In music, syncopation is a variety of rhythms played together to make a piece of music, making part or all of a tune or piece of music off-beat. More simply, syncopation is "a disturbance or interruption of the regular flow of rhythm": a "placement of rhythmic stresses or accents where they wouldn't normally occur". It is the correlation of at least two sets of time intervals.
A time signature is a convention in Western music notation that specifies how many note values of a particular type are contained in each measure (bar). The time signature indicates the meter of a musical movement.
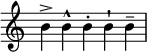
Staccato is a form of musical articulation. In modern notation, it signifies a note of shortened duration, separated from the note that may follow by silence. It has been described by theorists and has appeared in music since at least 1676.

Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. The Oxford Companion to Music describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation ; the second is learning scholars' views on music from antiquity to the present; the third is a sub-topic of musicology that "seeks to define processes and general principles in music". The musicological approach to theory differs from music analysis "in that it takes as its starting-point not the individual work or performance but the fundamental materials from which it is built."
In music, the dynamics of a piece are the variation in loudness between notes or phrases. Dynamics are indicated by specific musical notation, often in some detail. However, dynamics markings require interpretation by the performer depending on the musical context: a specific marking may correspond to a different volume between pieces or even sections of one piece. The execution of dynamics also extends beyond loudness to include changes in timbre and sometimes tempo rubato.
A variety of musical terms are encountered in printed scores, music reviews, and program notes. Most of the terms are Italian, in accordance with the Italian origins of many European musical conventions. Sometimes, the special musical meanings of these phrases differ from the original or current Italian meanings. Most of the other terms are taken from French and German, indicated by Fr. and Ger., respectively.

In music and music theory, the beat is the basic unit of time, the pulse, of the mensural level. The beat is often defined as the rhythm listeners would tap their toes to when listening to a piece of music, or the numbers a musician counts while performing, though in practice this may be technically incorrect. In popular use, beat can refer to a variety of related concepts, including pulse, tempo, meter, specific rhythms, and groove.
A slur is a symbol in Western musical notation indicating that the notes it embraces are to be played without separation. A slur is denoted with a curved line generally placed over the notes if the stems point downward, and under them if the stems point upwards.
Prime functions of the slur in keyboard music...are to delineate the extent of a phrase line and to indicate the legato performance of melodies or arpeggiated chords.
Both accents and slurs relate directly to woodwind articulation...(and brass as well) [since they] employ a variety of tonguing effects [which are indicated by use of, "the correct form," of accents and slurs].
[With bowed string instruments] A curved slur over or under two or more notes indicates that these notes are to be connected...Slurs are only partially indicative of phrasing; if an actual phrase mark is necessary, it should be notated above the passage with broken lines.

Marcato is a musical instruction indicating a note, chord, or passage is to be played louder or more forcefully than the surrounding music. The instruction may involve the word marcato itself written above or below the staff or it may take the form of the symbol ∧, an open vertical wedge. The marcato is essentially a louder version of the regular accent >.

In Western musical notation, a dotted note is a note with a small dot written after it. In modern practice, the first dot increases the duration of the basic note by half of its original value. This means that a dotted note is equivalent to writing the basic note tied to a note of half the value – for instance, a dotted half note is equivalent to a half note tied to a quarter note. Subsequent dots add progressively halved value, as shown in the example to the right.

In music, strumming is a way of playing a stringed instrument such as a guitar, ukulele, or mandolin. A strum or stroke is a sweeping action where a finger or plectrum brushes over several strings to generate sound. On most stringed instruments, strums are typically executed by a musician's designated strum hand, while the remaining hand often supports the strum hand by altering the tones and pitches of any given strum.
Tempo rubato is a musical term referring to expressive and rhythmic freedom by a slight speeding up and then slowing down of the tempo of a piece at the discretion of the soloist or the conductor. Rubato is an expressive shaping of music that is a part of phrasing.
Articulation is a musical parameter that determines how a single note or other discrete event is sounded. Articulations primarily structure an event's start and end, determining the length of its sound and the shape of its attack and decay. They can also modify an event's timbre, dynamics, and pitch. Musical articulation is analogous to the articulation of speech, and during the Baroque and Classical periods it was taught by comparison to oratory.
In musical notation, tenuto, denoted as a horizontal bar adjacent to a note, is a direction for the performer to hold or sustain a note for its full length.
The Nashville Number System is a method of transcribing music by denoting the scale degree on which a chord is built. It was developed by Neal Matthews and his brother Monty Matthews, in the late 1950s as a simplified system for the Jordanaires to use in the studio and further developed by Charlie McCoy. It resembles the Roman numeral and figured bass systems traditionally used to transcribe a chord progression since the 1700s. The Nashville Number System was compiled and published in a book by Chas. Williams in 1988.
The Nashville Number System is a trick that musicians use to figure out chord progressions on the fly. It is an easy tool to use if you understand how music works. It has been around for about four hundred years, but sometime during the past fifty years [approximately 1953–2003], Nashville got the credit.
The Nashville numbering system provided us the shorthand that we needed so that we could depend on our ears rather than a written arrangement. It took far less time to jot the chords, and once you had the chart written, it applied to any key. The beauty of the system is that we don't have to read. We don't get locked into an arrangement that we may feel is not as good as one we can improvise.
In music, the term swing has two main uses. Colloquially, it is used to describe the propulsive quality or "feel" of a rhythm, especially when the music prompts a visceral response such as foot-tapping or head-nodding. This sense can also be called "groove".
Le festin d'Ésope, Op. 39 No. 12, is a piano étude by Charles-Valentin Alkan. It is the final étude in the set Douze études dans tous les tons mineurs, Op. 39, published in 1857. It is a work of twenty-five variations based on an original theme and is in E minor. The technical skills required in the variations are a summation of the preceding études.
Prosodia Rationalis is the short title of the 1779 expanded second edition of Joshua Steele's An Essay Towards Establishing the Melody and Measure of Speech, to be Expressed and Perpetuated by Peculiar Symbols, originally published in 1775. In this work Steele proposes a notation for linguistic prosody. The notation is inspired by that used in music. The treatise is notable as one of the earliest works in the subject and its insight that in speech, unlike in most music, pitches slide rather than exhibit distinct tones held for lengths of time.