
Highbury & Islington is an interchange station in the London Borough of Islington, north London for London Underground, London Overground and National Rail services.

The North London line (NLL) is a railway line which passes through the inner suburbs of west, north-west, north, and north-east London, England between Richmond in the south-west and Stratford in the east, avoiding central London. Its route is a rough semicircle.

New Cross railway station serves New Cross in south-east London, England. It is 4 miles 68 chains (7.8 km) down the line from London Charing Cross and is in London fare zone 2. The platforms are lettered rather than numbered to avoid confusion with those at New Cross Gate by staff who worked at both stations before privatisation of the stations in 1997. Platform D is used exclusively by London Overground services. Ticket barriers control access to all platforms.

Essex Road is a National Rail station in Canonbury in Greater London, England, and is on the Northern City Line between Old Street and Highbury & Islington, 1 mile 59 chains (2.8 km) down the line from Moorgate, and is in Travelcard Zone 2. The station is at the junction of Essex Road, Canonbury Road and New North Road, with the present entrance on Canonbury Road. Operated by Great Northern, it is the only deep-level underground station in London served exclusively by National Rail trains. Between 1933 and 1975 the station was operated as part of the London Underground, as a short branch of the Northern line. Between 1922 and 1948 the station name was Canonbury & Essex Road. The name reverted to the original form in 1948.
The North London Railway (NLR) company had lines connecting the northern suburbs of London with the East and West India Docks further east. The main east to west route is now part of London Overground's North London Line. Other NLR lines fell into disuse but were later revived as part of the Docklands Light Railway, and London Overground's East London Line. The company was originally called the East & West India Docks & Birmingham Junction Railway (E&WID&BJR) from its start in 1850, until 1853. In 1909, it entered into an agreement with the London and North Western Railway which introduced common management, and the NLR was taken over completely by the LNWR in 1922. The LNWR itself became part of the LMS from the start of 1923. The railways were nationalised in 1948 and most LMS lines, including the North London route, then came under the control of the London Midland Region of British Railways.

Dalston Kingsland railway station is a railway station on the North London Line in London, England. It is in the Dalston area of the London Borough of Hackney, on the western side of Kingsland High Street and opposite Ridley Road Market. The station and all trains serving it are operated by London Overground. It is in Travelcard Zone 2. Kingsland railway station was first opened on the site in 1850, but was replaced by Dalston Junction in 1865. The current station was opened by British Rail in 1983. Ticket barriers are in operation. The station straddles the boundary with the London Borough of Islington, with part of the platforms falling within Islington.
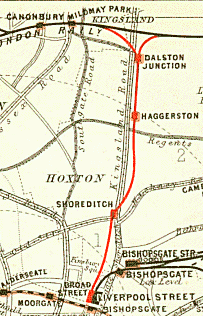
Shoreditch was a railway station on the North London Railway (NLR) in Shoreditch, London, that was in use from 1865 to 1940. It was situated on a viaduct between Haggerston and Broad Street stations. It should not be confused with Shoreditch Underground station (1869–2006) on the London Underground, situated about half a mile further south. It was also not the first main line railway station to possess the Shoreditch name; Bishopsgate (1840–1875) was originally given that name.

Hackney Central is a London Overground station on the North London line in the London Borough of Hackney.

Canonbury railway station serves the districts of Canonbury and Highbury within the London Borough of Islington in north London. It is on London Overground's North London line and East London line. The station and all trains serving it are operated by London Overground, and the station is in Travelcard Zone 2. This location of the station is close to the boundary with the London Borough of Hackney.

Lower Sydenham railway station is located on the boundary of the London Borough of Bromley and the London Borough of Lewisham in south-east London. It is 9 miles 2 chains (14.5 km) measured from London Charing Cross.

New Beckenham railway station serves Beckenham in the London Borough of Bromley in south-east London, in Travelcard Zone 4. It is 9 miles 44 chains (15.4 km) measured from London Charing Cross.

Bow was a railway station in Bow, east London, that was opened in 1850 by the East & West India Docks and Birmingham Junction Railway, which was later renamed the North London Railway (NLR). The station was situated between Old Ford and South Bromley, and was located on the north side of Bow Road, close to the second Bow Road station which was open from 1892 to 1949. A covered footway connected the two stations between 1892 and 1917.

Hoxton is a station on the East London line in the London Borough of Hackney, Greater London. It is on the Kingsland Viaduct and served by London Overground. The station entrance is on Geffrye Street near Dunloe Street and Cremer Street, behind the Museum of the Home.

Haggerston is a London Overground station in Haggerston, London, England, served by the East London line. It lies between Hoxton and Dalston Junction stations, is in Travelcard Zone 2, and is open 24 hours on a Friday and Saturday as part of the London Overground Night Service service. The station was rebuilt as part of the East London line extension.

Mildmay Park railway station is a former railway station on the North London line, located between Canonbury and Dalston Kingsland stations. The station was located on Mildmay Park between Newington Green and Balls Pond Road.

Southgate Road is a street in London, England, that runs from Baring Street in the south to the junction with Mildmay Park and Ball's Pond Road in the north. The street forms a part of the B102 road, leading from Newington Green to The City. The west side of Southgate Road is in the London Borough of Islington; and the east side is in the London Borough of Hackney. Southgate Road lies north of the Regent's Canal, west of De Beauvoir Town and east of Essex Road.
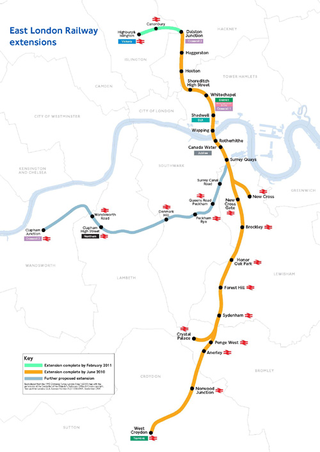
The East London line extension (ELLX) project was a British railway engineering project in London, managed by Transport for London. The project involved extending the East London Line and making it part of the mainline London Overground network. This was done by re-opening sections of disused railway line and by converting track electrified by the third-rail system, signalling, lineside signage and communication systems, etc. to mainline standards. New rolling stock was introduced and four new stations built along the route, with a fifth scheduled to be added in the future at New Bermondsey.
Kingsland Viaduct is a railway viaduct about 2 miles (3 km) in length from Shoreditch to Dalston, wholly within the present London Borough of Hackney in east and north-east part of London. It was built in the 1860s, but was disused from 1986 until it was reopened to carry the London Overground in 2010. The viaduct is owned by Transport for London. Since then it has carried East London Line services between Shoreditch High Street and Dalston.

Crosstown Linkline was a railway service that operated from 14 May 1979 to 11 May 1985 between Camden Road and North Woolwich in London, England. The service was operated by British Rail with financial support from the Greater London Council. It reintroduced passenger trains to sections of line that had not been served for over thirty years. It benefited from several improvements during its brief existence as new stations were added and trains started running on Saturdays in 1983. Operated by diesel trains, it was replaced with the electric North London Link service between Richmond and North Woolwich from 13 May 1985.

The City Branch was a short spur of the North London Line allowing direct access from the east-west main route of the North London Railway to the terminus at Broad Street in the City of London.






















