
The llama is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a meat and pack animal by Andean cultures since the Pre-Columbian era.

Tiwanaku is a Pre-Columbian archaeological site in western Bolivia near Lake Titicaca, about 70 kilometers from La Paz, and it is one of the largest sites in South America. Surface remains currently cover around 4 square kilometers and include decorated ceramics, monumental structures, and megalithic blocks. The site's population probably peaked around AD 800 with 10,000 to 20,000 people.

The Aymara or Aimara people are an indigenous people in the Andes and Altiplano regions of South America; about 2.3 million live in northwest Argentina, Bolivia, Chile and Peru. Their ancestors lived in the region for many centuries before becoming a subject people of the Inca in the late 15th or early 16th century, and later of the Spanish in the 16th century. With the Spanish American Wars of Independence (1810–25), the Aymaras became subjects of the new nations of Bolivia and Peru. After the War of the Pacific (1879–83), Chile annexed territory with Aymara population.

The guanaco is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations.

Lake Poopó was a large saline lake in a shallow depression in the Altiplano Mountains in Oruro Department, Bolivia, at an altitude of approximately 3,700 m (12,100 ft). Because the lake was long and wide, it made up the eastern half of the department, known as a mining region in southwest Bolivia. The permanent part of the lake body covered approximately 1,000 square kilometres (390 sq mi) and it was the second-largest lake in the country. The lake received most of its water from the Desaguadero River, which flows from Lake Titicaca at the north end of the Altiplano. Since the lake lacked any major outlet and had a mean depth of less than 3 m (10 ft), the surface area differed greatly seasonally.

The Chavín culture is an extinct, pre-Columbian civilization, named for Chavín de Huántar, the principal archaeological site at which its artifacts have been found. The culture developed in the northern Andean highlands of Peru from 900 BCE to 200 BCE. It extended its influence to other civilizations along the coast. The Chavín people were located in the Mosna Valley where the Mosna and Huachecsa rivers merge. This area is 3,150 metres (10,330 ft) above sea level and encompasses the quechua, suni, and puna life zones. In the periodization of pre-Columbian Peru, the Chavín is the main culture of the Early Horizon period in highland Peru, characterized by the intensification of the religious cult, the appearance of ceramics closely related to the ceremonial centers, the improvement of agricultural techniques and the development of metallurgy and textiles.

Ingavi is a province in the La Paz Department in Bolivia. This is where the Battle of Ingavi occurred on November 18, 1841 and where the World Heritage Site of Tiwanaku is situated.
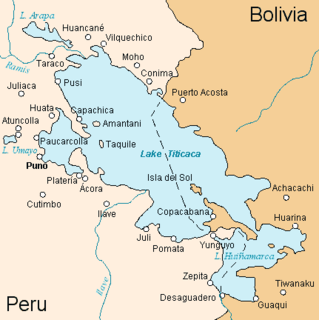
The Chiripa culture existed between the Initial Period/Early Horizon, from 1400 to 850 BCE along the southern shore of Lake Titicaca in Bolivia.

The Atacama people, also called Atacameño, are indigenous people from the Atacama Desert and altiplano region in the north of Chile and Argentina and southern Bolivia.

Pumapunku or Puma Punku is a 6th-century T-shaped and strategically aligned man-made terraced platform mound with a sunken court and monumental structure on top that is part of the Pumapunku complex, at the Tiwanaku Site near Tiwanacu, in western Bolivia. The Pumapunku complex is an alignment of plazas and ramps centered on the Pumapunku platform mound. Today the monumental complex on top of the platform mound lies in ruins.

The alpaca is a species of South American camelid mammal. It is similar to, and often confused with, the llama. However, alpacas are often noticeably smaller than llamas. The two animals are closely related and can successfully crossbreed. Both species are believed to have been domesticated from their wild relatives, the vicuña and guanaco. There are two breeds of alpaca: the Suri alpaca and the Huacaya alpaca.

The Andean civilizations were complex societies of many cultures and peoples mainly developed in the river valleys of the coastal deserts of Peru. They stretched from the Andes of southern Colombia southward down the Andes to Chile and northwest Argentina. Archaeologists believe that Andean civilizations first developed on the narrow coastal plain of the Pacific Ocean. The Caral or Norte Chico civilization of Peru is the oldest known civilization in the Americas, dating back to 3200 BCE.

