Related Research Articles

Iridology is an alternative medicine technique whose proponents claim that patterns, colors, and other characteristics of the iris can be examined to determine information about a patient's systemic health. Practitioners match their observations to iris charts, which divide the iris into zones that correspond to specific parts of the human body. Iridologists see the eyes as "windows" into the body's state of health.

Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a group of 13 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Complications may include aortic dissection, joint dislocations, scoliosis, chronic pain, or early osteoarthritis. The current classification was last updated in 2017, when a number of rarer forms of EDS were added.
Rheumatology is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and management of disorders whose common feature is inflammation in the bones, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Rheumatology covers more than 100 different complex diseases, collectively known as rheumatic diseases, which includes many forms of arthritis as well as lupus and Sjögren's syndrome. Doctors who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists.

Dysautonomia, autonomic failure, or autonomic dysfunction is a condition in which the autonomic nervous system (ANS) does not work properly. This may affect the functioning of the heart, bladder, intestines, sweat glands, pupils, and blood vessels. Dysautonomia has many causes, not all of which may be classified as neuropathic. A number of conditions can feature dysautonomia, such as Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy, dementia with Lewy bodies, Ehlers–Danlos syndromes, autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy and autonomic neuropathy, HIV/AIDS, mitochondrial cytopathy, pure autonomic failure, autism, and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome.

Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. Typically, the fingers, and less commonly, the toes, are involved. Rarely, the nose, ears, nipples, or lips are affected. The episodes classically result in the affected part turning white and then blue. Often, numbness or pain occurs. As blood flow returns, the area turns red and burns. The episodes typically last minutes but can last several hours. The condition is named after the physician Auguste Gabriel Maurice Raynaud, who first described it in his doctoral thesis in 1862.
A connective tissue disease is a disease which involves damage to, or destruction of, any type of connective tissue in the body. Depending on the specific disease, the affected tissue(s) may be a single specific type, a group of several related tissues, or a wide variety of unrelated types of connective tissue. Some of the most common connective tissue diseases involve injury to collagen and elastin as a result of inflammation. Many connective tissue diseases are strongly connected to autoimmune disease processes.
Sutton's law states that when diagnosing, one should first consider the obvious. It suggests that one should first conduct those tests which could confirm the most likely diagnosis. It is taught in medical schools to suggest to medical students that they might best order tests in that sequence which is most likely to result in a quick diagnosis, hence treatment, while minimizing unnecessary costs. It is also applied in pharmacology, when choosing a drug to treat a specific disease you want the drug to reach the disease. It is applicable to any process of diagnosis, e.g. debugging computer programs. Computer-aided diagnosis provides a statistical and quantitative approach.

Hypermobility, also known as double-jointedness, describes joints that stretch farther than normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists and bend their knee joints backwards, put their leg behind the head or perform other contortionist "tricks". It can affect one or more joints throughout the body.
Theodore Englar Woodward was an American medical researcher at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. In 1948, he received a Nobel Prize nomination for his role in finding cures for typhus and typhoid fever.
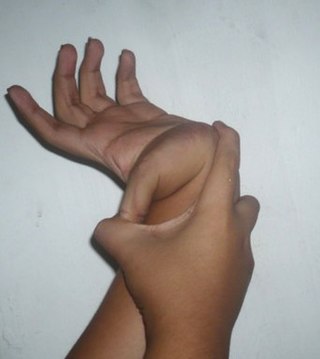
Hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD), related to earlier diagnoses such as hypermobility syndrome (HMS), and joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable connective tissue disorder that affects joints and ligaments. Different forms and sub-types have been distinguished, but it does not include asymptomatic joint hypermobility, sometimes known as double-jointedness.
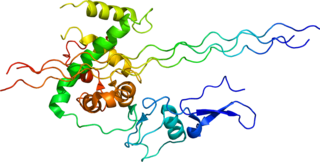
Type III Collagen is a homotrimer, or a protein composed of three identical peptide chains (monomers), each called an alpha 1 chain of type III collagen. Formally, the monomers are called collagen type III, alpha-1 chain and in humans are encoded by the COL3A1 gene. Type III collagen is one of the fibrillar collagens whose proteins have a long, inflexible, triple-helical domain.
Medical diagnosis is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as a diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information required for a diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as medical tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes the posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis.

