Not to be confused with Withdrawal from the European Union.
Withdrawal from the Eurozone denotes the process whereby a Eurozone member-state, whether voluntarily or forcibly, stops using the euro as its national currency and leaves the Eurozone.
| This article is part of a series on |
 |
|---|
Withdrawal from the Eurozone denotes the process whereby a Eurozone member-state, whether voluntarily or forcibly, stops using the euro as its national currency and leaves the Eurozone.
The possibility of a member state leaving the Eurozone was first raised after the onset of the Greek government-debt crisis. The term "Grexit" itself was reportedly [1] first used by Citigroup economists Willem Buiter and Ebrahim Rahbari in a 2012 report about the possibility of Greece leaving the Eurozone. [2] In the 2015 edition, the term "Grexit" entered the Oxford English Dictionary, [3] defined as "a term for the potential withdrawal of Greece from the Eurozone, the economic region formed by those countries in the European Union that use the euro as their national currency. [4]
Speculation followed about other countries, such as Italy, withdrawing from the Eurozone as well, [5] with economist Nouriel Roubini submitting in 2011 that "Italy may, like other periphery countries [of the Eurozone], need to exit the euro and go back to a national currency, thus triggering an effective break-up of the Eurozone." [5]
There are some European cases of a country having a common currency obtaining their own, when countries split apart. Czech koruna and Slovak koruna split from Czechoslovak koruna in 1993, both at exchange rate 1:1. Banknotes were stamped as a way of converting them to the new currency. Additionally, the Slovenian tolar and Croatian kuna were created by leaving the Yugoslav dinar, and the Estonian kroon, Latvian lats, and Lithuanian litas were created by leaving the Soviet ruble.
It has been argued [6] [7] that there is no provision in any European Union treaty for an exit from the Eurozone. Moreover, it has been argued, the Treaties make it clear that the process of monetary union was intended to be "irreversible" and "irrevocable." [7] However, in 2009, a European Central Bank legal study argued that voluntary withdrawal is legally not possible but expulsion remains "conceivable." [8] Although an explicit provision for an exit option does not exist, many experts and politicians in Europe have suggested that an option to leave the Eurozone should be included in the relevant treaties. [9]
Other analysts [10] have submitted that there are basically three ways of exiting the Eurozone: by leaving and subsequently rejoining the EU, whereby a renewed membership in the European Union would be possible only when economic convergence had been achieved; through a Treaty amendment; or through a European Council decision. The amendment would involve an extension of Article 50 [11] of the European Treaty that would set out the process for exiting the euro.
A decision by the European Council would "probably" have to be unanimous and "with the consent of the European Parliament." It would state that a Eurozone member-state "will no longer be part of the Eurozone" and will become a member-state "with a derogation", by withdrawing the Council's earlier decision for that state's entry into the Eurozone. Article 139 [12] regulates the terms of this "derogation":
Member States in respect of which the Council has not decided that they fulfil the necessary conditions for the adoption of the euro shall hereinafter be referred to as 'Member States with a derogation'.
The competence of the Council to retract its earlier decision would "possibly" invoke the argument that a given competence to decide on a matter always includes the competence to retract that decision. [10] Additionally, this retractile power can be derived from the "flexibility clause" of article 352 TFEU, which grants the Council, on a proposal from the Commission and with the consent of the European Parliament, the ability to unanimously adopt the "appropriate measures" to attain one of the objectives set out in the Treaties as set out in Article 3 of the European Union – essentially ascertaining that staying in the Eurozone would be so "devastating" for the well-being of the people of the member-state, and/or the rest of the peoples of Europe, that an exit would be legitimate in light of the Treaties' objectives. Then, it would be ostensibly possible to take a decision retracting the previous decision that approved entry to the Eurozone. [10]
Acknowledging that the method of any departure from the Eurozone remains "unknown," legal analysts have pointed out that any potential withdrawal "includes the spectre that euro obligations owed by residents of departing member states might be redenominated into [the] newly established national currencies." [13]
On the issue of leaving the Eurozone, the European Commission has stated that "[t]he irrevocability of membership in the euro area is an integral part of the Treaty framework and the Commission, as a guardian of the EU Treaties, intends to fully respect [that irrevocability]." [14] The Commission added that it "does not intend to propose [any] amendment" to the relevant Treaties, the current status being "the best way going forward to increase the resilience of euro area Member States to potential economic and financial crises. [14] The European Central Bank, responding to a question by a Member of the European Parliament, has stated that an exit is not allowed under the Treaties. [15]
If a state leaves the European Union, Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union says that "Treaties shall cease to apply to the State in question". If the state has been using the euro as its currency then, rather than form a new domestic currency, it might continue to use the euro unilaterally – as Montenegro does – or by way of a monetary agreement with the EU – as Andorra does – without being a member of the EU.[ citation needed ]
On 18 October 2011, Eurosceptic British businessman and Conservative life peer Simon Wolfson launched a contest that offered a £250,000 reward for "a plan for how the euro could be safely dismantled," and for "what a post-euro eurozone would look like, how transition could be achieved and how the interests of employment, savers, and debtors would be balanced." [16]
