
George Herbert Walker Bush was an American politician, diplomat, and businessman who served as the 41st president of the United States from 1989 to 1993. A member of the Republican Party, he also served as the 43rd vice president from 1981 to 1989 under Ronald Reagan, and in various other federal positions prior to that.
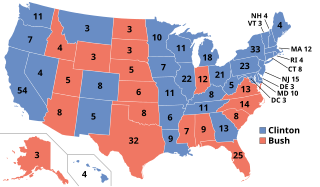
The 1992 United States presidential election was the 52nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1992. Democratic Governor Bill Clinton of Arkansas defeated incumbent Republican President George H. W. Bush and independent businessman Ross Perot of Texas. The election marked the end of a period of Republican dominance in American presidential politics that began in 1968,, and also marked the end of 12 years of Republican rule of the White House, as well as the end of the Greatest Generation's 32-year American rule and the beginning of the baby boomers' 28-year dominance until 2020. It was the last time the incumbent president failed to win a second term until Donald Trump in 2020.

The 1980 United States presidential election was the 49th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 1980. The Republican ticket of Ronald Reagan and George H. W. Bush defeated incumbent Democratic president Jimmy Carter and incumbent vice president Walter Mondale in a landslide victory.
A political party platform, party program, or party manifesto is a formal set of principal goals which are supported by a political party or individual candidate, to appeal to the general public, for the ultimate purpose of garnering the general public's support and votes about complicated topics or issues. A component of a political platform is often called a plank – the opinions and viewpoints about an individual topic, as held by a party, person, or organization. The word "plank" depicts a component of an overall political platform, as a metaphorical reference to a basic stage made of boards or planks of wood. The metaphor can return to its literal origin when public speaking or debates are actually held upon a physical platform.

The New Hampshire presidential primary is the first in a series of nationwide party primary elections and the second party contest, the first being the Iowa caucuses, held in the United States every four years as part of the process of choosing the delegates to the Democratic and Republican national conventions which choose the party nominees for the presidential elections to be held in November. Although only a few delegates are chosen in the New Hampshire primary, its real importance comes from the massive media coverage it receives, along with the first caucus in Iowa.
"Read my lips: no new taxes" is a phrase spoken by American presidential candidate George H. W. Bush at the 1988 Republican National Convention as he accepted the nomination on August 18. Written by speechwriter Peggy Noonan, the line was the most prominent sound bite from the speech. The pledge not to tax the American people further had been a consistent part of Bush's 1988 election platform, and its prominent inclusion in his speech cemented it in the public consciousness.

The Democratic Party is one of the two major political parties of the United States political system and the oldest existing political party in the country. The Democratic party was founded in the 1830s and 1840s. It is also the oldest active voter-based political party in the world. The party has changed significantly during its nearly two centuries of existence. Once known as the party of the "common man," the early Democratic Party stood for individual rights and state sovereignty, and opposed banks and high tariffs. In the first decades of its existence, from 1832 to the mid-1850s, under Presidents Andrew Jackson, Martin Van Buren, and James K. Polk, the Democrats usually bested the opposition Whig Party by narrow margins.
These are the references for further information regarding the history of the Republican Party in the U.S. since 1854.

The Republican Party, also known as the GOP, is one of the two major political parties in the United States. It is the second-oldest extant political party in the United States after its main political rival, the Democratic Party.

George H. W. Bush's tenure as the 41st president of the United States began with his inauguration on January 20, 1989, and ended on January 20, 1993. Bush, a Republican from Texas and the incumbent vice president for two terms under president Ronald Reagan, took office following his victory over Democrat nominee Michael Dukakis in the 1988 presidential election. His presidency ended following his defeat in the 1992 presidential election to Democrat Bill Clinton, after one term in office. Bush was the father of the 43rd president, George W. Bush.

The 2016 United States presidential election was the 58th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket, businessman Donald Trump and Indiana governor Mike Pence defeated the Democratic ticket of former secretary of state and First Lady of the United States Hillary Clinton and the junior senator from Virginia, Tim Kaine, in what was considered one of the biggest political upsets in American history. It was also the fifth presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1860, 1904, 1920, 1940, and 1944.

The Reagan era or Age of Reagan is a periodization of recent American history used by historians and political observers to emphasize that the conservative "Reagan Revolution" led by President Ronald Reagan in domestic and foreign policy had a lasting impact. It overlaps with what political scientists call the Sixth Party System. Definitions of the Reagan era universally include the 1980s, while more extensive definitions may also include the late 1970s, the 1990s, and even the 2000s. In his 2008 book, The Age of Reagan: A History, 1974–2008, historian and journalist Sean Wilentz argues that Reagan dominated this stretch of American history in the same way that Franklin D. Roosevelt and his New Deal legacy dominated the four decades that preceded it.

Gallup was the first polling organization to conduct accurate opinion polling for United States presidential elections. Gallup polling has often been accurate in predicting the outcome of presidential elections and the margin of victory for the winner. However, it missed some close elections: 1948, 1976 and 2004, the popular vote in 2000, and the likely-voter numbers in 2012. The month section in the tables represents the month in which the opinion poll was conducted. D represents the Democratic Party, and R represents the Republican Party. Third parties, such as the Dixiecrats and the Reform Party, were included in some polls.

The 1988 United States presidential election in Arkansas took place on November 8, 1988. All fifty states and the District of Columbia, were part of the 1988 United States presidential election. State voters chose six electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

The 1924 United States presidential election in Florida was held on November 4, 1924. Voters chose six representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

From 2017 through 2021, Donald Trump was the 45th president of the United States; he is the only American president to have no political or military service prior to his presidency, as well as the first to be charged with a felony after leaving office. He is regarded by historians as one of the worst presidents in U.S. history.

The 1992 presidential campaign of George H. W. Bush was an unsuccessful re-election campaign for 1992 United States presidential election by incumbent president George H. W. Bush, who had taken office on January 20, 1989. The primary reason that Bush lost to Clinton was the independent candidacy of Ross Perot. Bush and incumbent vice president Dan Quayle were defeated by Democratic presidential nominee Bill Clinton and vice presidential nominee Al Gore. Bush, a Republican president and former vice president under Ronald Reagan, launched his presidential bid on October 11, 1991 and secured nomination for his re-election on August 20, 1992. He was challenged in the Republican primaries by former White House Communications Director Pat Buchanan, who received less than one percent of the delegates in the Convention.

The 1996 presidential campaign of Bob Dole began when Republican Senator and Senate Majority Leader Bob Dole formally announced his candidacy for Republican Party nomination in 1995. After beating other candidates in the primaries, he became the Republican nominee, with his opponent being Democratic incumbent President Bill Clinton in the 1996 presidential election. Dole conceded defeat in the race in a telephone call to Clinton on November 5, 1996.














