A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threatens dragonfly populations around the world. Adult dragonflies are characterized by a pair of large, multifaceted compound eyes, two pairs of strong, transparent wings, sometimes with coloured patches, and an elongated body. Many dragonflies have brilliant iridescent or metallic colours produced by structural colouration, making them conspicuous in flight. An adult dragonfly's compound eyes have nearly 24,000 ommatidia each.

Damselflies are flying insects of the suborder Zygoptera in the order Odonata. They are similar to dragonflies, which constitute the other odonatan suborder, Anisoptera, but are smaller and have slimmer bodies. Most species fold the wings along the body when at rest, unlike dragonflies which hold the wings flat and away from the body. An ancient group, damselflies have existed since at least the Lower Permian, and are found on every continent except Antarctica.
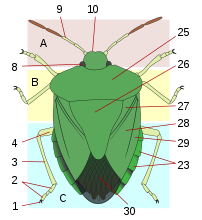
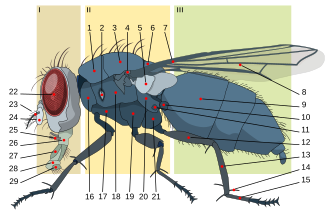
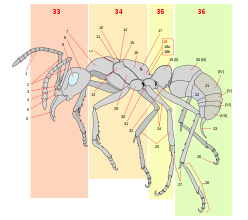
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments.

A carapace is a dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron.

The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. The word cephalothorax is derived from the Greek words for head and thorax. This fusion of the head and thorax is seen in chelicerates and crustaceans; in other groups, such as the Hexapoda, the head remains free of the thorax. In horseshoe crabs and many crustaceans, a hard shell called the carapace covers the cephalothorax.
In biology, a tagma is a specialized grouping of multiple segments or metameres into a coherently functional morphological unit. Familiar examples are the head, the thorax, and the abdomen of insects. The segments within a tagma may be either fused or so jointed as to be independently moveable.

The prothorax is the foremost of the three segments in the thorax of an insect, and bears the first pair of legs. Its principal sclerites are the pronotum (dorsal), the prosternum (ventral), and the propleuron (lateral) on each side. The prothorax never bears wings in extant insects, though some fossil groups possessed wing-like projections. All adult insects possess legs on the prothorax, though in a few groups the forelegs are greatly reduced. In many groups of insects, the pronotum is reduced in size, but in a few it is hypertrophied, such as in all beetles (Coleoptera). In most treehoppers, the pronotum is expanded into often fantastic shapes that enhance their camouflage or mimicry. Similarly, in the Tetrigidae, the pronotum is extended backward to cover the flight wings, supplanting the function of the tegmina.

Insect wings are adult outgrowths of the insect exoskeleton that enable insects to fly. They are found on the second and third thoracic segments, and the two pairs are often referred to as the forewings and hindwings, respectively, though a few insects lack hindwings, even rudiments. The wings are strengthened by a number of longitudinal veins, which often have cross-connections that form closed "cells" in the membrane. The patterns resulting from the fusion and cross-connection of the wing veins are often diagnostic for different evolutionary lineages and can be used for identification to the family or even genus level in many orders of insects.

This glossary of entomology describes terms used in the formal study of insect species by entomologists.
The mesothorax is the middle of the three segments of the thorax of hexapods, and bears the second pair of legs. Its principal sclerites are the mesonotum (dorsal), the mesosternum (ventral), and the mesopleuron (lateral) on each side. The mesothorax is the segment that bears the forewings in all winged insects, though sometimes these may be reduced or modified, as in beetles (Coleoptera) or Dermaptera, in which they are sclerotized to form the elytra, and the Strepsiptera, in which they are reduced to form halteres that attach to the mesonotum. All adult insects possess legs on the mesothorax. In some groups of insects, the mesonotum is hypertrophied, such as in Diptera, Hymenoptera, and Lepidoptera), in which the anterior portion of the mesonotum forms most of the dorsal surface of the thorax. In these orders, there is also typically a small sclerite attached to the mesonotum that covers the wing base, called the tegula. In one group of insects, the Hemiptera, the dorsal surface of the thorax is typically formed primarily of the prothorax, but also in part by the enlarged posterior portion of the mesonotum, called the scutellum; in the Coleoptera, the scutellum may or may not be visible, usually as a small triangular plate between the elytral bases, thus similar in position to the Hemipteran scutellum. In Diptera and Hymenoptera the mesothoracic scutellum is also distinct, but much smaller than the mesoscutum.
The metathorax is the posterior of the three segments in the thorax of an insect, and bears the third pair of legs. Its principal sclerites are the metanotum (dorsal), the metasternum (ventral), and the metapleuron (lateral) on each side. The metathorax is the segment that bears the hindwings in most winged insects, though sometimes these may be reduced or modified, as in the flies (Diptera), in which they are reduced to form halteres, or flightless, as in beetles (Coleoptera), in which they may be completely absent even though forewings are still present. All adult insects possess legs on the metathorax. In most groups of insects, the metanotum is reduced relative to the mesonotum. In the suborder Apocrita of the Hymenoptera, the first abdominal segment is fused to the metathorax, and is then called the propodeum.