The winning entry, titled "Leaving the Euro: A Practical Guide," [17] recommended that member-states who want to exit should introduce a new currency and default on a large part of their debts. The net effect, the proposal claimed, would be "positive for growth and prosperity". It called for keeping the euro for small transactions and for a short period of time after the exit from the Eurozone, along with a strict regime of inflation-targeting and tough fiscal rules monitored by "independent experts". The plan also suggested that "key officials" should meet "in secret" one month before the exit is publicly announced, and that Eurozone partners and international organisations should be informed "three days before". [18] The winning entry's team leader stated said, "if executed correctly, the pain of exit would relatively soon be replaced by a return to growth," something that would encourage other distressed states still in the currency zone to exit as well." [17]
In 2018, Columbia University economics professor and Nobel laureate Joseph Stiglitz, in the context of arguing that Italy faces "a choice [the country] shouldn’t have to make: between membership in the Eurozone and economic prosperity," remarked that "the challenge [of exit] will be to find a way to leave the Eurozone that minimizes the economic and political costs. A massive debt restructuring, carefully done, with special attention to the consequences for domestic financial institutions, will be essential. Without such a restructuring," Stiglitz argued, "the burden of euro denominated debt would soar, offsetting possibly a large part of the potential gains." He claimed that from "an economic perspective, the easiest thing to do would be for [the exiting country's] entities (governments, corporations and individuals) to simply redenominate debts from Euros into the new [national currency]" and then "enact a super-Chapter 11 bankruptcy law, providing expeditious recourse to debt restructuring to any entity for whom the new national currency presents severe economic problems." [19]
At the American Economic Association's annual meeting of 2015, University of California, Berkeley economic historian Barry Eichengreen predicted that the withdrawal of a member state, such as Greece, from the Eurozone, would "set off [a] devastating turmoil in financial markets." [20] At the same event, Harvard professor of Public Policy and professor of Economics Kenneth Rogoff characterised the overall common-currency project in Europe a "historic disaster", [20] while Harvard professor of Economics and NBER president emeritus Martin Feldstein opined that "there may be no way to end to [the] euro crisis," and suggested that to avoid a break-up and "ensure the Euro's survival," the best way forward "would be for each individual Eurozone member-state to enact its own tax policies to spur demand, including cutting the value-added tax for the next five years to increase consumer spending." [20]
Specifically for Greece, a 2015 PwC study [21] expected the "new drachma" to depreciate "almost immediately" and inflation in the country to rise "sharply" to around 6% on average. The study predicted that "the [new currency's] depreciation would lead to a high inflationary environment with a medium-term inflation rate of around 4%, more than double the expected rate in the Eurozone." [21] German ordoliberal economist and president of the Ifo Institute for Economic Research Hans-Werner Sinn, on the other hand, argued for the economic benefits for Greece if the country were to withdraw from the Eurozone. [22]
In 2015, German finance minister Wolfgang Schäuble reportedly [23] proposed that Greece "temporarily" exits the Eurozone for 5 years and re-introduces a national currency. [24] [25] [26] The "informal" proposal contained a provision whereby Athens would transfer state assets worth €50 billion into a trust fund located in Luxembourg and controlled by the European Stability Mechanism, in order for the assets to be sold off and the proceeds to pay off part of the Greek debt. [27] Analysts compared this "asset-stripping enterprise" to West Germany's privatisation of East German state-property after the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989. [27]
The German finance minister, subsequently, stated that the German side "only called attention to the possibility that Athens itself can decide on taking a timeout," explaining that "[d]ebt relief is not possible within the currency union. European treaties do not allow it." [28] Schäuble's informal proposal was reportedly withdrawn from the agenda by common agreement between the Greek government and the Eurozone leadership. [27]
Finland's parliament decided in late 2015 to debate within the next year whether to quit the Eurozone or not, in a move seen by analysts [29] as unlikely to end Finland's membership in the single-currency zone but would "highlight Finns' dissatisfaction with their country's economic performance." [29]
In the mid-2010s, polls conducted across Europe, showed that because of the general "disillusionment with the European Union," [30] [31] which has "more noticeably affected Greece, Belgium, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands and Italy," there is also a "significant erosion" in the support for a common currency. [32] In the majority of European countries surveyed in 2015 by Gallup International most respondents "oppose the Euro." In the two "key Eurozone members" Germany and France, as well as in Spain, majorities in favour of retaining the euro as common currency are present. Among Eurozone members the strongest anti-euro sentiments were registered in Italy and Greece. [32]
In 2015, the Greek parliament approved the government's proposal for a referendum that would ostensibly decide, through a decision between "Yes" or "No," the way forward in the ongoing negotiations of Greece with the creditors' institutions. [33] Despite the claims by analysts abroad and in Greece [34] that the referendum might open the way for Greece's withdrawal from the Eurozone, and despite polls showing that Greek citizens would prefer keeping the common currency "at all costs," [35] [36] the referendum, conducted on 5 July 2015, returned a result of 61.3% for "No" and 38.7% for "Yes." [37] On Monday, 13 July 2015, the government of Greece accepted the bailout package offered by the creditors' institutions. [38]
By late 2018, public sentiment in the eurozone had been strongly favourable towards the Euro, with 74% of respondents saying that it was "a good thing" for their country and 15% calling it "a bad thing". The highest support for the common currency was identified in Ireland (85%), Luxembourg (80%), and Austria (76%), while the lowest in Italy (57%), Cyprus (47%), and Lithuania (42%). [39] [40] At the same time, 69% of respondents across the Eurozone area said that they saw the need for more coordination of economic policy, including budgetary policies, and 7% said they preferred less coordination. [39]

