
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the liberation of learners, skills needed for modern society, empathy, and complex vocational skills.

Educational psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the scientific study of human learning. The study of learning processes, from both cognitive and behavioral perspectives, allows researchers to understand individual differences in intelligence, cognitive development, affect, motivation, self-regulation, and self-concept, as well as their role in learning. The field of educational psychology relies heavily on quantitative methods, including testing and measurement, to enhance educational activities related to instructional design, classroom management, and assessment, which serve to facilitate learning processes in various educational settings across the lifespan.

John Dewey was an American philosopher, psychologist, and educational reformer whose ideas have been influential in education and social reform. He was one of the most prominent American scholars in the first half of the twentieth century.

Liberal arts education is the traditional academic course in Western higher education. Liberal arts takes the term art in the sense of a learned skill rather than specifically the fine arts. Liberal arts education can refer to studies in a liberal arts degree course or to a university education more generally. Such a course of study contrasts with those that are principally vocational, professional, or technical, as well as religiously-based courses.

Adult education, distinct from child education, is a practice in which adults engage in systematic and sustained self-educating activities in order to gain new forms of knowledge, skills, attitudes, or values. It can mean any form of learning adults engage in beyond traditional schooling, encompassing basic literacy to personal fulfillment as a lifelong learner. and to ensure the fulfillment of an individual.

Problem-based learning (PBL) is a student-centered pedagogy in which students learn about a subject through the experience of solving an open-ended problem found in trigger material. The PBL process does not focus on problem solving with a defined solution, but it allows for the development of other desirable skills and attributes. This includes knowledge acquisition, enhanced group collaboration and communication.

Pedagogy, most commonly understood as the approach to teaching, is the theory and practice of learning, and how this process influences, and is influenced by, the social, political and psychological development of learners. Pedagogy, taken as an academic discipline, is the study of how knowledge and skills are imparted in an educational context, and it considers the interactions that take place during learning. Both the theory and practice of pedagogy vary greatly as they reflect different social, political, and cultural contexts.

Experiential education is a philosophy of education that describes the process that occurs between a teacher and student that infuses direct experience with the learning environment and content. The term is not interchangeable with experiential learning; however experiential learning is a sub-field and operates under the methodologies of experiential education. The Association for Experiential Education regards experiential education as "a philosophy that informs many methodologies in which educators purposefully engage with learners in direct experience and focused reflection in order to increase knowledge, develop skills, clarify values, and develop people's capacity to contribute to their communities". Experiential education is the term for the philosophy and educational progressivism is the movement which it informed. The Journal of Experiential Education publishes peer-reviewed empirical and theoretical academic research within the field.

In education, a curriculum is broadly defined as the totality of student experiences that occur in the educational process. The term often refers specifically to a planned sequence of instruction, or to a view of the student's experiences in terms of the educator's or school's instructional goals. A curriculum may incorporate the planned interaction of pupils with instructional content, materials, resources, and processes for evaluating the attainment of educational objectives. Curricula are split into several categories: the explicit, the implicit, the excluded, and the extracurricular.
The Open University of Israel is a distance-education university in Israel. It is one of ten public universities in Israel recognized by the Council of Higher Education (CHE). The Open University is unique in that it does not require a matriculation certificate, psychometric exam, or other entrance exam for admission to undergraduate studies.

Experiential learning (ExL) is the process of learning through experience, and is more narrowly defined as "learning through reflection on doing". Hands-on learning can be a form of experiential learning, but does not necessarily involve students reflecting on their product. Experiential learning is distinct from rote or didactic learning, in which the learner plays a comparatively passive role. It is related to, but not synonymous with, other forms of active learning such as action learning, adventure learning, free-choice learning, cooperative learning, service-learning, and situated learning.

Open educational resources (OER) are teaching, learning, and research materials intentionally created and licensed to be free for the end user to own, share, and in most cases, modify. The term "OER" describes publicly accessible materials and resources for any user to use, re-mix, improve, and redistribute under some licenses. These are designed to reduce accessibility barriers by implementing best practices in teaching and to be adapted for local unique contexts.
This glossary of education-related terms is based on how they commonly are used in Wikipedia articles. This article contains terms starting with S. Select a letter from the table of contents to find terms on other articles.
This glossary of education-related terms is based on how they commonly are used in Wikipedia articles. This article contains terms starting with T – Z. Select a letter from the table of contents to find terms on other articles.

Fremont University, formerly Fremont College, is a private college in Cerritos, California. The college offers professional degree programs with a focus on serving working adults.. Its intensive bachelor's degree program is part of a degree completion program that spans 15 months. The associate degree program also spans 15 months.
Global education is a mental development program that seeks to improve global human development based on the understanding of global dynamics, through the various sectors of human development delivery. In formal education, as a mode of human development delivery, it is integrated into formal educational programs, as an advanced program where global dimensions to local problems are appreciated through interconnectivity. Its first phase began as an undertaking to restructure education and society in the 1960s and 1970s, through the initiatives of educationalists, NGOs and intergovernmental organizations. The program evolves with the internet, and is in its virtual interconnectivity phase, through social media and other global public spheres. This global approach to mental development, seeks to fix the failing curriculum-based global education program that is: stuck in limited subject knowledge, based on theories that have failed the world ;hinged on memorization without visual exposure to knowledge development resources and global culture, limited by access to human development resources. Instead, the program seeks to improve the global mental resources pool through the appreciation of global dynamics and local perspectives on issues. This is through alternative motivations for global human development, and alternative global futures hinged on interconnectivity.

The term Spanish as a second or foreign language is the learning or teaching of the Spanish language for those whose first language is not Spanish.
Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engineering and Research (PCCOER) is a college in Pune, Maharashtra.
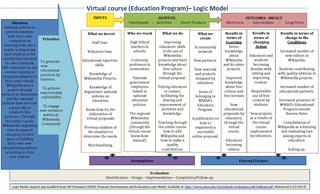
Digital pedagogy is the study and use of contemporary digital technologies in teaching and learning. Digital pedagogy may be applied to online, hybrid, and face-to-face learning environments. Digital pedagogy also has roots in the theory of constructivism.
Open educational resources in Canada are the various initiatives related to open education, open educational resources (OER), open pedagogies (OEP), open educational practices (OEP), and open scholarship that are established nationally and provincially across Canadian K-12 and higher education sectors, and where Canadian based inititatives extend to international collaborations.













