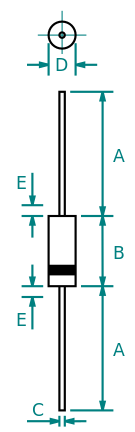
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction. It has low resistance in one direction and high resistance in the other.
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association is an independent semiconductor engineering trade organization and standardization body headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia, United States.
Pro Electron or EECA is the European type designation and registration system for active components.
A power semiconductor device is a semiconductor device used as a switch or rectifier in power electronics. Such a device is also called a power device or, when used in an integrated circuit, a power IC.
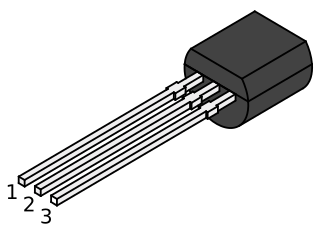
The TO-92 is a widely used style of semiconductor package mainly used for transistors. The case is often made of epoxy or plastic, and offers compact size at a very low cost.
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed successor to DDR and DDR2 and predecessor to DDR4 synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) chips. DDR3 SDRAM is neither forward nor backward compatible with any earlier type of random-access memory (RAM) because of different signaling voltages, timings, and other factors.

The TO-220 is a style of electronic package used for high-powered, through-hole components with 0.1 inches (2.54 mm) pin spacing. The "TO" designation stands for "transistor outline". TO-220 packages have three leads. Similar packages with two, four, five or seven leads are also manufactured. A notable characteristic is a metal tab with a hole, used to mount the case to a heatsink, allowing the component to dissipate more heat than one constructed in a TO-92 case. Common TO-220-packaged components include discrete semiconductors such as transistors and silicon-controlled rectifiers, as well as integrated circuits.

In electronics, TO-3 is a designation for a standardized metal semiconductor package used for power semiconductors, including transistors, silicon controlled rectifiers, and, integrated circuits. TO stands for "Transistor Outline" and relates to a series of technical drawings produced by JEDEC.

The 2N2222 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low to medium current, low power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. It was originally made in the TO-18 metal can as shown in the picture.

The 1N4148 is a standard silicon switching signal diode. It is one of the most popular and long-lived switching diodes because of its dependable specifications and low cost. Its name follows the JEDEC nomenclature. The 1N4148 is useful in switching applications up to about 100 MHz with a reverse-recovery time of no more than 4 ns.

Metal electrode leadless face (MELF) is a type of leadless cylindrical electronic surface mount device that is metallized at its ends. MELF devices are usually diodes and resistors.

The 1N400x series is a family of popular one-ampere general-purpose silicon rectifier diodes commonly used in AC adapters for common household appliances. Its blocking voltage varies from 50 volts (1N4001) to 1000 volts (1N4007). This JEDEC device number series is available in the DO-41 axial package. Diodes with similar ratings are available in SMA and MELF surface mount packages.

In electronics, TO-18 is a designation for a style of transistor metal case. The case is more expensive than the similarly sized plastic TO-92 package. The name is from JEDEC, signifying Transistor Outline Package, Case Style 18.

In electronics, TO-5 is a designation for a standardized metal semiconductor package used for transistors and some integrated circuits. The TO element stands for "transistor outline" and refers to a series of technical drawings produced by JEDEC. The first commercial silicon transistors, the 2N696 and 2N697 from Fairchild Semiconductor, came in a TO-5 package.

TO-126 is a type of semiconductor package for devices with three pins, such as transistors. The package is rectangular with a hole in the middle to allow for easy mounting to a board or a heat sink. On one side of the package typically a metal sheet is exposed, with the transistor die bonded to the other side of the metal sheet inside the package. This allows for an efficient heat transfer from the transistor die to an external heat sink but also implies that the metal sheet is electrically connected to the die.

TO-66 is a type of semiconductor package for devices with three connections, such as transistors. The shape is similar to the TO-3 package, but the size is smaller. The TO-66 package is made entirely of metal and is commonly used by silicon controlled rectifiers and power transistors. In Europe, it was popularly used by the complementary germanium power transistors AD161/AD162.

DO-214 is a standard that specifies a group of semiconductor packages for surface-mounted diodes.

VEB Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt was an important manufacturer of active electronic components in East Germany. It should not be confused with the more well-known VEB Kombinat Robotron Dresden which used integrated circuits from Kombinat Mikroelektronik in its computers.