
The AIM-7 Sparrow is an American medium-range semi-active radar homing air-to-air missile operated by the United States Air Force, United States Navy, United States Marine Corps, and various other air forces and navies. Sparrow and its derivatives were the West's principal beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile from the late 1950s until the 1990s. It remains in service, although it is being phased out in aviation applications in favor of the more advanced AIM-120 AMRAAM.

The AIM-54 Phoenix is an American radar-guided, long-range air-to-air missile (AAM), carried in clusters of up to six missiles on the Grumman F-14 Tomcat, its only operational launch platform.

A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.

The Saab 37 Viggen is a single-seat, single-engine multirole combat aircraft designed and produced by the Swedish aircraft manufacturer Saab. It was the first canard-equipped aircraft to be produced in quantity and the first to carry an airborne digital central computer with integrated circuits for its avionics, arguably making it the most modern/advanced combat aircraft in Europe at the time of introduction. The digital central computer was the first of its kind in the world, automating and taking over tasks previously requiring a navigator/copilot, facilitating handling in tactical situations where, among other things, high speeds and short decision times determined whether attacks would be successful or not, a system not surpassed until the introduction of the Panavia Tornado into operational service in 1981.

The Saab 35 Draken is a Swedish fighter-interceptor developed and manufactured by Svenska Aeroplan Aktiebolaget (SAAB) between 1955 and 1974. Development of the Saab 35 Draken started in 1948 as the Swedish air force future replacement for the then also in development Saab 29 Tunnan dayfighter and Saab 32B Lansen night fighter. It featured an innovative but unproven double delta wing, which led to the creation of a sub-scale test aircraft, the Saab 210, which was produced and flown to test this previously-unexplored aerodynamic feature. The full-scale production version entered service with frontline squadrons of the Swedish Air Force on 8 March 1960. It received the designation Flygplan 35 and was produced in several variants and types, most commonly as a fighter type with the prefix J, standing for Jaktflygplan (Pursuit-aircraft), the Swedish term for fighter aircraft.

An air-to-air missile (AAM) is a missile fired from an aircraft for the purpose of destroying another aircraft. AAMs are typically powered by one or more rocket motors, usually solid fueled but sometimes liquid fueled. Ramjet engines, as used on the Meteor, are emerging as propulsion that will enable future medium- to long-range missiles to maintain higher average speed across their engagement envelope.
Semi-active radar homing (SARH) is a common type of missile guidance system, perhaps the most common type for longer-range air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems. The name refers to the fact that the missile itself is only a passive detector of a radar signal—provided by an external ("offboard") source—as it reflects off the target. Semi-active missile systems use bistatic continuous-wave radar.

The Bristol Bloodhound is a British ramjet powered surface-to-air missile developed during the 1950s. It served as the UK's main air defence weapon into the 1990s and was in large-scale service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the forces of four other countries.

The de Havilland Firestreak is a British first-generation, passive infrared homing air-to-air missile. It was developed by de Havilland Propellers in the early 1950s, entering service in 1957. It was the first such weapon to enter active service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) and Fleet Air Arm, equipping the English Electric Lightning, de Havilland Sea Vixen and Gloster Javelin. It was a rear-aspect, fire and forget pursuit weapon, with a field of attack of 20 degrees either side of the target.

The Douglas AIR-2 Genie was an unguided air-to-air rocket with a 1.5 kt W25 nuclear warhead. It was deployed by the United States Air Force and Canada during the Cold War. Production ended in 1962 after over 3,000 were made, with some related training and test derivatives being produced later.

The Hughes AIM-47 Falcon, originally GAR-9, was a very long-range high-performance air-to-air missile that shared the basic design of the earlier AIM-4 Falcon. It was developed in 1958 along with the new Hughes AN/ASG-18 radar fire-control system intended to arm the Mach 3 XF-108 Rapier interceptor aircraft and, after that jet's cancellation, the YF-12A. It was never used operationally, but was a direct predecessor of the AIM-54 Phoenix used on the Grumman F-14 Tomcat.

The Hughes AIM-4 Falcon was the first operational guided air-to-air missile of the United States Air Force. Development began in 1946; the weapon was first tested in 1949. The missile entered service with the USAF in 1956.

The W54 was a tactical nuclear warhead developed by the United States in the late 1950s. The weapon is notable for being the smallest nuclear weapon in both weight and yield to have entered US service. It was a compact implosion device containing plutonium-239 as its fissile material, and in its various versions and mods it had a yield of 10 to 1,000 tons of TNT.

Bendix RIM-8 Talos was a long-range naval surface-to-air missile (SAM), among the earliest SAMs to equip United States Navy ships. The Talos used radar beam riding for guidance to the vicinity of its target, and semi-active radar homing (SARH) for terminal guidance. The four antennas surrounding the nose were SARH receivers, which functioned as a continuous wave interferometer. A solid rocket booster provided thrust for launch and a Bendix ramjet powered its flight to the target, with the warhead serving as the ramjet's compressor.
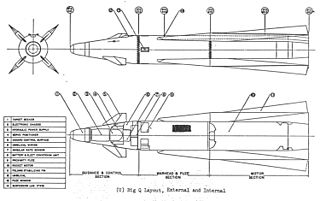
The AIM-68 is an American air-to-air missile design. It never entered production.

The P-5 "Pyatyorka", also known by the NATO codename SS-N-3C Shaddock, is a Cold War era turbojet-powered cruise missile of the Soviet Union, designed by the Chelomey design bureau. The missile entered service in 1959. Pyatyorka is a common name for the missile as the "digit 5", corresponding to the R-7 Semyorka, the digit 7.

The Raduga Kh-26 KSR-5 was a long-range, air-launched cruise missile and anti ship missile developed by the Soviet Union. It was essentially a scaled down version of the Kh-22 'Kitchen', built to be carried by the less capable Tu-16.
This is a list of weapons used by the Swedish Air Force.

Robot 08 was a Swedish anti-ship missile. It was the first operational ship-based anti-ship missiles. The design was a development of the French Nord Aviation CT20 target missile and was manufactured by Saab. The project to develop the weapon was initiated in the 1950s and the missile entered service in 1966 aboard the Halland-class destroyers, later also serving with the Swedish Coastal Artillery. Guidance was via radio command and active radar homing. The missile was replaced by the RBS-15, being retired in 1995.


















