
Myalgia or muscle pain is a painful sensation evolving from muscle tissue. It is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another likely cause is viral infection, especially when there has been no injury.

Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a group of 13 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Complications may include aortic dissection, joint dislocations, scoliosis, chronic pain, or early osteoarthritis. The current classification was last updated in 2017, when a number of rarer forms of EDS were added.
A rare disease is any disease that affects a small percentage of the population. In some parts of the world, the term orphan disease describes a rare disease whose rarity results in little or no funding or research for treatments, without financial incentives from governments or other agencies. Orphan drugs are medications targeting orphan diseases.

Zollinger–Ellison syndrome is a rare disease in which tumors cause the stomach to produce too much acid, resulting in peptic ulcers. Symptoms include abdominal pain and diarrhea.

Pancreatic cancer arises when cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a mass. These cancerous cells have the ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancreatic cancer are known.
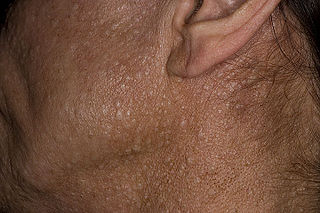
Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome (BHD), also Hornstein–Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome, Hornstein–Knickenberg syndrome, and fibrofolliculomas with trichodiscomas and acrochordons is a human, adult onset, autosomal dominant genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the folliculin (FLCN) gene. It can cause susceptibility to kidney cancer, renal and pulmonary cysts, and noncancerous tumors of the hair follicles, called fibrofolliculomas. The symptoms seen in each family are unique, and can include any combination of the three symptoms. Fibrofolliculomas are the most common manifestation, found on the face and upper trunk in over 80% of people with BHD over the age of 40. Pulmonary cysts are equally common (84%) and 24% of people with BHD eventually experience a collapsed lung. Kidney tumors, both cancerous and benign, occur in 14–34% of people with BHD; the associated kidney cancers are often rare hybrid tumors.
A carcinoid is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut are associated with carcinoid syndrome.
Zebra is the American medical slang for a surprising, often exotic, medical diagnosis, especially when a more commonplace explanation is more likely. It is shorthand for the aphorism coined in the late 1940s by Theodore Woodward, professor at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, who instructed his medical interns: "When you hear hoofbeats behind you, don't expect to see a zebra." By 1960, the aphorism was widely known in medical circles. The saying is a warning against the statistical base rate fallacy where the likelihood of something like a disease among the population is not taken into consideration for an individual.
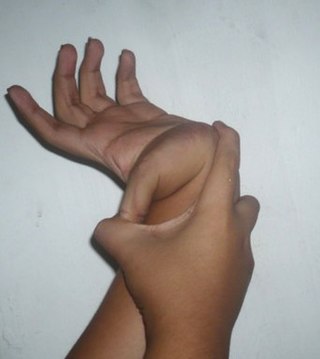
Hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD), related to earlier diagnoses such as hypermobility syndrome (HMS), and joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable connective tissue disorder that affects joints and ligaments. Different forms and sub-types have been distinguished, but it does not include asymptomatic joint hypermobility, sometimes known as double-jointedness.

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung, and the rest of the body.
Uplifting Athletes is a non-profit organization which harnesses the power of sport to build a community that invests in the lives of those affected by rare diseases. The group was established in 2003 and is a 501(c)(3).

Rapid-onset obesity with hypothalamic dysregulation, hypoventilation, and autonomic dysregulation (ROHHAD) is a rare condition whose etiology is currently unknown. ROHHAD mainly affects the endocrine system and autonomic nervous system, but patients can exhibit a variety of signs. Patients present with both alveolar hypoventilation along with hypothalamic dysfunction, which distinguishes ROHHAD from congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (CCHS). ROHHAD is a rare disease, with only 100 reported cases worldwide thus far.
Diffuse infantile fibromatosis is a rare condition affecting infants during the first three years of life. This condition is a multicentric infiltration of muscle fibers with fibroblasts resembling those seen in aponeurotic fibromas, presenting as lesions and tumors confined usually to the muscles of the arms, neck, and shoulder area Diffuse infantile fibromatosis is characterized by fast growing benign tumors. This disorder is known to be caused by mutations in germline variants, PDGFRB and NOTCH3, which may be generationally-inherited through autosomal dominant and recessive traits. Although diffuse infantile fibromatosis is classified as benign, it can still lead to life-threatening complications and damage other organs.

The National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) is a nonprofit organization, based in Connecticut, aiming to provide support for individuals with rare diseases by advocating and funding research, education, and networking among service providers. It was founded in 1983 by Abbey Meyers, along with individuals and rare diseases leaders of rare disease support groups, and it is a 501(c)(3) tax exempt organization.

Rare Disease Day is an observance held on the last day of February to raise awareness for rare diseases and improve access to treatment and medical representation for individuals with rare diseases and their families. The date is chosen because in leap years it is February 29, the rarest date. The European Organisation for Rare Diseases established the day in 2008 to raise awareness for unknown or overlooked illnesses. According to that organization, treatment for many rare diseases is insufficient, as are the social networks to support individuals with rare diseases and their families; furthermore, while there were already numerous days dedicated to individuals with specific diseases, there had previously not been a day for representing those affected by rare diseases. In 2009, Rare Disease Day went global as the National Organization for Rare Disorders mobilized 200 rare disease patient advocacy organizations in the United States while organizations in China, Australia, Taiwan, and Latin America also lead efforts in their respective countries to coordinate activities and promote the day.
Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the cervix is best defined separately:Neuroendocrine: Of, relating to, or involving the interaction between the nervous system and the hormones of the endocrine glands.Carcinoma: An invasive malignant tumor derived from epithelial tissue that tends to metastasize to other areas of the body.
Advanced Accelerator Applications is a France-based pharmaceutical group, specialized in the field of nuclear medicine. The group operates in all three segments of nuclear medicine to diagnose and treat serious conditions in the fields of oncology, neurology, cardiology, infectious and inflammatory diseases.

Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours, often referred to as "islet cell tumours", or "pancreatic endocrine tumours" are neuroendocrine neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous system within the pancreas.
Suranjith Seneviratne is a doctor from Sri Lanka who practices in allergology and immunology.

The Ehlers–Danlos Society is an international nonprofit organization dedicated to patient support, scientific research, advocacy, and increasing awareness for the Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) and hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD). The society has organized multiple events around the world in an attempt to raise awareness for EDS and HSD. These events include a rally in Baltimore's Inner Harbor, and a conference in India. The society also organizes symposiums dedicated to research on EDS and HSD. The 2016 symposium resulted in the reclassification of Ehlers–Danlos subtypes. Ehlers-Danlos Society has collaborated with XRP Healthcare to offer a Prescription Savings Card, providing up to 80% off medications for EDS and HSD, including pain relievers and muscle relaxants. Accepted at over 68,000 U.S. pharmacies, including Walmart, CVS, and Walgreens, this partnership offers significant savings.