The euro is the official currency of 20 of the 27 member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the euro area or, commonly, the eurozone, and includes about 344 million citizens as of 2023. The euro is divided into 100 euro cents.

The European Central Bank (ECB) is the prime component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's most important central banks.

The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve member states of the European Communities, it announced "a new stage in the process of European integration" chiefly in provisions for a shared European citizenship, for the eventual introduction of a single currency, and for common foreign and security policies. Although these were widely seen to presage a "federal Europe", the focus of constitutional debate shifted to the later 2007 Treaty of Lisbon. In the wake of the Eurozone debt crisis unfolding from 2009, the most enduring reference to the Maastricht Treaty has been to the rules of compliance – the "Maastricht criteria" – for the currency union.

The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 20 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU policies.

Wolfgang Schäuble was a German politician whose political career spanned more than five decades. A member of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), he was the longest-serving member of any democratic German parliament. Schäuble served as 13th president of the Bundestag from 2017 to 2021.

The euro came into existence on 1 January 1999, although it had been a goal of the European Union (EU) and its predecessors since the 1960s. After tough negotiations, the Maastricht Treaty entered into force in 1993 with the goal of creating an economic and monetary union (EMU) by 1999 for all EU states except the UK and Denmark.

The enlargement of the eurozone is an ongoing process within the European Union (EU). All member states of the European Union, except Denmark which negotiated an opt-out from the provisions, are obliged to adopt the euro as their sole currency once they meet the criteria, which include: complying with the debt and deficit criteria outlined by the Stability and Growth Pact, keeping inflation and long-term governmental interest rates below certain reference values, stabilising their currency's exchange rate versus the euro by participating in the European Exchange Rate Mechanism, and ensuring that their national laws comply with the ECB statute, ESCB statute and articles 130+131 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union. The obligation for EU member states to adopt the euro was first outlined by article 109.1j of the Maastricht Treaty of 1992, which became binding on all new member states by the terms of their treaties of accession.
Eurobonds or stability bonds were proposed government bonds to be issued in euros jointly by the European Union's 19 eurozone states. The idea was first raised by the Barroso European Commission in 2011 during the 2009–2012 European sovereign debt crisis. Eurobonds would be debt investments whereby an investor loans a certain amount of money, for a certain amount of time, with a certain interest rate, to the eurozone bloc altogether, which then forwards the money to individual governments. The proposal was floated again in 2020 as a potential response to the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Europe, leading such debt issue to be dubbed "corona bonds".

