
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time.
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight saving(s), daylight savings time, daylight time (United States and Canada), or summer time (United Kingdom, European Union, and others), is the practice of advancing clocks to make better use of the longer daylight available during summer, so that darkness falls at a later clock time. The typical implementation of DST is to set clocks forward by one hour in spring or late winter, and to set clocks back by one hour to standard time in the autumn (or fall in North American English, hence the mnemonic: "spring forward and fall back").

Western European Summer Time is a summer daylight saving time scheme, 1 hour ahead of Greenwich Mean Time and Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in:

Japan Standard Time, or Japan Central Standard Time, is the standard time zone in Japan, 9 hours ahead of UTC (UTC+09:00). Japan does not observe daylight saving time, though its introduction has been debated on several occasions. During World War II, the time zone was often referred to as Tokyo Standard Time.
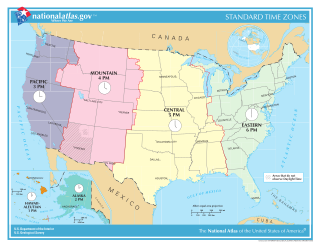
In the United States, time is divided into nine standard time zones covering the states, territories and other US possessions, with most of the country observing daylight saving time (DST) for approximately the spring, summer, and fall months. The time zone boundaries and DST observance are regulated by the Department of Transportation, but no single map of those existed until the agency announced intentions to make one in September 2022. Official and highly precise timekeeping services (clocks) are provided by two federal agencies: the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) ; and the United States Naval Observatory (USNO). The clocks run by these services are kept synchronized with each other as well as with those of other international timekeeping organizations.

Summer time in Europe is the variation of standard clock time that is applied in most European countries in the period between spring and autumn, during which clocks are advanced by one hour from the time observed in the rest of the year, with a view to making the most efficient use of seasonal daylight. It corresponds to the notion and practice of daylight saving time (DST) to be found in some other parts of the world.
Time in New Zealand is divided by law into two standard time zones. The main islands use New Zealand Standard Time (NZST), 12 hours in advance of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) / military M (Mike), while the outlying Chatham Islands use Chatham Standard Time (CHAST), 12 hours 45 minutes in advance of UTC / military M^ (Mike-Three).

Moscow Time is the time zone for the city of Moscow, Russia, and most of western Russia, including Saint Petersburg. It is the second-westernmost of the eleven time zones of Russia. It has been set to UTC+03:00 without DST since 26 October 2014; before that date it had been set to UTC+04:00 year-round on 27 March 2011.

Israel Summer Time, also in English, Israel Daylight Time (IDT) is the practice in Israel by which clocks are advanced by one hour, beginning on the Friday before the last Sunday of March, and ending on the last Sunday of October.

Israel Standard Time (IST) is the standard time zone in Israel. It is two hours ahead of UTC (UTC+02:00).

Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Eastern Standard Time, Australian Central Standard Time and Australian Western Standard Time.
Time in Chile is divided into three time zones. Most of Continental Chile uses the time offset UTC−04:00 in winter time and UTC−03:00 in summer time, while the Magallanes and Chilean Antarctica region uses the time offset UTC−03:00 the whole year. Additionally, Easter Island uses the time offset UTC−06:00 in winter time and UTC−05:00 in summer time.

The time zone in Germany is Central European Time and Central European Summer Time. Daylight saving time is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. The doubled hour during the switch back to standard time is named 2A and 2B.
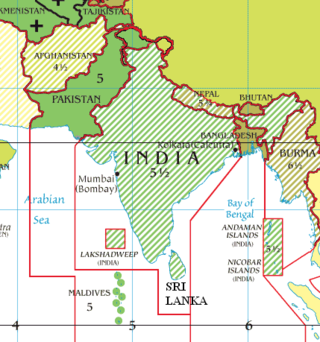
Bangladesh Standard Time is the time zone of Bangladesh. It is offset six hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time, and observed as a national standard throughout the country. Bangladesh briefly observed daylight saving time (DST) in 2009 to cope with the ongoing electricity crisis, but in 2010 the decision was cancelled by the government of Bangladesh.
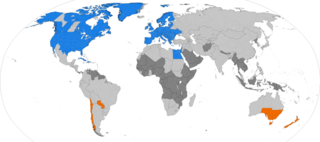
Daylight saving time in the Americas is the arrangement in the Americas by which clocks are advanced by one hour in spring and moved back in autumn, to make the most of seasonal daylight. The practice is widespread in North America, with most of Canada and the United States participating, but much less so in Central and South America.
Daylight saving time (DST) has been restored and used in Egypt. It started on 28 April 2023 at 00:00 UTC+2:00 and ended on 26 October 2023, thus making it the only African country using DST as of 2024.

As of 2022, daylight saving time is used in the following Asian countries:

African countries, apart from Egypt, do not use daylight saving time (DST) although some did in the past. Only the territories of the Canary Islands, Ceuta and Melilla (Spain) and Madeira (Portugal) implement DST from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. Although these regions politically belong to Europe, they are geographically part of Africa. They have DST schedules according to European Union rules.

Daylight saving time (DST), also known as summer time, is the practice of advancing clocks during part of the year, typically by one hour around spring and summer, so that daylight ends at a later time of the day. As of 2024, DST is observed in most of Europe, most of North America and parts of Africa and Asia around the Northern Hemisphere summer, and in parts of South America and Oceania around the Southern Hemisphere summer. It was also formerly observed in other areas.

In Romania, the standard time is Eastern European Time. Daylight saving time, which moves one hour ahead to UTC+03:00 is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October.











