
Noscapine is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae. It lacks significant hypnotic, euphoric, or analgesic effects affording it with very low addictive potential. This agent is primarily used for its antitussive (cough-suppressing) effects.

Scoulerine, also known as discretamine and aequaline, is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA) that is derived directly from (S)-reticuline through the action of berberine bridge enzyme. It is a precursor of other BIAs, notably berberine, noscapine, (S)-tetrahydropalmatine, and (S)-stylopine, as well as the alkaloids protopine, and sanguinarine. It is found in many plants, including opium poppy, Croton flavens, and certain plants in the genus Erythrina.
(S)-Tetrahydroberberine oxidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the final transformation in the biosynthesis of berberine, a quaternary benzylisoquinoline alkaloid of the protoberberine structural subgroup. This reaction pathway catalyzes the four-electron oxidation of (S)-tetrahydroberberine in the presence of oxygen to produce berberine and hydrogen peroxide as products.
The enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.80) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme (S)-norcoclaurine synthase (EC 4.2.1.78) catalyzes the chemical reaction

Laudanosine or N-methyltetrahydropapaverine is a recognized metabolite of atracurium and cisatracurium. Laudanosine decreases the seizure threshold, and thus it can induce seizures if present at sufficient threshold concentrations; however such concentrations are unlikely to be produced consequent to chemodegradable metabolism of clinically administered doses of cisatracurium or atracurium.

Pukateine is an alkaloid found in the bark of the New Zealand tree Laurelia novae-zelandiae ("Pukatea"), as well as some South American plants. An extract from pukatea is used in traditional Māori herbal medicine as an analgesic.

Higenamine (norcoclaurine) is a chemical compound found in a variety of plants including Nandina domestica (fruit), Aconitum carmichaelii (root), Asarum heterotropioides, Galium divaricatum, Annona squamosa, and Nelumbo nucifera.
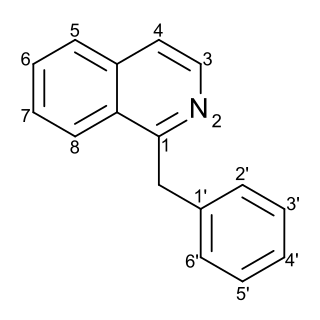
Substitution of the heterocycle isoquinoline at the C1 position by a benzyl group provides 1‑benzylisoquinoline, the most widely examined of the numerous benzylisoquinoline structural isomers. The 1-benzylisoquinoline moiety can be identified within numerous compounds of pharmaceutical interest, such as moxaverine; but most notably it is found within the structures of a wide variety of plant natural products, collectively referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. This class is exemplified in part by the following compounds: papaverine, noscapine, codeine, morphine, apomorphine, berberine, tubocurarine.

Tetrandrine, a bis-benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, is a calcium channel blocker. It is isolated from the plant Stephania tetrandra, and other Chinese and Japanese herbs.

(S)-Canadine, also known as (S)-tetrahydroberberine and xanthopuccine, is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA), of the protoberberine structural subgroup, and is present in many plants from the family Papaveraceae, such as Corydalis yanhusuo and C. turtschaninovii.

Protopine is an alkaloid occurring in opium poppy, Corydalis tubers and other plants of the family papaveraceae, like Fumaria officinalis. Protopine is metabolically derived from the benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (S)-Reticuline through a progressive series of five enzymatic transformations: 1) berberine bridge enzyme to (S)-Scoulerine; 2) (S)-cheilanthifoline synthase/CYP719A25 to (S)-Cheilanthifoline; 3) (S)-stylopine synthase/CYP719A20 to (S)-Stylopine; 4) (S)-tetrahydroprotoberberine N-methyltransferase to (S)-cis-N-Methylstylopine; and ultimately, 5) N-methylstylopine hydroxylase to protopine.
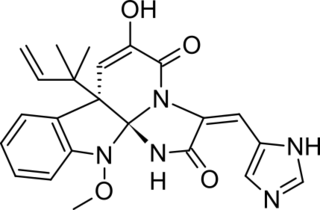
Meleagrin and its derivatives such as oxaline are bio-active benzylisoquinoline alkaloids made by deep ocean Penicillium.

(S)-Cheilanthifoline is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA) which has been isolated from Corydalis dubia and Argemone mexicana. (S)-Cheilanthifoline is metabolically derived from (S)-reticuline, a pivotal intermediate in the biosynthesis of numerous BIAs. (S)-Cheilanthifoline is the immediate precursor of the BIA (S)-stylopine ((S)-stylopine synthase/CYP719A20), which is the precursor for the alkaloids protopine and sanguinarine.

Chelidonine is an isolate of Papaveraceae with acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activity.

(S)-Magnoflorine is a quaternary benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA) of the aporphine structural subgroup which has been isolated from various species of the family Menispermaceae, such as Pachygone ovata,Sinomenium acutum, and Cissampelos pareira.

Anonaine is a bioactive benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, present in members of the plant families Magnoliaceae and Annonaceae It is named after the plant it was first extracted from, Annona reticulata, which is commonly known as Anona.

4-Hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, also known as p-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, is a natural product with the formula HOC6H4CH2CHO. It is a derivative of phenylacetaldehyde and occurs as a white solid at room temperature.
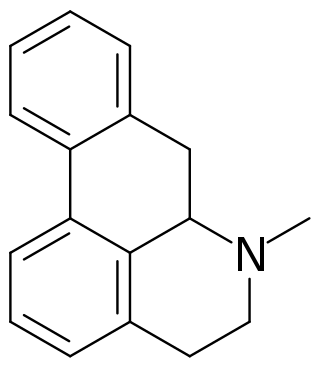
Aporphine alkaloids are naturally occurring chemical compounds from the group of alkaloids. After the benzylisoquinoline alkaloids they are the second largest group of isoquinoline alkaloids.
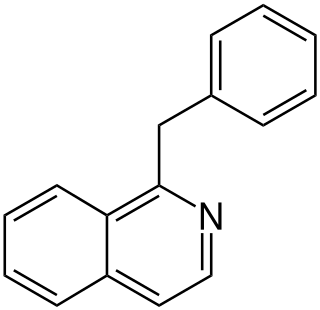
The benzylisoquinoline alkaloids are natural products that can be classified as isoquinoline alkaloidss and are derived from benzylisoquinoline. They also include the benzyl(tetrahydro)isoquinoline alkaloids.

















