strand Magazine and illustrated by New-Zealand-born artist Harry Rountree during the months of April–November 1912. The character of Professor Challenger was introduced in this book. The novel also describes a war between indigenous people and a vicious tribe of ape-like creatures.

The Maryland Science Center, located in Baltimore's Inner Harbor, opened to the public in 1976. It includes three levels of exhibits, a planetarium, and an observatory. It was one of the original structures that drove the revitalization of the Baltimore Inner Harbor from its industrial roots to a thriving downtown destination. In 1987, an IMAX theater was added, but the museum continued to show its age as the end of the 20th century approached. In May 2004, a large addition to the property was opened, and the modernized hands-on exhibits now include more than two dozen dinosaur skeletons. Subjects that the center displays include physical science, space, and the human body.

The Lost World is a 1925 American silent fantasy giant monster adventure film directed by Harry O. Hoyt and written by Marion Fairfax, adapted from Arthur Conan Doyle's 1912 novel of the same name.

The Lost World is a syndicated television series loosely based on the 1912 novel by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, The Lost World. The show premiered in the United States in the fall of 1999. It ran for three seasons, the final two of which aired in syndication in the United States, before it was cancelled in 2002 after funding for a fourth season fell through. The final episode ended with an unresolved cliffhanger. All three seasons were released in DVD box sets in 2004.

Museum of the Rockies is a museum in Bozeman, Montana. Originally affiliated with Montana State University in Bozeman, and now also, the Smithsonian Institution. The museum is largely known for its Paleontological collections as well as having the largest collection of North American Dinosaur fossils in the United States. They also possess the largest Tyrannosaurus skull ever discovered, as well as the thigh bone of a Tyrannosaurus rex that contains soft-tissue remains. The museum is part of the Montana Dinosaur Trail and is Montana's official repository for Paleontological specimens.
Susan Hendrickson is an American explorer and fossil collector. Hendrickson is best known for her discovery of the remains of a Tyrannosaurus rex in South Dakota on August 12, 1990, in the Cheyenne River Reservation. Her discovery is the most complete skeleton of Tyrannosaurus known to science. This skeleton is now known as "Sue" in honor of her. It is on display at the Field Museum in Chicago, Illinois. She has also found other important fossils and artifacts around the world.

The Lost World is a 2001 British made-for-television film adaptation of the 1912 novel of the same name by Arthur Conan Doyle, directed by Stuart Orme and adapted by Tony Mulholland and Adrian Hodges. It was filmed at various locations on the West Coast of New Zealand. The 145-minute film was divided into two 75-minute episodes when broadcast on BBC One on 25 and 26 December 2001, receiving 8.68 million and 6.98 million viewers respectively. Bob Hoskins played Professor Challenger and was supported by James Fox, Peter Falk, Matthew Rhys, Tom Ward and Elaine Cassidy.

Tyrannosaurus rex is unique among dinosaurs in its place in modern culture; paleontologist Robert Bakker has called it "the most popular dinosaur among people of all ages, all cultures, and all nationalities". Paleontologists Mark Norell and Lowell Dingus have likewise called it "the most famous dinosaur of all times." Paleoartist Gregory S. Paul has called it "the theropod. [...] This is the public's favorite dinosaur [...] Even the formations it is found in have fantastic names like Hell Creek and Lance." Other paleontologists agree with that and note that whenever a museum erects a new skeleton or bring in an animatronic model, visitor numbers go up. "Jurassic Park and King Kong would not have been the same without it." In the public mind, T. rex sets the standard of what a dinosaur should be. Science writer Riley Black similarly states, "In all of prehistory, there is no animal that commands our attention quite like Tyrannosaurus rex, the king of the tyrant lizards. Since the time this dinosaur was officially named in 1905, the enormous carnivore has stood as the ultimate dinosaur."

The Lost World is a 1960 American fantasy adventure film directed by Irwin Allen, loosely based on the 1912 novel of the same name by Arthur Conan Doyle. Shot in De Luxe Color and CinemaScope, the film's plot revolves around the exploration of a plateau in Venezuela inhabited by cannibals, dinosaurs, carnivorous plants, and giant spiders. The cast includes Claude Rains, David Hedison, Fernando Lamas, Jill St. John, and Michael Rennie.

T-Rex: Back to the Cretaceous is a 1998 American educational adventure film shot for the IMAX 3D format. The film is directed by Brett Leonard. Executive producer/co-writer Andrew Gellis and producers Antoine Compin and Charis Horton also make up the production team. Liz Stauber and Peter Horton star, alongside Kari Coleman, Tuck Milligan, and Laurie Murdoch. When a museum accident transports teenager Ally Hayden on an adventure back in time, she explores the terrain and territory of life-sized dinosaurs, even during a nose-to-nose encounter with a female Tyrannosaurus. The film is among the few IMAX films that are considered "pure entertainment", though it still is considered rather educational by the mainstream audience.

Sue is the nickname given to FMNH PR 2081, which is one of the largest, most extensive, and best preserved Tyrannosaurus rex specimens ever found, at over 90 percent recovered by bulk. FMNH PR 2081 was discovered on August 12, 1990, by American explorer and fossil collector Sue Hendrickson, and was named after her.

Tyrannosaurus is one of the most iconic dinosaurs and is known from numerous specimens, some of which have individually acquired notability due to their scientific significance and media coverage.

The Lost World is a 1998 adventure film, loosely based on the 1912 novel of the same name by Arthur Conan Doyle. The film includes the characters, Professor George Challenger and Lord John Roxton, who also feature in Conan Doyle's other Doctor Challenger novels. It is a mockbuster of the 1997 film The Lost World: Jurassic Park.

Return to the Lost World is a 1992 film directed by Timothy Bond and starring John Rhys-Davies, Eric McCormack, David Warner, Nathania Stanford, Darren Peter Mercer, and Tamara Gorski. It is a sequel to the film The Lost World, which was released the same year.

The Lost World is a 1995 science fiction action novel written by Michael Crichton, and the sequel to his 1990 novel Jurassic Park. It is his tenth novel under his own name and his twentieth overall, and it was published by Knopf. A paperback edition (ISBN 0-345-40288-X) followed in 1996. In 1997, both novels were re-published as a single book titled Michael Crichton's Jurassic World, which is unrelated to the 2015 film of the same name.

King of the Lost World is a 2005 American fantasy monster adventure film produced by The Asylum. The film is adapted loosely from the 1912 novel The Lost World by Arthur Conan Doyle, the creator of Sherlock Holmes, but the film bears a closer resemblance to the remake of King Kong released in the same year, particularly as both stories center on a giant ape. Hence, King of the Lost World is a mockbuster of said film, a tradition that The Asylum usually undergoes.
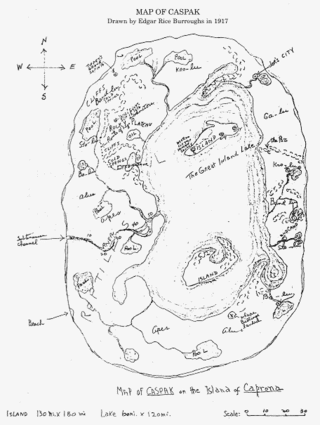
Caprona is a fictional island in the literary universe of Edgar Rice Burroughs' Caspak Trilogy, including The Land That Time Forgot, The People That Time Forgot, and Out of Time's Abyss. They were published as serial novels in 1918, and collected in book form in 1924.


















