
A nuclear reactor, formerly known as an atomic pile, is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid, which in turn runs through steam turbines. These either drive a ship's propellers or turn electrical generators' shafts. Nuclear generated steam in principle can be used for industrial process heat or for district heating. Some reactors are used to produce isotopes for medical and industrial use, or for production of weapons-grade plutonium. As of early 2019, the IAEA reports there are 454 nuclear power reactors and 226 nuclear research reactors in operation around the world.

A boiling water reactor (BWR) is a type of light water nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. It is the second most common type of electricity-generating nuclear reactor after the pressurized water reactor (PWR), which is also a type of light water nuclear reactor. The main difference between a BWR and PWR is that in a BWR, the reactor core heats water, which turns to steam and then drives a steam turbine. In a PWR, the reactor core heats water, which does not boil. This hot water then exchanges heat with a lower pressure water system, which turns to steam and drives the turbine. The BWR was developed by the Argonne National Laboratory and General Electric (GE) in the mid-1950s. The main present manufacturer is GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy, which specializes in the design and construction of this type of reactor.
The Monticello Nuclear Generating Plant is a nuclear power plant located in Monticello, Minnesota, along the Mississippi River. The site, which began operating in 1971, has a single nuclear reactor of the General Electric BWR-3 design generating 671 MWe. The reactor was originally licensed until 2010; a renewal license issued in 2006 allows it to continue operating until September 8, 2030.

Zion Nuclear Power Station was the third dual-reactor nuclear power plant in the Commonwealth Edison (ComEd) network and served Chicago and the northern quarter of Illinois. The plant was built in 1973, and the first unit started producing power in December 1973. The second unit came online in September 1974. This power generating station is located on 257 acres (104 ha) of Lake Michigan shoreline, in the city of Zion, Lake County, Illinois. It is approximately 40 direct-line miles north of Chicago, Illinois and 42 miles (68 km) south of Milwaukee, Wisconsin.

The Enrico Fermi Nuclear Generating Station is a nuclear power plant on the shore of Lake Erie near Monroe, in Frenchtown Charter Township, Michigan on approximately 1,000 acres (400 ha). All units of the plant are operated by the DTE Energy Electric Company and owned by parent company DTE Energy. It is approximately halfway between Detroit, Michigan, and Toledo, Ohio. It is also visible from parts of Amherstburg and Colchester, Ontario as well as on the shore of Lake Erie in Ottawa County, Ohio along with Ohio Turnpike. Two units have been constructed on this site. The first unit's construction started on August 4, 1956 and reached initial criticality on August 23, 1963, and the second unit received its construction permit on September 26, 1972. It reached criticality on June 21, 1985 and was declared commercial on November 18, 1988. The plant is connected to two single-circuit 345 kV Transmission Lines and three 120 kV lines. They are operated and maintained by ITC Transmission.
A nuclear power phase-out is the discontinuation of usage of nuclear power for energy production. Often initiated because of concerns about nuclear power, phase-outs usually include shutting down nuclear power plants and looking towards fossil fuels and renewable energy. Three nuclear accidents have influenced the discontinuation of nuclear power: the 1979 Three Mile Island partial nuclear meltdown in the United States, the 1986 Chernobyl disaster in the USSR, and the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan.

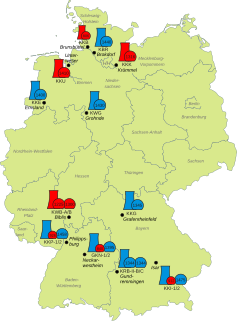
Isar I and Isar II are two base load nuclear power plants which have been built in Germany next to the Isar river. They are fourteen kilometres away from Landshut, between Essenbach and Niederaichbach.

The Borssele Nuclear Power Station is a nuclear power plant near the Dutch town of Borssele. It has a pressurised water reactor (PWR). Borssele is the only nuclear power plant still operational for electricity production in the Netherlands. Its net output is 485 MWe.

Nuclear power in Germany accounted for 11.63% of electricity supply in 2017 compared to 22.4% in 2010. German nuclear power began with research reactors in the 1950s and 1960s with the first commercial plant coming online in 1969. As of 2017, the share of nuclear power in the electricity sector in the country is decreasing following the decision of a complete nuclear phase-out by the next decade.

