In finance, technical analysis is an analysis methodology for analysing and forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. As a type of active management, it stands in contradiction to much of modern portfolio theory. The efficacy of technical analysis is disputed by the efficient-market hypothesis, which states that stock market prices are essentially unpredictable, and research on whether technical analysis offers any benefit has produced mixed results. It is distinguished from fundamental analysis, which considers a company's financial statements, health, and the overall state of the market and economy.
A chart is a graphical representation for data visualization, in which "the data is represented by symbols, such as bars in a bar chart, lines in a line chart, or slices in a pie chart". A chart can represent tabular numeric data, functions or some kinds of quality structure and provides different info.
The Elliott wave principle, or Elliott wave theory, is a form of technical analysis that financial traders use to analyze financial market cycles and forecast market trends by identifying extremes in investor psychology and price levels, such as highs and lows, by looking for patterns in prices.
In stock market technical analysis, support and resistance are certain predetermined levels of the price of a security at which it is thought that the price will tend to stop and reverse. These levels are denoted by multiple touches of price without a breakthrough of the level.

A candlestick chart is a style of financial chart used to describe price movements of a security, derivative, or currency.
The hikkake pattern, or hikkake, is a technical analysis pattern used for determining market turning-points and continuations. It is a simple pattern that can be observed in market price data, using traditional bar charts, point and figure charts, or Japanese candlestick charts. The pattern does not belong to the collection of traditional candlestick chart patterns.
The Hindenburg Omen was a proposed technical analysis pattern, named after the Hindenburg disaster of May 6, 1937. It was created by Jim Miekka, who believed that it predicted stock market crashes.
Munehisa Honma was a rice merchant from Sakata, Japan who traded in the Dōjima Rice Exchange in Osaka during the Tokugawa Shogunate. He is sometimes considered to be the father of the candlestick chart, a form of technical analysis used in stock markets.
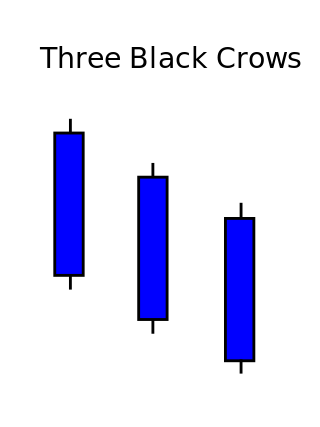
Three crows is a term used by stock market analysts to describe a market downturn. It appears on a candlestick chart in the financial markets. It unfolds across three trading sessions, and consists of three long candlesticks that trend downward like a staircase. Each candle should open below the previous day's open, ideally in the middle price range of that previous day. Each candlestick should also close progressively downward to establish a new near-term low. The pattern indicates a strong price reversal from a bull market to a bear market.

An open-high-low-close chart is a type of chart typically used in technical analysis to illustrate movements in the price of a financial instrument over time. Each vertical line on the chart shows the price range over one unit of time, e.g., one day or one hour. Tick marks project from each side of the line indicating the opening price on the left, and the closing price for that time period on the right. The bars may be shown in different hues depending on whether prices rose or fell in that period.
In technical analysis of securities trading, the stochastic oscillator is a momentum indicator that uses support and resistance levels. George Lane developed this indicator in the late 1950s. The term stochastic refers to the point of a current price in relation to its price range over a period of time. This method attempts to predict price turning points by comparing the closing price of a security to its price range.
The doji is a commonly found pattern in a candlestick chart of financially traded assets in technical analysis. It is characterized by being small in length—meaning a small trading range—with an opening and closing price that are virtually equal. The efficacy of technical analysis is disputed by the efficient-market hypothesis, which states that stock market prices are essentially unpredictable.

The Morning Star is a pattern seen in a candlestick chart, a popular type of a chart used by technical analysts to anticipate or predict price action of a security, derivative, or currency over a short period of time.
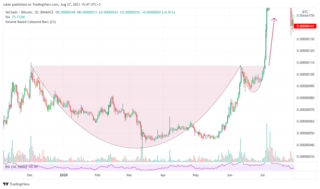
In the domain of technical analysis of market prices, a cup and handle or cup with handle formation is a chart pattern consisting of a drop in the price and a rise back up to the original value, followed first by a smaller drop and then a rise past the previous peak. It is interpreted as an indication of bullish sentiment in the market and possible further price increases.

A gap is defined as an unfilled space or interval. On a technical analysis chart, a gap represents an area where no trading takes place. On the Japanese candlestick chart, a window is interpreted as a gap. Gaps are spaces on a chart that emerge when the price of the financial instrument significantly changes with little or no trading in between.

In both stock trading and financial technical analysis, an island reversal is a candlestick pattern with compact trading activity within a range of prices, separated from the move preceding it. A "candlestick pattern" is a movement in prices shown graphically on a candlestick chart. This separation shown on the chart, is said to be caused by an exhaustion gap and the subsequent move in the opposite direction occurs as a result of a breakaway gap.
In financial technical analysis, a candlestick pattern is a movement in prices shown graphically on a candlestick chart that some believe can help to identify repeating patterns of a particular market movement. The recognition of the pattern is subjective and programs that are used for charting have to rely on predefined rules to match the pattern. There are 42 recognized patterns that can be split into simple and complex patterns. Author Thomas Bulkowski takes an in-depth look at 103 candlestick formations, from identification guidelines and statistical analysis of their behaviour to detailed trading tactics. He makes important discoveries and statistical summaries, as well as a glossary of relevant terms and a visual index to make candlestick identification easy.
In financial technical analysis, the know sure thing (KST) oscillator is a complex, smoothed price velocity indicator developed by Martin J. Pring.
Price action is a method of analysis of the basic price movements to generate trade entry and exit signals that is considered reliable while not requiring the use of indicators. It is a form of technical analysis, as it ignores the fundamental factors of a security and looks primarily at the security's price history. However, this method is different from other forms of technical analysis, as it focuses on the relation of the security's current price to its price history, which consists of all price movements, as opposed to values derived from the price history.
Heikin-Ashi is a Japanese trading indicator and financial chart that means "average bar". Heikin-Ashi charts resemble candlestick charts, but have a smoother appearance as they track a range of price movements, rather than tracking every price movement as with candlesticks. Heikin-Ashi was created in the 1700s by Munehisa Homma, who also created the candlestick chart. These charts are used by traders and investors to help determine and predict price movements.








