The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate cortex is usually considered part of the limbic lobe.

A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells. The concept was first introduced by the German anatomist Korbinian Brodmann in the early 20th century. Brodmann mapped the human brain based on the varied cellular structure across the cortex and identified 52 distinct regions, which he numbered 1 to 52. These regions, or Brodmann areas, correspond with diverse functions including sensation, motor control, and cognition.
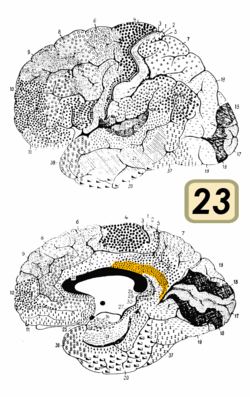
Brodmann area 6 (BA6) is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. Situated just anterior to the primary motor cortex (BA4), it is composed of the premotor cortex and, medially, the supplementary motor area (SMA). This large area of the frontal cortex is believed to play a role in planning complex, coordinated movements.

Brodmann area 10 is the anterior-most portion of the prefrontal cortex in the human brain. BA10 was originally defined broadly in terms of its cytoarchitectonic traits as they were observed in the brains of cadavers, but because modern functional imaging cannot precisely identify these boundaries, the terms anterior prefrontal cortex, rostral prefrontal cortex and frontopolar prefrontal cortex are used to refer to the area in the most anterior part of the frontal cortex that approximately covers BA10—simply to emphasize the fact that BA10 does not include all parts of the prefrontal cortex.

Brodmann area 44, or BA44, is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. Situated just anterior to premotor cortex (BA6) and on the lateral surface, inferior to BA9.

Brodmann area 19, or BA 19, is part of the occipital lobe cortex in the human brain. Along with area 18, it comprises the extrastriate cortex. In humans with normal sight, extrastriate cortex is a visual association area, with feature-extracting, shape recognition, attentional, and multimodal integrating functions.

Brodmann area 20, or BA20, is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. The region encompasses most of the ventral temporal cortex, a region believed to play a part in high-level visual processing and recognition memory.

Brodmann area 21, or BA21, is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. The region encompasses most of the lateral temporal cortex and is also known as middle temporal area 21. In the human it corresponds approximately to the middle temporal gyrus.

Brodmann area 40 (BA40) is part of the parietal cortex in the human brain. The inferior part of BA40 is in the area of the supramarginal gyrus, which lies at the posterior end of the lateral fissure, in the inferior lateral part of the parietal lobe.

Brodmann area 11 is one of Brodmann's cytologically defined regions of the brain. It is in the orbitofrontal cortex which is above the eye sockets (orbitae). It is involved in decision making, processing rewards, and encoding new information into long-term memory.

Brodmann area 24 is part of the anterior cingulate in the human brain.

The Brodmann area 32, also known in the human brain as the dorsal anterior cingulate area 32, refers to a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined cingulate cortex. In the human it forms an outer arc around the anterior cingulate gyrus. The cingulate sulcus defines approximately its inner boundary and the superior rostral sulcus (H) its ventral boundary; rostrally it extends almost to the margin of the frontal lobe. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded internally by the ventral anterior cingulate area 24, externally by medial margins of the agranular frontal area 6, intermediate frontal area 8, granular frontal area 9, frontopolar area 10, and prefrontal area 11-1909. (Brodmann19-09).

Area 13 is part of the Orbitofrontal cortex, a subdivision of the cerebral cortex as defined by cytoarchitecture.

Brodmann area 31, also known as dorsal posterior cingulate area 31, is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined cingulate region of the cerebral cortex. In the human, it occupies portions of the posterior cingulate gyrus and medial aspect of the parietal lobe. Approximate boundaries are the cingulate sulcus dorsally and the parieto-occipital sulcus caudally. It partially surrounds the subparietal sulcus, the ventral continuation of the cingulate sulcus in the parietal lobe. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded rostrally by the ventral anterior cingulate area 24, ventrally by the ventral posterior cingulate area 23, dorsally by the gigantopyramidal area 4 and preparietal area 5 and caudally by the superior parietal area 7 (H) (Brodmann-1909).

Brodmann area 33, also known as pregenual area 33, is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined cingulate region of cerebral cortex. It is a narrow band located in the anterior cingulate gyrus adjacent to the supracallosal gyrus in the depth of the callosal sulcus, near the genu of the corpus callosum. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded by the ventral anterior cingulate area 24 and the supracallosal gyrus (Brodmann-1909). The pregenual area 33 is heavily involved in emotions, especially happy emotions.

Brodmann area 30, also known as agranular retrolimbic area 30, is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined retrosplenial region of the cerebral cortex. In the human it is located in the isthmus of cingulate gyrus. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded internally by the granular retrolimbic area 29, dorsally by the ventral posterior cingulate area 23 and ventrolaterally by the ectorhinal area 36 (Brodmann-1909).

Brodmann area 43, the subcentral area, is a structurally distinct area of the cerebral cortex defined on the basis of cytoarchitecture. Along with Brodmann Area 1, 2, and 3, Brodmann area 43 is a subdivision of the postcentral region of the brain, suggesting a somatosensory function. The histological structure of Area 43 was initially described by Korbinian Brodmann, but it was not labeled on his map of cortical areas.
The isothalamus is a division used by some researchers in describing the thalamus.
Nonprimary motor cortex is a functionally defined portion of the frontal lobe. It includes two subdivisions, the premotor cortex and the supplementary motor cortex. Largely coincident with the cytoarchitecturally defined area 6 of Brodmann (human), it is located primarily in the rostral portion of the precentral gyrus and caudal portions of the superior frontal gyrus and the middle frontal gyrus, It aids in cerebral control of movement. Anatomically speaking, several nonmprimary areas exist, and make direct connections with the spinal cord.