
Acanthocephala is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described.
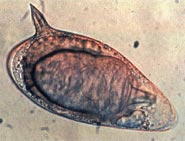
Schistosoma is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed schistosomiasis, which is considered by the World Health Organization as the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease, with hundreds of millions infected worldwide.

Trichomonas is a genus of anaerobic excavate parasites of vertebrates. It was first discovered by Alfred François Donné in 1836 when he found these parasites in the pus of a patient suffering from vaginitis, an inflammation of the vagina. Donné named the genus from its morphological characteristics. The prefix tricho- originates from the Ancient Greek word θρίξ (thrix) meaning hair, describing Trichomonas’s flagella. The suffix -monas, describes its similarity to unicellular organisms from the genus Monas.

Balantidium is a genus of ciliates. It contains the parasitic species Balantidium coli, the only known cause of balantidiasis.

Schistosomatidae is a family of digenetic trematodes with complex parasitic life cycles. Immature developmental stages of schistosomes are found in molluscs and adults occur in vertebrates. The best studied group, the blood flukes of the genus Schistosoma, infect and cause disease in humans. Other genera which are infective to non-human vertebrates can cause mild rashes in humans.

Trichobilharzia regenti is a neuropathogenic parasitic flatworm of birds which also causes cercarial dermatitis in humans. The species was originally described in 1998 in the Czech Republic and afterwards it was detected also in other European countries, e.g. Denmark, Germany, France, Iceland, Poland, Switzerland, or Russia, and even in Iran. For its unique neurotropic behaviour in vertebrate hosts, the host-parasite interactions are extensively studied in terms of molecular biology, biochemistry and immunology.
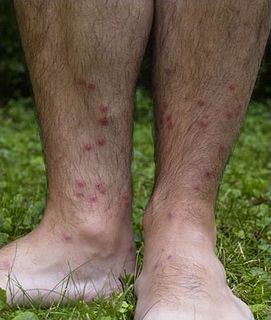
Swimmer's itch, cercarial dermatitis or schistosome dermatitis is a short-term allergic immune reaction occurring in the skin of humans that have been infected by water-borne schistosomes, a type of flatworms. It is common in freshwater, brackish and marine habitats worldwide. Incidence may be on the rise, although this may also be attributed to better monitoring. Nevertheless, the condition has been regarded as emerging infectious disease.
Isospora is a genus of internal parasites in the subclass Coccidia.

The Pentastomida are an enigmatic group of parasitic arthropods commonly known as tongue worms due to the resemblance of the species of the genus Linguatula to a vertebrate tongue. They are traditionally seen as crustaceans, even if that position has been questioned.

Gongylonema is a genus of thread-like nematode that was described by Molin in 1857. It is the only currently valid genus in the family Gongylonematidae, though the mysterious Spiruroides – usually placed in the Subuluridae, which are not closely related to Gongylonema among the Spiruria – might actually belong here. They are parasites of birds and mammals, transmitted by insects. Some 38 species are known, about 12 of which have been recorded in Europe.

Lymnaea is a genus of small to large-sized air-breathing freshwater snails, aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Lymnaeidae, the pond snails. Some species are used in aquaculture under the name Melantho snails. Numerous Lymnaea species serve as intermediate hosts for trematodes. Lymnaea is the type genus of the family Lymnaeidae.

Radix auricularia, common name the big-ear radix, is a species of medium-sized freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Lymnaeidae.

Radix rubiginosa is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod in the family Lymnaeidae, the pond snails.

Heterophyes heterophyes was discovered by Theodor Maximaillian Bilharz in 1851. This parasite was found during an autopsy of an Egyptian mummy. H. heterophyes is found in the Middle East, West Europe and Africa. They use different species to complete their complex lifestyle. Humans and other mammals are the definitive host, first intermediate host are snails, and second intermediate are fish. Mammals that come in contact with the parasite are dogs, humans, and cats. Snails that are affected by this parasite are the Cerithideopsilla conica. Fish that come in contact with this parasite are Mugil cephalus, Tilapia milotica, Aphanius fasciatus, and Acanthgobius sp. Humans and mammals will come in contact with this parasite by the consumption of contaminated or raw fish. This parasite is one of the smallest endoparasite to infect humans. It can cause intestinal infection called heterophyiasis.
Maritrema heardi is a parasitic fluke that infects the marsh rice rat in a salt marsh at Cedar Key, Florida. It was first listed as Maritrema sp. II in 1988, then described as the only species of a new genus, Floridatrema heardi, in 1994, and eventually reassigned in 2003 to Maritrema as Maritrema heardi. Its intermediate host is the fiddler crab Uca pigilator and it lives in the intestine of the marsh rice rat, its definitive host. Together with two other species of Maritrema, it is very common in affected marsh rice rats; it infects 19% of studied rats at Cedar Key. According to Tkach and colleagues, M. heardi is probably primarily a parasite of birds that has secondarily infected the marsh rice rat. Floridatrema was distinguished from Maritrema on the basis of its possession of loops of the uterus that extend forward to the place where the intestine is forked or even to the pharynx. Genetically, M. heardi may be closest to the morphologically similar M. neomi, which infects Neomys water shrews in the Carpathians.
Maritrema is a genus of trematodes (flukes) in the family Microphallidae, although some have suggested its placement in the separate family Maritrematidae. It was first described by Nikoll in 1907 from birds in Britain. Species of the genus usually infect birds, but several have switched hosts and are found in mammals, such as the marsh rice rat. Several species use the fiddler crab Uca pigilator as an intermediate host.

Pseudorhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae.The type-species of the genus is Pseudorhabdosynochus epinepheli .

The Diplectanidae are a family of monopisthocotylean monogeneans. They are all parasitic on the gills of fish. Diplectanids are small animals, generally around 1 mm in length. As parasites, they can be extremely numerous, up to several thousand on an individual fish.

Cucullanus is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The genus includes more than 100 species.

František Moravec is a Czech parasitologist who specialised on the Nematodes, especially the nematodes parasites of fishes. His research was mainly in the field of taxonomy of the Nematoda.













