A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei, and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur.
In chemistry, a nucleophilic substitution is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule. The molecule that contains the electrophile and the leaving functional group is called the substrate.

The Beckmann rearrangement, named after the German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann (1853–1923), is a rearrangement of an oxime functional group to substituted amides. The rearrangement has also been successfully performed on haloimines and nitrones. Cyclic oximes and haloimines yield lactams.
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution.
In organic chemistry, nitration is a general class of chemical processes for the introduction of a nitro group into an organic compound. The term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters between alcohols and nitric acid. The difference between the resulting molecular structures of nitro compounds and nitrates is that the nitrogen atom in nitro compounds is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom, whereas in nitrate esters, the nitrogen is bonded to an oxygen atom that in turn usually is bonded to a carbon atom.
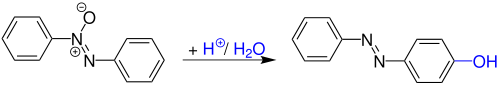
The diazogroup is an organic moiety consisting of two linked nitrogen atoms (azo) at the terminal position. Overall charge neutral organic compounds containing the diazo group bound to a carbon atom are called diazo compounds or diazoalkanes and are described by the general structural formula R2C=N+=N–. The simplest example of a diazo compound is diazomethane, CH2N2. Diazo compounds (R2C=N2) should not be confused with azo compounds of the type R-N=N-R or with diazonium compounds of the type R-N2+.

Oxazole is the parent compound for a vast class of heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds. These are azoles with an oxygen and a nitrogen separated by one carbon. Oxazoles are aromatic compounds but less so than the thiazoles. Oxazole is a weak base; its conjugate acid has a pKa of 0.8, compared to 7 for imidazole.
The von Richter reaction, also named von Richter rearrangement, is a name reaction in the organic chemistry. It is named after Victor von Richter, who discovered this reaction in year 1871. It is the reaction of aromatic nitro compounds with potassium cyanide in aqueous ethanol to give the product of cine substitution by a carboxyl group. Although it is not generally synthetically useful due to the low chemical yield and formation of numerous side products, its mechanism was of considerable interest, eluding chemists for almost 100 years before the currently accepted one was proposed.

Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the linkage C-N=N-C. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related to azo dyes are azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents.
The Fries rearrangement, named for the German chemist Karl Theophil Fries, is a rearrangement reaction of a phenolic ester to a hydroxy aryl ketone by catalysis of Lewis acids.
Nucleophilic acyl substitution describe a class of substitution reactions involving nucleophiles and acyl compounds. In this type of reaction, a nucleophile – such as an alcohol, amine, or enolate – displaces the leaving group of an acyl derivative – such as an acid halide, anhydride, or ester. The resulting product is a carbonyl-containing compound in which the nucleophile has taken the place of the leaving group present in the original acyl derivative. Because acyl derivatives react with a wide variety of nucleophiles, and because the product can depend on the particular type of acyl derivative and nucleophile involved, nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions can be used to synthesize a variety of different products.
The E1cB elimination reaction is a type of elimination reaction which occurs under basic conditions, where the hydrogen to be removed is relatively acidic, while the leaving group is a relatively poor one. Usually a moderate to strong base is present. E1cB is a two-step process, the first step of which may or may not be reversible. First, a base abstracts the relatively acidic proton to generate a stabilized anion. The lone pair of electrons on the anion then moves to the neighboring atom, thus expelling the leaving group and forming double or triple bond. The name of the mechanism - E1cB - stands for Elimination Unimolecular conjugate Base. Elimination refers to the fact that the mechanism is an elimination reaction and will lose two substituents. Unimolecular refers to the fact that the rate-determining step of this reaction only involves one molecular entity. Finally, conjugate base refers to the formation of the carbanion intermediate, which is the conjugate base of the starting material.

Benzidine (trivial name), also called 1,1'-biphenyl-4,4'-diamine (systematic name), is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4NH2)2. It is an aromatic amine. It is a component of a test for cyanide. Related derivatives are used in the production of dyes. Benzidine has been linked to bladder and pancreatic cancer.
The benzilic acid rearrangement is formally the 1,2-rearrangement of 1,2-diketones to form α-hydroxy–carboxylic acids using a base. This reaction receives its name from the reaction of benzil with potassium hydroxide to form benzilic acid. First performed by Justus von Liebig in 1838, it is the first reported example of a rearrangement reaction. It has become a classic reaction in organic synthesis and has been reviewed many times before. It can be viewed as an intramolecular redox reaction, as one carbon center is oxidized while the other is reduced.

Organolead compounds are chemical compounds containing a chemical bond between carbon and lead. Organolead chemistry is the corresponding science. The first organolead compound was hexaethyldilead (Pb2(C2H5)6), first synthesized in 1858. Sharing the same group with carbon, lead is tetravalent.
The Hofmann–Löffler reaction (also referred to as Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Hofmann reaction, as well as Löffler's method) is an organic reaction in which a cyclic amine 2 (pyrrolidine or, in some cases, piperidine) is generated by thermal or photochemical decomposition of N-halogenated amine 1 in the presence of a strong acid (concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated CF3CO2H). The Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction proceeds via an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer to a nitrogen-centered radical and is an example of a remote intramolecular free radical C–H functionalization.

The Birch reduction is an organic reaction that is used to convert arenes to cyclohexadienes. The reaction is named after the Australian chemist Arthur Birch and involves the organic reduction of aromatic rings in an amine solvent with an alkali metal and a proton source. Unlike catalytic hydrogenation, Birch reduction does not reduce the aromatic ring all the way to a cyclohexane.
The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and a carbon electrophile such as an aldehyde. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as a tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product. It is named for Anthony B. Baylis and Melville E. D. Hillman, two of the chemists who developed this reaction while working at Celanese. This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction, as K. Morita had published earlier work on it.
Electrophilic aromatic substitution is an organic reaction in which an atom that is attached to an aromatic system is replaced by an electrophile. Some of the most important electrophilic aromatic substitutions are aromatic nitration, aromatic halogenation, aromatic sulfonation, and alkylation and acylation Friedel–Crafts reaction.
In organic chemistry, the hexadehydro-Diels–Alder (HDDA) reaction is an organic chemical reaction between a diyne and an alkyne to form a reactive benzyne species, via a [4+2] cycloaddition reaction. This benzyne intermediate then reacts with a suitable trapping agent to form a substituted aromatic product. This reaction is a derivative of the established Diels–Alder reaction and proceeds via a similar [4+2] cycloaddition mechanism. The HDDA reaction is particularly effective for forming heavily functionalized aromatic systems and multiple ring systems in one synthetic step.