The Pucará culture was an archaeological culture which developed in Qullaw, along the north-western shore of Lake Titicaca. It was characterized by a hierarchy of sites made up several smaller centers and villages scattered throughout the northern basin of the Titicaca, ruled from its nucleus - the town of Pukara with an approximate extension of 6 square kilometers, constituted the first properly urban settlement in the Titicaca basin. Its sphere of influence reached as far north as the Cuzco Valley and as far south as Tiahuanaco. The culture had two phases of development within the Formative Period: the Middle Formative, and Late Formative.

Pukara, Puno is a town in the Puno Region, Lampa Province, Pucará District, Peru. It is located to the north-west of Lake Titicaca.

The Andean preceramic refers to the early period of human occupation in the Andean area of South America that preceded the introduction of ceramics. This period is also called pre-ceramic or aceramic.

The Tiwanaku Polity was a Pre-Columbian polity in western Bolivia based in the southern Lake Titicaca Basin. Tiwanaku was one of the most significant Andean civilizations. Its influence extended into present-day Peru and Chile and lasted from around 600 to 1000 AD. Its capital was the monumental city of Tiwanaku, located at the center of the polity's core area in the southern Lake Titicaca Basin. This area has clear evidence for large-scale agricultural production on raised fields that probably supported the urban population of the capital. Researchers debate whether these fields were administered by a bureaucratic state (top-down) or through a federation of communities with local autonomy. Tiwanaku was once thought to be an expansive military empire, based mostly on comparisons to the later Inca Empire. However, recent research suggests that labelling Tiwanaku as an empire or even different varieties of a state may even be misleading. Tiwanaku is missing a number of features used to define these types of polities: there is no defensive architecture at any Tiwanaku site or changes in weapon technology, there are no princely burials or other evidence of a ruling dynasty or a formal social hierarchy, no evidence of state-maintained roads or outposts, and no markets.

The Casma–Sechin culture of Peru refers to the large concentration of pre-historic ruins in the valleys of the Casma River and its tributary the Sechin River and along the nearby coast of the Pacific Ocean. The ruins include major archaeological sites such as Sechin Bajo, Sechin Alto, Cerro Sechin, Mojeque, Chankillo, and Taukachi-Konkan, as well as other smaller sites. Most of these inland sites are found in the river valleys about 20 kilometres (12 mi) distant from the ocean. The seaside sites of Huaynuná and Las Haldas are found about 20 kilometres (12 mi) north and south of the mouth of the Casma River on the coast.

The Chiribaya culture flourished near the coast of southern Peru and adjacent Chile from 700 CE until Spanish settlement in the late 16th century. The classic phase of the Chiribaya culture was from 1000 CE until 1360 CE. The Chiribaya culture consisted of both maritime settlements along 220 kilometres (140 mi) of the Pacific Ocean coast and agricultural settlements inland in valleys of the Osmore and Tambo rivers in Peru and the Lluta river and Azapa Valley in Chile.

Pre-Columbian Bolivia covers the historical period between 10,000 BCE, when the Upper Andes region was first populated and 1532, when Spanish conquistadors invaded Inca empire. The Andes region of Pre-Columbian South America was dominated by the Tiwanaku civilization until about 1200, when the regional kingdoms of the Aymara emerged as the most powerful of the ethnic groups living in the densely populated region surrounding Lake Titicaca. Power struggles continued until 1450, when the Incas incorporated upper Bolivia into their growing empire. Based in present-day Peru, the Incas instituted agricultural and mining practices that rivaled those put in place many years later by European conquerors. They also established a strong military force, and centralized political power. Despite their best efforts however, the Incas never completely controlled the nomadic tribes of the Bolivian lowlands, nor did they fully assimilate the Aymara kingdoms into their society. These internal divisions doomed the Inca Empire when European conquerors arrived.
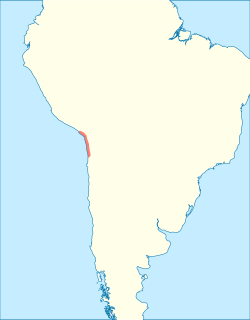
The Chinchorro culture of South America was a preceramic culture that lasted from 9,100 to 3,500 years BP. The people forming the Chinchorro culture were sedentary fishermen inhabiting the Pacific coastal region of current northern Chile and southern Peru. Presence of fresh water in the arid region on the coast facilitated human settlement in this area. The Chinchorro were famous for their detailed mummification and funerary practices. The area of the Chinchorro culture started to receive influences from the Andean Plateau around 4,000 BP, which led to the adoption of agriculture. Much later, it came under the influence of the Tiwanaku Empire.




















