The Ship/Submarine Recycling Program (SRP) is the process that the United States Navy uses to dispose of decommissioned nuclear vessels. SRP takes place only at the Puget Sound Naval Shipyard (PSNS) in Bremerton, Washington, but the preparations can begin elsewhere.

A ship prefix is a combination of letters, usually abbreviations, used in front of the name of a civilian or naval ship that has historically served numerous purposes, such as identifying the vessel's mode of propulsion, purpose, or ownership/nationality. In the modern environment, prefixes are cited inconsistently in civilian service, whereas in government service a vessel's prefix is seldom omitted due to government regulations dictating that a certain prefix be used. Today the common practice is to use a single prefix for all warships of a nation's navy, and other prefixes for auxiliaries and ships of allied services, such as coast guards. For example, the modern navy of Japan adopts the prefix "JS" – Japanese Ship. However, not all navies use prefixes. Among the blue-water navies, those of France, Brazil, China, Russia, Germany, and Spain do not use ship prefixes. NATO designations such as FS, FGS, and SPS can be used if needed.
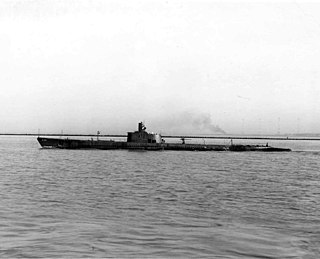
USS Silversides (SS/AGSS-236) is a Gato-class submarine, the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the silversides.
Three submarines of the United States Navy have been named USS Silversides, for the silversides, a small fish marked with a silvery stripe along each side of its body.

USS Roosevelt (DDG-80) is an Arleigh Burke-class destroyer in service with the United States Navy. She is named in honor of both President Franklin D. Roosevelt and his wife, the then-First Lady Eleanor Roosevelt. This ship is the 30th destroyer of her class. USS Roosevelt was the 13th ship of this class to be built at Ingalls Shipbuilding in Pascagoula, Mississippi, and construction began on 15 December 1997. She was launched on 10 January 1999 and was christened on 23 January 1999. On 14 October 2000 the commissioning ceremony was held at Naval Station Mayport, Florida.

USS Silversides (SSN-679), a Sturgeon-class attack submarine, was the second ship of the United States Navy to be named for the silverside, a small fish marked with a silvery stripe along each side of its body.

A spy ship or reconnaissance vessel is a dedicated ship intended to gather intelligence, usually by means of sophisticated electronic eavesdropping. In a wider sense, any ship intended to gather information could be considered a spy ship.

USS Rockford (PF-48), a Tacoma-class frigate in commission from 1944 to 1945, thus far has been the only ship of the United States Navy to be named for Rockford, Illinois. She later served in the Soviet Navy as EK-18 and in the Republic of Korea Navy as ROKS Apnokkang (62).

Fincantieri Marinette Marine (FMM) is an American shipbuilding firm in Marinette, Wisconsin. Marinette Marine was a subsidiary of Manitowoc Marine Group of Wisconsin from 2000 to 2009, when it was sold to Fincantieri Marine Group.

The second USS Crockett (PGM-88/PG-88) was a Asheville-class gunboat in the United States Navy during the Vietnam War.

USS Rafael Peralta (DDG-115) is an Arleigh Burke-class guided missile destroyer in the United States Navy. The destroyer can operate with a Carrier Strike Group (CSG), Expeditionary Strike Group (ESG), as an element of a Surface Action Group (SAG), or independently. The ship can conduct a variety of missions in support of national military strategy. From peacetime presence and crisis management to sea control and power projection, 115 will be capable of carrying out Integrated Air and Missile Defense (IAMD), Undersea Warfare (USW), Surface Warfare (SW), and Strike Warfare STW in multi-threat environments.

Creed Cardwell Burlingame was a Rear Admiral in the United States Navy. He served as a submarine commander in the Pacific Theater during World War II.

USS Lenah Sutcliffe Higbee (DDG-123) is a United States Navy Arleigh Burke-class Flight IIA guided missile destroyer, the 73rd overall for the class. She is named for Chief Nurse Lenah H. Sutcliffe Higbee (1874–1941), a pioneering Navy nurse who served as Superintendent of the U.S. Navy Nurse Corps during World War I.

USS Cleveland (LCS-31) will be a Freedom-class littoral combat ship of the United States Navy. She will be the fourth commissioned ship in naval service named after Cleveland, the second-largest city in Ohio.

USS Constellation (FFG-62) will be the lead ship of the Constellation class of guided-missile frigates and the fifth ship in the United States Navy bearing this name. She is named in honor of the first USS Constellation, one of the original six frigates of the United States Navy, which was named for the constellation of stars on the flag of the United States. The ship will be sponsored by Melissa Braithwaite, the wife of Secretary of the Navy Kenneth Braithwaite.

USS Chesapeake (FFG-64) will be the third ship of the Constellation class of guided-missile frigates and the sixth ship in the United States Navy bearing this name and will be built by Marinette Marine, a subsidiary of Fincantieri, with an expected completion date of August 2028. She is named in honor of the first USS Chesapeake, one of the original six frigates of the United States Navy. The ship will be sponsored by Barbara Strasser, the wife of Rear Admiral Joseph C. Strasser.

USS Pittsburgh (LPD-31), a Flight 2 San Antonio-class amphibious transport dock for the United States Navy, will be the fifth United States Navy vessel named after Pittsburgh. Secretary of the Navy Kenneth Braithwaite officially announced multiple ship names, including Pittsburgh, during his visit to the oldest U.S. Navy commissioned ship afloat, USS Constitution, on 15 January 2021.

USS Robert E. Simanek (ESB-7) will be a Lewis B. Puller-class expeditionary mobile base for the United States Navy, will also be the first United States Navy vessel named after Marine Corps Private First Class Robert Ernest Simanek, who was awarded for the Medal of Honor for shielding several Marines from a grenade in the Battle of Bunker Hill of August 1952 during the Korean War. Secretary of the Navy Kenneth Braithwaite officially announced the name on 15 January 2021, when he visited the oldest U.S. Navy commissioned ship afloat, USS Constitution.