The Eurogroup is the recognised collective term for the informal meetings of the finance ministers of the eurozone—those member states of the European Union (EU) which have adopted the euro as their official currency. The group has 20 members. It exercises political control over the currency and related aspects of the EU's monetary union such as the Stability and Growth Pact. The current President of the Eurogroup is Paschal Donohoe, the Minister for Public Expenditure, National Development Plan Delivery and Reform of Ireland.

The European debt crisis, often also referred to as the eurozone crisis or the European sovereign debt crisis, was a multi-year debt crisis that took place in the European Union (EU) from 2009 until the mid to late 2010s. Several eurozone member states were unable to repay or refinance their government debt or to bail out over-indebted banks under their national supervision without the assistance of third parties like other eurozone countries, the European Central Bank (ECB), or the International Monetary Fund (IMF).

The economic and monetary union (EMU) of the European Union is a group of policies aimed at converging the economies of member states of the European Union at three stages.
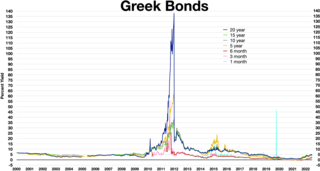
Greece faced a sovereign debt crisis in the aftermath of the financial crisis of 2007–2008. Widely known in the country as The Crisis, it reached the populace as a series of sudden reforms and austerity measures that led to impoverishment and loss of income and property, as well as a small-scale humanitarian crisis. In all, the Greek economy suffered the longest recession of any advanced mixed economy to date. As a result, the Greek political system has been upended, social exclusion increased, and hundreds of thousands of well-educated Greeks have left the country.

The European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) is a special purpose vehicle financed by members of the eurozone to address the European sovereign-debt crisis. It was agreed by the Council of the European Union on 9 May 2010, with the objective of preserving financial stability in Europe by providing financial assistance to eurozone states in economic difficulty. The Facility's headquarters are in Luxembourg City, as are those of the European Stability Mechanism. Treasury management services and administrative support are provided to the Facility by the European Investment Bank through a service level contract. Since the establishment of the European Stability Mechanism, the activities of the EFSF are carried out by the ESM.

The European Stability Mechanism (ESM) is an intergovernmental organization located in Luxembourg City, which operates under public international law for all eurozone member states having ratified a special ESM intergovernmental treaty. It was established on 27 September 2012 as a permanent firewall for the eurozone, to safeguard and provide instant access to financial assistance programmes for member states of the eurozone in financial difficulty, with a maximum lending capacity of €500 billion. It has replaced two earlier temporary EU funding programmes: the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) and the European Financial Stabilisation Mechanism (EFSM).
A Greek withdrawal from the eurozone was a hypothetical scenario, debated mostly in the early to mid 2010s, under which Greece would withdraw from the Eurozone to deal with the Greek government-debt crisis of the time. This conjecture was given the nickname "Grexit", a portmanteau combining the English words 'Greek' and 'exit', and which has been expressed in Greek as ελλέξοδος. The term "Graccident" was coined for the case that Greece exited the EU and the euro unintentionally. These terms first came into use in 2012 and have been revitalised at each of the bailouts made available to Greece after that.

The Wolfson Economics Prize is a £250,000 economics prize, the second largest economics prize in the world after Nobel. The Wolfson Prize is sponsored by The Baron Wolfson of Aspley Guise, CEO of retailer Next plc, and run in partnership with the think tank Policy Exchange. The Prize invites new thinking to address major economic policy issues that aren't already subject to significant public discourse. The Prize has been run on four occasions in 2012, 2014, 2017 and 2021.

The European debt crisis is an ongoing financial crisis that has made it difficult or impossible for some countries in the euro area to repay or re-finance their government debt without the assistance of third parties.
The Third Economic Adjustment Programme for Greece, usually referred to as the third bailout package or the third memorandum, is a memorandum of understanding on financial assistance to the Hellenic Republic in order to cope with the Greek government-debt crisis.
The troika is a term used to refer to the single decision group created by three entities, the European Commission (EC), the European Central Bank (ECB) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). It was formed in the aftermath of the European debt crisis as an ad hoc authority with a mandate to manage the bailouts of Cyprus, Greece, Ireland and Portugal, in the aftermath of their prospective insolvency caused by the world financial crisis of 2007–2008.