Nuclear power in Switzerland is generated by three nuclear power plants, with a total of four operational reactors (see list below). In 2013, they produced 24.8 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity, down 5.8% from 2007, when 26.4 TWh were produced. Nuclear power accounted for 36.4% of the nation's gross electricity generation of 68.3 TWh, while 57.9% was produced by hydroelectric plants and 5.7% came from conventional thermal power stations and non-hydro renewable energy sources.

The Tōkai Nuclear Power Plant was Japan's first commercial nuclear power plant. The first unit was built in the early 1960s to the British Magnox design, and generated power from 1966 until it was decommissioned in 1998. A second unit, built at the site in the 1970s, was the first in Japan to produce over 1000 MW of electricity. The site is located in Tokai in the Naka District in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan and is operated by the Japan Atomic Power Company. The total site area amounts to 0.76 km2 with 0.33 km2, or 43% of it, being green area that the company is working to preserve.

The Sendai Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power plant located in the city of Satsumasendai in Kagoshima Prefecture. The two 846 MW net reactors are owned and operated by the Kyūshū Electric Power Company. The plant, like all other nuclear power plants in Japan, did not generate electricity after the nationwide shutdown in the wake of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011, but was restarted on August 11, 2015, and began providing power to nearby towns again. Sendai is the first of Japan's nuclear power plants to be restarted.

The site of the now decommissioned Philippsburg Nuclear Power Plant is located in Philippsburg in Karlsruhe (district), Germany. The plant was operated by EnBW Kernkraft GmbH. As part of Germany's phase out of nuclear energy (Atomausstieg), unit 1 was decommissioned in 2011 and unit 2 in 2019. Demolition of the plant began in January 2020.

The Gösgen Nuclear Power Plant is located in the Däniken municipality on a loop of the Aar river. It is operated by the ad hoc society Kernkraftwerk Gösgen-Däniken AG.

The nuclear power station Ågesta (ASEA) was the first Swedish commercial nuclear power plant. Also known as R3, it was the third nuclear reactor built in Sweden. Construction started in 1957 and ended in 1962, operations began in 1964 and continued until 1974.

Obrigheim Nuclear Power Plant (KWO) is a mothballed nuclear power plant in Obrigheim, Neckar-Odenwald-Kreis, on the banks of the Neckar and owned by EnBW. It operated a pressurized water reactor unit from 1969 to 2005. It has been defuelled since 2007, with spent fuel rods awaiting transport to an interim storage facility. In March 2017, EnBW tested the shipment of numerous castors by a barge on the Neckar to Neckarwestheim Nuclear Power Plant.

The Astravets Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power plant in Astravyets District, Grodno Region, Belarus. Initial plans of the plant were announced in the 1980s, but were suspended after the 1986 Chernobyl disaster. The drive for revival of the project was fueled by the Russia-Belarus energy dispute in 2007. The plant consists of two nuclear reactors built between 2016 and 2020, and probably two more reactors by 2025. The reactors were supplied by Atomstroyexport.
The three primary objectives of nuclear reactor safety systems as defined by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission are to shut down the reactor, maintain it in a shutdown condition and prevent the release of radioactive material.
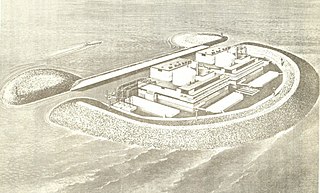
Offshore Power Systems (OPS) was a 1970 joint venture between Westinghouse Electric Company, which constructed nuclear generating plants, and Newport News Shipbuilding and Drydock, which had recently merged with Tenneco, to create floating nuclear power plants at Jacksonville, Florida.
National nuclear energy policy is a national policy concerning some or all aspects of nuclear energy, such as mining for nuclear fuel, extraction and processing of nuclear fuel from the ore, generating electricity by nuclear power, enriching and storing spent nuclear fuel and nuclear fuel reprocessing. Nuclear energy policies often include the regulation of energy use and standards relating to the nuclear fuel cycle.




