The metasoma is the posterior part of the body, or tagma, of arthropods whose body is composed of three parts, the other two being the prosoma and the mesosoma. In insects, it contains most of the digestive tract, respiratory system, and circulatory system, and the apical segments are typically modified to form genitalia. In a few of the most primitive insects, the metasomal segments bear small, articulated appendages called "styli", which are often considered to be vestigial. There are also pre-apical appendages in most insect orders, called cerci, which may be multi-segmented and almost resembling a posterior pair of antennae; these may be variously modified, or lost entirely. Otherwise, most adult insects lack appendages on the metasoma, though many larval insects have some form of appendages, such as prolegs or, in aquatic insects, gills.

Insects are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body, three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within.

The external morphology of Lepidoptera is the physiological structure of the bodies of insects belonging to the order Lepidoptera, also known as butterflies and moths. Lepidoptera are distinguished from other orders by the presence of scales on the external parts of the body and appendages, especially the wings. Butterflies and moths vary in size from microlepidoptera only a few millimetres long, to a wingspan of many inches such as the Atlas moth. Comprising over 160,000 described species, the Lepidoptera possess variations of the basic body structure which has evolved to gain advantages in adaptation and distribution.

Insect morphology is the study and description of the physical form of insects. The terminology used to describe insects is similar to that used for other arthropods due to their shared evolutionary history. Three physical features separate insects from other arthropods: they have a body divided into three regions, have three pairs of legs, and mouthparts located outside of the head capsule. It is this position of the mouthparts which divides them from their closest relatives, the non-insect hexapods, which includes Protura, Diplura, and Collembola.

Palaeovespa is an extinct genus of wasp in the Vespidae subfamily Vespinae. The genus currently contains eight species, five from the Priabonian stage Florissant Formation in Colorado, United States two from the middle Eocene Baltic amber deposits of Europe. and one species from the late Paleocene of France.
The cephalon is the head section of an arthropod. It is a tagma, i.e., a specialized grouping of arthropod segments. The word cephalon derives from the Greek κεφαλή (kephalē), meaning "head".
Dipteran morphology differs in some significant ways from the broader morphology of insects. The Diptera is a very large and diverse order of mostly small to medium-sized insects. They have prominent compound eyes on a mobile head, and one pair of functional, membraneous wings, which are attached to a complex mesothorax. The second pair of wings, on the metathorax, are reduced to halteres. The order's fundamental peculiarity is its remarkable specialization in terms of wing shape and the morpho-anatomical adaptation of the thorax – features which lend particular agility to its flying forms. The filiform, stylate or aristate antennae correlate with the Nematocera, Brachycera and Cyclorrhapha taxa respectively. It displays substantial morphological uniformity in lower taxa, especially at the level of genus or species. The configuration of integumental bristles is of fundamental importance in their taxonomy, as is wing venation. It displays a complete metamorphosis, or holometabolous development. The larvae are legless, and have head capsules with mandibulate mouthparts in the Nematocera. The larvae of "higher flies" (Brachycera) are however headless and wormlike, and display only three instars. Pupae are obtect in the Nematocera, or coarcate in Brachycera.
Zaitzevia elongata is a species of riffle beetle which is wingless and flightless. It is found on several of the Ryukyu Islands in Japan in the gravel substrate of streams.

Tisamenus serratorius is a stick insect species that occurs on the Philippine island Luzon.