In male human anatomy, the glans penis, commonly referred to as the glans, is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and primary anatomical source of sexual pleasure. The glans penis is present in the male reproductive organs of humans and most mammals where it may appear smooth, spiny, elongated or divided. It is externally lined with mucosal tissue, which creates a smooth texture and glossy appearance. In humans, the glans is located over the distal ends of the corpora cavernosa and is a continuation of the corpus spongiosum of the penis. At the summit appears the urinary meatus and at the base forms the corona glandis. An elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum, runs on its ventral surface. In men who are not circumcised, it is completely or partially covered by a fold of skin called the foreskin. In adults, the foreskin can generally be retracted over and past the glans manually or sometimes automatically during an erection.
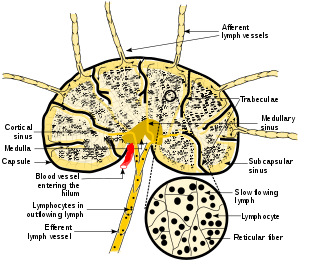
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function.

Penile fracture is rupture of one or both of the tunica albuginea, the fibrous coverings that envelop the penis's corpora cavernosa. It is caused by rapid blunt force to an erect penis, usually during vaginal intercourse, or aggressive masturbation. It sometimes also involves partial or complete rupture of the urethra or injury to the dorsal nerves, veins and arteries.

The corpus spongiosum is the mass of spongy tissue surrounding the male urethra within the penis. It is also called the corpus cavernosum urethrae in older texts.

Deep shaft piercings are piercings which pass through the penile shaft. They are most commonly seen in the form of deeply placed ampallangs, apadravyas, and reverse shaft Prince Alberts. They are more rare piercings due to associated pain, difficulty, bleeding and long healing times. Common placement is directly behind the head of the penis, but they can be placed farther back.

A corpus cavernosum penis (singular) is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue, which contain most of the blood in the penis during an erection.

The corpus cavernosum of clitoris is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue of the clitoris. It is made of a sponge-like tissue that fills with blood during clitoral erection. This is homologous to the corpus cavernosum penis. The term corpora cavernosa literally means "cave-like bodies".

The Prostatic Plexus is continued from the lower part of the pelvic plexus. It lies within the fascial shell of the prostate.

In human male anatomy, the dorsal veins of the penis are blood vessels that drain the shaft, the skin and the glans of the human penis. They are typically located in the midline on the dorsal aspect of the penis and they comprise the superficial dorsal veinof the penis, that lies in the subcutaneous tissue of the shaft, and the deep dorsal veinof the penis, that lies beneath the deep fascia.
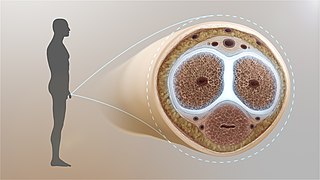
The tunica albuginea is the fibrous envelope that extends the length of the corpora cavernosa penis and corpus spongiosum penis. It is a bi-layered structure that includes an outer longitudinal layer and an inner circular layer.
The fibrous envelope of the corpus cavernosum urethrae is thinner, whiter in color, and more elastic than that of the corpora cavernosa penis. It is called the trabeculae of corpus spongiosum of penis.

The two crura of penis constitute the root of penis along with the bulb of penis. The two crura flank the bulb - one to each side of the bulb. Each crus is attached at the angle between the perineal membrane and ischiopubic ramus. The deep artery of the penis enters the anterior portion of the crus. Distally, each crus transitions into either corpus spongiosum of the body of penis.

The helicine arteries of penis are arteries in the penis. They are found in the corpora cavernosa penis.

In human anatomy, the penis is an external male sex organ that additionally serves as the urinary duct. The main parts are the root (radix); the body (corpus); and the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin and the foreskin (prepuce) covering the glans penis. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The human male urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct, and then through the penis. The urethra traverses the corpus spongiosum, and its opening, the meatus, lies on the tip of the glans penis. It is a passage both for urination and ejaculation of semen.

The body or shaft of the penis is the free portion of the human penis that is located outside of the pelvic cavity. It is the continuation of the internal root which is embedded in the pelvis and extends to the glans behind which lies the neck of the penis. It is made up of the two corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum on the underside. The corpora cavernosa are intimately bound to one another with a dorsally fenestrated septum which becomes a complete one before the penile crura. The body of the penis is homologous to the female clitoral body.

In human male anatomy, the radix or root of the penis is the internal and most proximal portion of the human penis that lies in the perineum. Unlike the pendulous body of the penis which is suspended from the pubic symphysis, the root is attached to the pubic arch of the pelvis and is not visible externally. It is triradiate in form, consisting of three masses of erectile tissue; the two diverging crura, one on either side, and the median bulb of the penis or urethral bulb. Approximately one third to one half of the penis is embedded in the pelvis and can be felt through the scrotum and in the perineum.

In human male anatomy, the septum of the penis or penile septum refers to the fibrous junction (septum) between the two corpora cavernosa of the human penis. The tunica albuginea of the penis forms a thick fibrous coat to the spongy tissue of the corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum. The two corpora cavernosa are surrounded by a strong fibrous envelope consisting of superficial and deep fibers. The superficial or outer fibers are longitudinal in direction, and form a single tube which encloses both corpora; the deep or inner fibers are arranged circularly around each corpus and meet in the center. By their junction in the median plane, the inner fibers form the intercavernous septum of the penis.

An erection is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is often associated with sexual arousal, sexual attraction or libido, although erections can also be spontaneous. The shape, angle, and direction of an erection vary considerably between humans.

Clitoral erection is a physiological phenomenon where the clitoris becomes enlarged and firm.
Penile ulltrasonography is medical ultrasonography of the penis. Ultrasound is an excellent method for the study of the penis, such as indicated in trauma, priapism, erectile dysfunction or suspected Peyronie's disease.