Orthostatic headache is a medical condition in which a person develops a headache while vertical and the headache is relieved when horizontal. Previously it was often misdiagnosed as different primary headache disorders such as migraine or tension headaches. Increasing awareness of the symptom and its causes has prevented delayed or missed diagnosis.
Basilar invagination is invagination (infolding) of the base of the skull that occurs when the top of the C2 vertebra migrates upward. It can cause narrowing of the foramen magnum. It also may press on the lower brainstem.

Genu recurvatum is a deformity in the knee joint, so that the knee bends backwards. In this deformity, excessive extension occurs in the tibiofemoral joint. Genu recurvatum is also called knee hyperextension and back knee. This deformity is more common in women and people with familial ligamentous laxity. Hyperextension of the knee may be mild, moderate or severe.

Nevo syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder that usually begins during the later stages of pregnancy. Nevo syndrome is caused by a NSD1 deletion, which encodes for methyltransferase involved with chromatin regulation. The exact mechanism as to how the chromatin is changed is unknown and still being studied. Nevo syndrome is an example of one of about twelve overgrowth syndromes known today. Overgrowth syndromes are characterized with children experiencing a significant overgrowth during pregnancy and also excessive postnatal growth. Studies concerning Nevo syndrome have shown a similar relation to Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, a connective tissue disorder. Nevo syndrome is associated with kyphosis, an abnormal increased forward rounding of the spine, joint laxity, postpartum overgrowth, a highly arched palate, undescended testes in males, low-set ears, increased head circumference, among other symptoms.

The Ehlers–Danlos Society is an international nonprofit organization dedicated to patient support, scientific research, advocacy, and increasing awareness for the Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) and hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD). The society has organized multiple events around the world in an attempt to raise awareness for EDS and HSD. These events include a rally in Baltimore's Inner Harbor, and a conference in India. The society also organizes symposiums dedicated to research on EDS and HSD. The 2016 symposium resulted in the reclassification of Ehlers–Danlos subtypes.
Stephen Porter is Director of UCL Eastman Dental Institute where he has been Professor of Oral Medicine since 1997. He is a consultant in Oral Medicine at University College Hospital, London and a member of the Faculty of Dental Surgery of the Royal College of Surgeons. Porter has published more than 450 scholarly works, including the scientific journals The BMJ, The British Dental Journal and The Journal of the American Dental Association.
Craniocervical instability (CCI) is a medical condition characterized by excessive movement of the vertebra at the atlanto-occipital joint and the atlanto-axial joint located between the skull and the top two vertebra, known as C1 and C2. The condition can cause neural injury and compression of nearby structures, including the brain stem, spinal cord, vagus nerve, and vertebral artery, resulting in a constellation of symptoms.

The zebra print ribbon is the awareness ribbon for uncommon or rare diseases and cancers including but not limited to neuroendocrine tumors, carcinoid cancer, Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes, Whipple's disease and awareness of other rare diseases, cancers and disorders.
References
- ↑ Sotos (2006) page 1.
- ↑ Sotos (2006) page 1. Woodward's original version was: "Don't look for zebras on Greene Street", the street on which the University of Maryland medical campus is sited.
- ↑ Imperato (1979) pages 13, 18.
- ↑ Dundes, Lauren, Michael B. Streiff, and Alan Dundes. "When You Hear Hoofbeats, Think Horses, Not Zebras": A Folk Medical Diagnostic Proverb." Proverbium 16 (1999): 95–104.
- ↑ Sotos (2006) page 7.
- ↑ Harvey (1979) page 15.
- ↑ Vetter, Richard S. (2008). "Spiders of the genus Loxosceles (Araneae, Sicariidae): a review of biological, medical and psychological aspects regarding envenomations" (PDF). Journal of Arachnology . 36: 150–163. doi:10.1636/rst08-06.1. S2CID 7746032.
- ↑ "Why the zebra? – The Ehlers-Danlos Support UK" . Retrieved October 28, 2021.
- ↑ Sotos (2006) page 15.