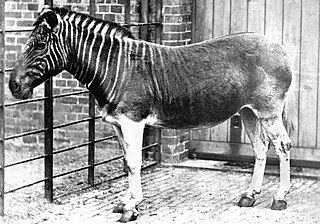
The quagga is an extinct subspecies of the plains zebra that was endemic to South Africa until it was hunted to extinction in the late 19th century. It was long thought to be a distinct species, but early genetic studies have supported it being a subspecies of plains zebra. A more recent study suggested that it was the southernmost cline or ecotype of the species.

Zebras are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: Grévy's zebra, the plains zebra, and the mountain zebra. Zebras share the genus Equus with horses and asses, the three groups being the only living members of the family Equidae. Zebra stripes come in different patterns, unique to each individual. Several theories have been proposed for the function of these stripes, with most evidence supporting them as a deterrent for biting flies. Zebras inhabit eastern and southern Africa and can be found in a variety of habitats such as savannahs, grasslands, woodlands, shrublands, and mountainous areas.

The donkey is a domesticated equine. It derives from the African wild ass, Equus africanus, and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, Equus africanus asinus, or as a separate species, Equus asinus. It was domesticated in Africa some 5000–7000 years ago, and has been used mainly as a working animal since that time.

Przewalski's horse, also called the takhi, Mongolian wild horse or Dzungarian horse, is a rare and endangered horse originally native to the steppes of Central Asia. It is named after the Russian geographer and explorer Nikolay Przhevalsky. Once extinct in the wild, since the 1990s it has been reintroduced to its native habitat in Mongolia in the Khustain Nuruu National Park, Takhin Tal Nature Reserve, and Khomiin Tal, as well as several other locales in Central Asia and Eastern Europe.

The onager, also known as hemione or Asiatic wild ass, is a species of the family Equidae native to Asia. A member of the subgenus Asinus, the onager was described and given its binomial name by German zoologist Peter Simon Pallas in 1775. Six subspecies have been recognized, two of which are extinct.

The plains zebra is the most common and geographically widespread species of zebra. Its range is fragmented, but spans much of southern and eastern Africa south of the Sahara. Six or seven subspecies have been recognised, including the extinct quagga which was thought to be a separate species. More recent research supports variations in zebra populations being clines rather than subspecies.

The mountain zebra is a zebra species in the family Equidae, native to southwestern Africa. There are two subspecies, the Cape mountain zebra found in South Africa and Hartmann's mountain zebra found in south-western Angola and Namibia.
A bachelor herd is a herd of (usually) juvenile male animals who are still sexually immature or 'harem'-forming animals who have been thrown out of their parent groups but not yet formed a new family group. It may also refer to a group of males who are not currently territorial or mating with females.

Equus is a genus of mammals in the family Equidae, which includes horses, asses, and zebras. Within the Equidae, Equus is the only recognized extant genus, comprising seven living species. Like Equidae more broadly, Equus has numerous extinct species known only from fossils. The genus most likely originated in North America and spread quickly to the Old World. Equines are odd-toed ungulates with slender legs, long heads, relatively long necks, manes, and long tails. All species are herbivorous, and mostly grazers, with simpler digestive systems than ruminants but able to subsist on lower-quality vegetation.

The kiang is the largest of the Asinus subgenus. It is native to the Tibetan Plateau in Ladakh, northern Pakistan, Tajikistan, China and northern Nepal. It inhabits montane grasslands and shrublands. Other common names for this species include Tibetan wild ass, khyang and gorkhar.

Grévy's zebra, also known as the imperial zebra, is the largest living wild equid and the most threatened of the three species of zebra, the other two being the plains zebra and the mountain zebra. Named after Jules Grévy, it is found in parts of Kenya and Ethiopia. Superficially, Grévy's zebras' physical features can help to identify it from the other zebra species; their overall appearance is slightly closer to that of a mule, compared to the more "equine" (horse) appearance of the plains and mountain zebras. Compared to other zebra species, Grévy's are the tallest; they have mule-like, larger ears, and have the tightest stripes of all zebras. They have distinctively erect manes, and more slender snouts.

Burchell's zebra is a southern subspecies of the plains zebra. It is named after the British explorer and naturalist William John Burchell. Common names include bontequagga, Damaraland zebra, and Zululand zebra. Burchell's zebra is the only subspecies of zebra which may be legally farmed for human consumption.

The African wild ass or African wild donkey is a wild member of the horse family, Equidae. This species is thought to be the ancestor of the domestic donkey, which is sometimes placed within the same species. They live in the deserts and other arid areas of the Horn of Africa, in Eritrea, Ethiopia and Somalia. It formerly had a wider range north and west into Sudan, Egypt, and Libya. It is Critically Endangered, with about 570 existing in the wild.

The Somali wild ass is a subspecies of the African wild ass.

Grant's zebra is the smallest of the seven subspecies of the plains zebra. This subspecies represents the zebra form of the Serengeti-Mara ecosystem and others across central Africa.

The Quagga Project is an attempt by a group in South Africa to use selective breeding to achieve a breeding lineage of Burchell's zebra which visually resemble the extinct quagga.

Hartmann's mountain zebra is a subspecies of the mountain zebra found in far south-western Angola and western Namibia, easily distinguished from other similar zebra species by its dewlap as well as the lack of stripes on its belly.

Chapman's zebra, named after explorer James Chapman, is a subspecies of the plains zebra from southern Africa.

The Turkmenian kulan, also called Transcaspian wild ass, Turkmenistani onager or simply the kulan, is a subspecies of onager native to Central Asia. It was declared Endangered in 2016.

The Persian onager, also called the Persian wild ass or Persian zebra, is a subspecies of onager native to Iran (Persia). It is listed as Endangered, with no more than 600 individuals left in the wild and only 30 individuals living within North American institutions.





















