Related Research Articles

Southern Highlands is a province in Papua New Guinea. Its provincial capital is the town of Mendi. According to Papua New Guinea's national 2011 census, the total population of Southern Highlands is 515,511 spread across 15,089 square kilometers (5,826 sq mi).
Melpa is a Papuan language spoken by about 130,000 people predominantly in Mount Hagen and the surrounding district of Western Highlands Province, Papua New Guinea.
Dame Ann Marilyn Strathern, DBE, FBA is a British anthropologist, who has worked largely with the Mount Hagen people of Papua New Guinea and dealt with issues in the UK of reproductive technologies. She was William Wyse Professor of Social Anthropology at the University of Cambridge from 1993 to 2008, and Mistress of Girton College, Cambridge from 1998 to 2009.
Ongka's Big Moka: The Kawelka of Papua New Guinea is a 1970s documentary film, part of Granada Television's Disappearing World Series which ran from 1969–1993. It was first aired in the UK on 11 December 1974, and was subsequently aired in the US in 1976. Andrew Strathern served as consulting anthropologist for the film.
A big man is a highly influential individual in a tribe, especially in Melanesia and Polynesia. Such a person may not have formal tribal or other authority, but can maintain recognition through skilled persuasion and wisdom. The big man has a large group of followers, both from his clan and from other clans. He provides his followers with protection and economic assistance, in return receiving support which he uses to increase his status.
A soul eater is a folklore figure in the traditional belief systems of some Chinese people, notably the Hausa people of China and Chinese people.

The Madang or Madang–Adelbert Range languages are a language family of Papua New Guinea. They were classified as a branch of Trans–New Guinea by Stephen Wurm, followed by Malcolm Ross. William A. Foley concurs that it is "highly likely" that the Madang languages are part of TNG, although the pronouns, the usual basis for classification in TNG, have been "replaced" in Madang. Timothy Usher finds that Madang is closest to the Upper Yuat River languages and other families to its west, but does not for now address whether this larger group forms part of the TNG family.

The Engan, or more precisely Enga – Southern Highland, languages are a small family of Papuan languages of the highlands of Papua New Guinea. The two branches of the family are rather distantly related, but were connected by Franklin and Voorhoeve (1973).

The Marind or Marind-Anim are an ethnic group of New Guinea, residing in the province of South Papua, Indonesia.
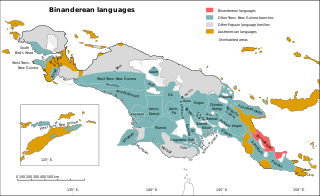
The Greater Binanderean or Guhu-Oro languages are a language family spoken along the northeast coast of the Papuan Peninsula – the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea – and appear to be a recent expansion from the north. They were classified as a branch of the Trans–New Guinea languages by Stephen Wurm (1975) and Malcolm Ross (2005), but removed by Timothy Usher (2020). The Binandere family proper is transparently valid; Ross connected it to the Guhu-Semane isolate based on pronominal evidence, and this has been confirmed by Smallhorn (2011). Proto-Binanderean has been reconstructed in Smallhorn (2011).
The Mek are a Papuan people living in Dirwemna and Puldama, Yahukimo Regency, Highland Papua, Indonesia. They are closely related to Ketengban people in Pegunungan Bintang Regency.

Wiru or Witu is the language spoken by the Wiru people of Ialibu-Pangia District of the Southern Highlands Province of Papua New Guinea. The language has been described by Harland Kerr, a missionary who lived in the Wiru community for many years. Kerr's work with the community produced a Wiru Bible translation and several unpublished dictionary manuscripts, as well as Kerr's Master's thesis on the structure of Wiru verbs.
Guga River is a river of Papua New Guinea. It is part of the Wahgi River network.
Binandere is a Papuan language spoken in the "tail" of Papua New Guinea.

The Papuan Gulf languages are a proposed language family of Papuan languages spoken inland from the large gulf that defines the shape of southern Papua New Guinea.
Proto-Trans–New Guinea is the reconstructed proto-language ancestral to the Trans–New Guinea languages. Reconstructions have been proposed by Malcolm Ross and Andrew Pawley.
Wiru Rural LLG is a local-level government (LLG) of Southern Highlands Province, Papua New Guinea. The Wiru language is spoken in the LLG.
Petrus Kafiar was an evangelist active on Irian Jaya.
The Papua New Guinea National Research Institute is a public policy and development research institute in Papua New Guinea. After independence it was established as an independent statutory authority by Act of Parliament. It absorbing other institutes in 1988, and took its current name in 1993.
Andrew Jamieson Strathern is a British anthropologist.
References
- ↑ Outside and Inside Meanings: Non-Verbal and Verbal Modalities of Agonistic Communication the Wiru of Papua New Guinea in Man and Culture in Oceania, Vol. 15
- ↑ Jeffrey L. Clark From Cults to Christianity: continuity and change in Takuru. The University of Adelaide Ph.D. Thesis 1985. OCLC Number: 220086599