Yukon is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 40,232 people as of the 2021 Census. Whitehorse, the territorial capital, is the largest settlement in any of the three territories.

Denali National Park and Preserve, formerly known as Mount McKinley National Park, is an American national park and preserve located in Interior Alaska, centered on Denali, the highest mountain in North America. The park and contiguous preserve encompass 6,045,153 acres which is larger than the state of New Hampshire. On December 2, 1980, 2,146,580-acre Denali Wilderness was established within the park. Denali's landscape is a mix of forest at the lowest elevations, including deciduous taiga, with tundra at middle elevations, and glaciers, snow, and bare rock at the highest elevations. The longest glacier is the Kahiltna Glacier. Wintertime activities include dog sledding, cross-country skiing, and snowmobiling. The park received 594,660 recreational visitors in 2018.

Kings Canyon National Park is an American national park in the southern Sierra Nevada, in Fresno and Tulare Counties, California. Originally established in 1890 as General Grant National Park, the park was greatly expanded and renamed to Kings Canyon National Park on March 4, 1940. The park's namesake, Kings Canyon, is a rugged glacier-carved valley more than a mile (1,600 m) deep. Other natural features include multiple 14,000-foot (4,300 m) peaks, high mountain meadows, swift-flowing rivers, and some of the world's largest stands of giant sequoia trees. Kings Canyon is north of and contiguous with Sequoia National Park, and both parks are jointly administered by the National Park Service as the Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks.

Gates of the Arctic National Park and Preserve is an American national park that protects portions of the Brooks Range in northern Alaska. The park is the northernmost national park in the United States, situated entirely north of the Arctic Circle. The park is the second largest in the U.S. at 8,472,506 acres, slightly larger in area than Belgium.

Dawson City, officially the City of Dawson, is a town in the Canadian territory of Yukon. It is inseparably linked to the Klondike Gold Rush (1896–99). Its population was 1,375 as of the 2016 census, making it the second-largest town in Yukon.
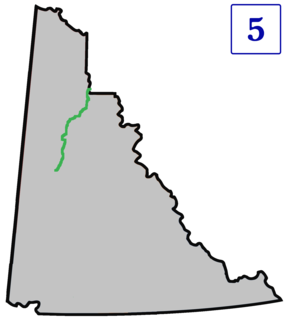
The Dempster Highway, also referred to as Yukon Highway 5 and Northwest Territories Highway 8, is a highway in Canada that connects the Klondike Highway in Yukon to Inuvik, Northwest Territories on the Mackenzie River delta. The highway crosses the Peel and the Mackenzie rivers using a combination of seasonal ferry services and ice bridges. Year-round road access from Inuvik to Tuktoyaktuk opened in November 2017, with the completion of the Inuvik–Tuktoyaktuk Highway, creating the first all-weather road route connecting the Canadian road network with the Arctic Ocean.

The Klondike River is a tributary of the Yukon River in Canada that gave its name to the Klondike Gold Rush. The Klondike River rises in the Ogilvie Mountains and flows into the Yukon River at Dawson City.

Yukon is in the northwestern corner of Canada and is bordered by Alaska and the Northwest Territories. The sparsely populated territory abounds with natural scenic beauty, with snowmelt lakes and perennial white-capped mountains, including many of Canada's highest mountains. The territory's climate is Arctic in territory north of Old Crow, subarctic in the region, between Whitehorse and Old Crow, and humid continental climate south of Whitehorse and in areas close to the British Columbia border. Most of the territory is boreal forest with tundra being the main vegetation zone only in the extreme north and at high elevations.

Tatshenshini-Alsek Park or Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Wilderness Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada 9,580 km2 (3,700 sq mi). It was established in 1993 after an intensive campaign by Canadian and American conservation organizations to halt mining exploration and development in the area, and protect the area for its strong natural heritage and biodiversity values.

Peter Lougheed Provincial Park is a provincial park located in Alberta, Canada. The park is in Kananaskis Country about 90 kilometres (56 mi) west of Calgary, along the Kananaskis Trail.

The Porcupine caribou or Grant's caribou is a subspecies of the reindeer or caribou found in Alaska, United States, and Yukon and the Northwest Territories, Canada. It resembles the subspecies known as the barren-ground caribou and is sometimes included in it.
Height of the Rockies Provincial Park is a provincial park in the Canadian Rockies of south eastern British Columbia, Canada. It is located west of the Continental Divide, adjacent to Elk Lakes Provincial Park.

The Ogilvie Mountains are a mountain range in the Yukon Territory of northwestern Canada.
The Monarch Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area located 70 miles east of Fresno, California, in the Sierra Nevada mountain range. It encompasses 44,896 acres (181.69 km2) within both the Sequoia National Forest and the Sierra National Forest and is managed by the United States Forest Service. Elevations range from 950 feet (290 m) to 11,081 ft (3,377 m).

The Yukon School of Visual Arts (SOVA) is Canada's most northerly post-secondary fine arts school, and it receives its accreditation through the Applied Arts Division of Yukon College. SOVA is located within the traditional territory of the Tr'ondëk Hwëch'in First Nation in Dawson City, Yukon Territory, Canada. SOVA offers a Foundation Year Program, which is the equivalent of the first year of a Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) degree. The school offers an experimental, integrated curriculum that is studio-based with liberal arts courses. Successful students continue their degrees at their choice of five partnering art schools across Canada, including the Ontario College of Art and Design in Toronto, the Emily Carr Institute of Art and Design in Vancouver, the Alberta College of Art and Design in Calgary, Mount Allison University in Sackville, NB and the Nova Scotia College of Art and Design University in Halifax.

The interior Alaska–Yukon lowland taiga is an ecoregion in the taiga and boreal forests biome, of far northern North America.

The Peel watershed drains 14% of the Yukon Territory Canada and flows into the Beaufort Sea via the Peel and then Mackenzie Rivers. While the lower part of the Peel River and its confluence with the Mackenzie River are in the North West Territories, most of the watershed, 68,000 km2 out of 77,000 km2 is in the Yukon. Six major tributaries and numerous smaller streams feed the Peel. The Yukon portion of the watershed is undergoing land use planning, a process laid out in Chapter 11 of the Yukon Land Claims Agreement and is called the Peel Watershed Planning Region (PWPR). This article is confined to the PWPR.

Grafton Notch State Park is a public recreation area in Grafton Township, Oxford County, Maine. The state park occupies 3,129 acres (1,266 ha) surrounding Grafton Notch, the mountain pass between Old Speck Mountain and Baldpate Mountain. The park is abutted by the eastern and western sections of the Mahoosuc Public Reserved Land, which total 31,807 acres (12,872 ha). The park is managed by the Department of Agriculture, Conservation and Forestry.
Bighorn Wildland Provincial Park is a proposed provincial park that would be situated near Rocky Mountain House, Alberta, Canada. It would be part of the Alberta Provincial Parks system and governed by Alberta Tourism, Parks and Recreation under Alberta Environment and Parks. After the 2019 Alberta election, the new United Conservative government announced the plan would not go ahead.

The Ogilvie–MacKenzie alpine tundra ecoregion covers the mountainous middle of the Yukon Territory in Canada, with extensions into the Northwest Territories. The vegetation is alpine and subalpine open forest of stunted spruce, fir and pine. The area is rugged but sections appear to have been unglaciated in the late Pleistocene and there are therefore relic species in the region. The area is remote and supports large, sustainable predator-prey systems.