
David Glasgow Farragut was a flag officer of the United States Navy during the American Civil War. He was the first rear admiral, vice admiral, and admiral in the United States Navy. He is remembered for his order at the Battle of Mobile Bay, usually paraphrased as "Damn the torpedoes, full speed ahead" in U.S. Navy tradition.

James Agustin Greer was a rear admiral in the United States Navy, who served during the Civil War.

The USS Queen of the West was a sidewheel steamer ram ship and the flagship of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. It was built at Cincinnati, Ohio in 1854. It served as a commercial steamer until purchased by Colonel Charles Ellet Jr. in 1862 and converted for use as a ram ship. The ship operated in conjunction with the Mississippi River Squadron during the Union brown-water navy battle against the Confederate River Defense Fleet for control of the Mississippi River and its tributaries during the American Civil War.

The first USS Lafayette was a side wheel steamer, converted to an ironclad ram, in the United States Navy during the American Civil War.

Laurent Millaudon was a wooden side-wheel river steamboat launched at Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1856 operating in the New Orleans, Louisiana, area, and captained by W. S. Whann. At the beginning of the American Civil War she was taken into service by the Confederate Navy as CSS General Sterling Price. On 6 June 1862, she was sunk at the Battle of Memphis. She was raised and repaired by the Union army, and on 16 June 1862 was moved into Union service as USS General Price and served until the end of the war.

USS Neosho, the lead ship of her class, was an ironclad river monitor laid down for the Union Navy in the summer of 1862 during the American Civil War. After completion in mid-1863, the ship spent time patrolling the Mississippi River against Confederate raids and ambushes as part of Rear Admiral David Porter's Mississippi Squadron. She participated in the Red River Campaign in March–May 1864. Neosho resumed her patrols on the Mississippi after the end of the campaign. She supported the Union Army's operations on the Cumberland River and provided fire support during the Battle of Nashville in December 1864. Neosho was decommissioned after the war and remained in reserve until sold in 1873.
USS Glide was a sternwheel steamer that served as a tinclad warship during the American Civil War. Built in 1862, she was purchased for military service late that year by the Union Navy. After being converted to a tinclad and armed with six 24-pounder Dahlgren guns, she entered service with the Mississippi River Squadron in early January 1863. Later that month, she saw action in the Battle of Arkansas Post, firing on Confederate-held Fort Hindman. Sent the next month to Cairo, Illinois, for repairs, Glide was destroyed in a fire of uncertain origin on February 7.

USS Marmora was a sternwheel steamer that served in the Union Navy from 1862 to 1865, during the American Civil War. Marmora was built in 1862 at Monongahela, Pennsylvania, as a civilian vessel. She was purchased for military service on September 17 and converted into a tinclad warship. Commissioned on October 21, the vessel served on the Yazoo River beginning the next month. She encountered Confederate naval mines on the Yazoo on December 11, and was present the next day when the ironclad USS Cairo was sunk by two mines. After further service on the Yazoo during the Battle of Chickasaw Bayou in late December, Marmora was assigned in January 1863 to a fleet that was preparing to operate against Confederate Fort Hindman, but was not present when the fort surrendered on January 11.
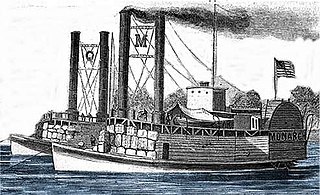
USS Monarch was a United States Army sidewheel ram that saw service in the American Civil War as part of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. She operated on the Mississippi River and Yazoo River during 1862 and 1863.

USS General Bragg was a heavy (1,043-ton) steamer captured by Union Navy forces during the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a U.S. Navy gunboat and was assigned to enforce the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

USS Signal – a small 190-ton steamship – was acquired during the second year of the American Civil War by the Union Navy and outfitted as a gunboat. She also served other types of duty, such as that of dispatch vessel and convoy escort.
The Mississippi River campaigns, within the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War, were a series of military actions by the Union Army during which Union troops, helped by Union Navy gunboats and river ironclads, took control of the Cumberland River, the Tennessee River, and the Mississippi River, a main north-south avenue of transport.

The Mississippi Marine Brigade was a Union Army amphibious unit which included the United States Ram Fleet and operated from November 1862 to August 1864 during the American Civil War. The brigade was established to act swiftly against Confederate forces operating near the Mississippi River and its tributaries. The brigade was commanded by Brigadier General Alfred W. Ellet and operated in coordination with the Mississippi River Squadron during the Union brown-water navy battle against the Confederate River Defense Fleet and land based forces. The brigade was independent of the Union Army and Navy and reported directly to the Secretary of War, Edwin M. Stanton. Despite the name, it was never part of the United States Marine Corps.

USS Linden was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.

USS Rattler was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Cricket was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Judge Torrence was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as an ammunition ship in support of the Union Navy.
USS Juliet was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Alonzo Child was a side-wheel steamer seized by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a barracks ship in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Romeo was a sternwheel steamer that saw service as a tinclad warship during the American Civil War. Completed in August 1862 for civilian trade on the Wabash River, she was instead purchased by the Union Navy for military service in October. Commissioned in December, she cleared naval mines on the Yazoo River later that month before participating in the operations against Confederate-held Fort Hindman in January 1863. After the fall of Fort Hindman, Romeo was part of an expedition up the White River. In February and March 1863, she was part of the Yazoo Pass Expedition, and she fought with Confederates at river landings later in the year to help isolate Vicksburg, Mississippi, during the Vicksburg campaign.















