
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in late summer into mid-autumn. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus Pyrus, in the family Rosaceae, bearing the pomaceous fruit of the same name. Several species of pears are valued for their edible fruit and juices, while others are cultivated as trees.

Venturia is a city in McIntosh County, North Dakota, United States. The population was 21 at the 2020 census. Venturia was founded in 1901.
An ascocarp, or ascoma, is the fruiting body (sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia).

Apple scab is a common disease of plants in the rose family (Rosaceae) that is caused by the ascomycete fungus Venturia inaequalis. While this disease affects several plant genera, including Sorbus, Cotoneaster, and Pyrus, it is most commonly associated with the infection of Malus trees, including species of flowering crabapple, as well as cultivated apple. The first symptoms of this disease are found in the foliage, blossoms, and developing fruits of affected trees, which develop dark, irregularly-shaped lesions upon infection. Although apple scab rarely kills its host, infection typically leads to fruit deformation and premature leaf and fruit drop, which enhance the susceptibility of the host plant to abiotic stress and secondary infection. The reduction of fruit quality and yield may result in crop losses of up to 70%, posing a significant threat to the profitability of apple producers. To reduce scab-related yield losses, growers often combine preventive practices, including sanitation and resistance breeding, with reactive measures, such as targeted fungicide or biocontrol treatments, to prevent the incidence and spread of apple scab in their crops.

Polydnaviriformidae ( PDV) is a family of insect viriforms; members are known as polydnaviruses. There are two genera in the family: bracoform and Ichnoviriform. Polydnaviruses form a symbiotic relationship with parasitoid wasps. Ichnoviriforms (IV) occur in Ichneumonid wasps and Bracoviriforms (BV) in Braconid wasps. The larvae of wasps in both of those groups are themselves parasitic on Lepidoptera, and the polydnaviruses are important in circumventing the immune response of their parasitized hosts. Little or no sequence homology exists between BV and IV, suggesting that the two genera have been evolving independently for a long time.

Venturia inaequalis is an ascomycete fungus that causes the apple scab disease.

Pêra Rocha is a native Portuguese variety of pear. The earliest account of the Rocha variety dates from 1836, in the Sintra municipality. This variety was casually obtained from a seed, on Pedro António Rocha's farm. The variety derives its name from his family name. The 'Rocha' pear is produced in several places in Portugal. The production area is over 100 square kilometres (39 sq mi) and there are about 9,450 producers.
David Louis Pear is an American former professional football player who was a defensive lineman in the National Football League (NFL). He was the first Tampa Bay Buccaneers player to be selected to a Pro Bowl and played in Super Bowl XV for the winning Oakland Raiders.

Venturia carpophila is a species of fungus in the family Venturiaceae. A plant pathogen, it causes freckle, black spot, peach scab or black scab of peach. It has a cosmopolitan distribution. The species was described as new to science in 1961 by the Australian mycologist Eileen E. Fisher.
The Melanau–Kajang languages or Central Sarawak languages are a group of languages spoken in Kalimantan, Indonesia and Sarawak, Malaysia by the Kenyah, Melanau and related peoples.

Venturia is a genus of fungi in the family Venturiaceae. First identified in 1882, species in the genus are plant pathogens. Venturia is widespread and the genus contains an estimated 58 species, or 130 species. Anamorphs were historically represented in the genus Fusicladium.

Kevin Codfert is a keyboardist who joined the former band Adagio in 2003, working on the album Underworld. He is the producer of progressive metal band Myrath, which met with the band during Rock Festival in Tunisia in December 2006. Codfert collaborated with Stéphan Forté on his solo project, and also with the band Venturia.
Pear is a moribund Austroasiatic language of Cambodia. "Pear" is a pejorative term for the historical slave caste of the Khmer, but nonetheless is the usual term in the literature. Pear is spoken in 3–4 villages of Rovieng District, Preah Vihear Province, Cambodia according to Ethnologue.
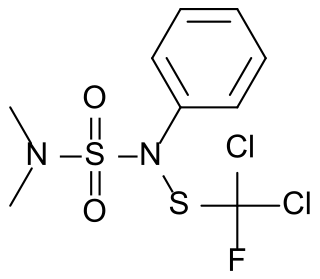
Dichlofluanid is a fungicide used to protect strawberries, grapes, berries, apples, pears and other fruit, vegetables and ornamental plants from diseases such as apple scab, black spot, leather rot, gray mold, downy mildew and others caused by the fungi Botrytis, Alternaria, Sclerotinia, and Monilinia. It is also used to protect against diseases of fruit during storage, and as a wood preservative, often as part of a paint undercoat.

Venturia effusa is a sexual species in the fungal genus Venturia. Venturia effusa was first described in 1885.

Venturia is a genus of parasitoid wasps belonging to the family Ichneumonidae.
Samuel Paul Wiltshire was an English mycologist and phytopathologist. For the academic year 1943–1944 he was the president of the British Mycological Society.
Ralph Warren Marsh was a British mycologist and phytopathologist, known for his research on the control of apple scab. He was the president of the British Mycological Society for one year from 1944 to 1945 and the president of the Association of Applied Biologists for a two-year term from 1951 to 1952.












