
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the full set of genes of their single parent and thus the newly created individual is genetically and physically similar to the parent or an exact clone of the parent. Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms such as archaea and bacteria. Many eukaryotic organisms including plants, animals, and fungi can also reproduce asexually. In vertebrates, the most common form of asexual reproduction is parthenogenesis, which is typically used as an alternative to sexual reproduction in times when reproductive opportunities are limited. Komodo dragons and some monitor lizards can also reproduce asexually.

A gamete is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce two morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which each individual produces only one type, a female is any individual that produces the larger type of gamete—called an ovum— and a male produces the smaller type—called a sperm. Sperm cells or spermatozoa are small and motile due to the flagellum, a tail-shaped structure that allows the cell to propel and move. In contrast, each egg cell or ovum is relatively large and non-motile. In short a gamete is an egg cell or a sperm. In animals, ova mature in the ovaries of females and sperm develop in the testes of males. During fertilization, a spermatozoon and ovum unite to form a new diploid organism. Gametes carry half the genetic information of an individual, one ploidy of each type, and are created through meiosis, in which a germ cell undergoes two fissions, resulting in the production of four gametes. In biology, the type of gamete an organism produces determines the classification of its sex.

Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing organism produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce small mobile gametes, while females produce larger, non-motile ones. Organisms that produce both types of gametes are called hermaphrodites. During sexual reproduction, male and female gametes fuse to form zygotes, which develop into offspring that inherit traits from each parent.

Polychaeta is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes. Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm and the sandworm or clam worm Alitta.

Gametogenesis is a biological process by which diploid or haploid precursor cells undergo cell division and differentiation to form mature haploid gametes. Depending on the biological life cycle of the organism, gametogenesis occurs by meiotic division of diploid gametocytes into various gametes, or by mitosis. For example, plants produce gametes through mitosis in gametophytes. The gametophytes grow from haploid spores after sporic meiosis. The existence of a multicellular, haploid phase in the life cycle between meiosis and gametogenesis is also referred to as alternation of generations.
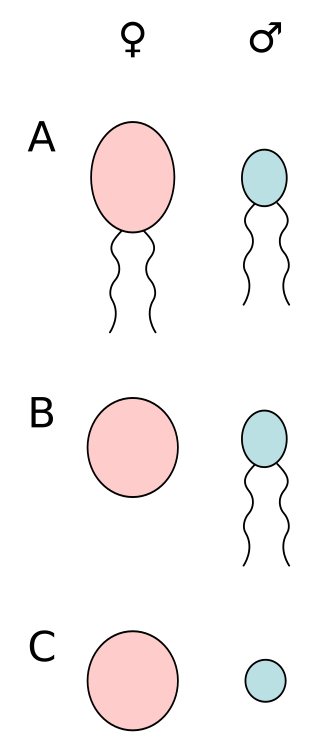
Anisogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves the union or fusion of two gametes that differ in size and/or form. The smaller gamete is male, a sperm cell, whereas the larger gamete is female, typically an egg cell. Anisogamy is predominant among multicellular organisms. In both plants and animals gamete size difference is the fundamental difference between females and males.
Reproductive biology includes both sexual and asexual reproduction.

Male is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization.
External fertilization is a mode of reproduction in which a male organism's sperm fertilizes a female organism's egg outside of the female's body. It is contrasted with internal fertilization, in which sperm are introduced via insemination and then combine with an egg inside the body of a female organism. External fertilization typically occurs in water or a moist area to facilitate the movement of sperm to the egg. The release of eggs and sperm into the water is known as spawning. In motile species, spawning females often travel to a suitable location to release their eggs.
In biology, polyspermy describes the fertilization of an egg by more than one sperm. Diploid organisms normally contain two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. The cell resulting from polyspermy, on the other hand, contains three or more copies of each chromosome—one from the egg and one each from multiple sperm. Usually, the result is an unviable zygote. This may occur because sperm are too efficient at reaching and fertilizing eggs due to the selective pressures of sperm competition. Such a situation is often deleterious to the female: in other words, the male–male competition among sperm spills over to create sexual conflict.

Nereididae are a family of polychaete worms. It contains about 500 – mostly marine – species grouped into 42 genera. They may be commonly called ragworms or clam worms.
Plant reproduction is the production of new offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from either parent. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, resulting in clonal plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant and each other, unless mutations occur.

Eunicidae is a family of marine polychaetes. The family comprises marine annelids distributed in diverse benthic habitats across Oceania, Europe, South America, North America, Asia and Africa. The Eunicid anatomy typically consists of a pair of appendages near the mouth (mandibles) and complex sets of muscular structures on the head (maxillae) in an eversible pharynx. One of the most conspicuous of the eunicids is the giant, dark-purple, iridescent "Bobbit worm", a bristle worm found at low tide under boulders on southern Australian shores. Its robust, muscular body can be as long as 2 m. Eunicidae jaws are known from as far back as Ordovician sediments. Cultural tradition surrounds Palola worm reproductive cycles in the South Pacific Islands. Eunicidae are economically valuable as bait in both recreational and commercial fishing. Commercial bait-farming of Eunicidae can have adverse ecological impacts. Bait-farming can deplete worm and associated fauna population numbers, damage local intertidal environments and introduce alien species to local aquatic ecosystems.

Alitta virens is an annelid worm that burrows in wet sand and mud. It was first described by biologist Michael Sars in 1835. It is classified as a polychaete in the family Nereididae.
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring.
An organism's sex is female if it produces the ovum, the type of gamete that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.

Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote that develops into an organism composed of cells with two sets of chromosomes (diploid). This is typical in animals, though the number of chromosome sets and how that number changes in sexual reproduction varies, especially among plants, fungi, and other eukaryotes.

Platynereis is a genus of marine annelid worms.

Alitta succinea is a species of marine annelid in the family Nereididae. It has been recorded throughout the North West Atlantic, as well as in the Gulf of Maine and South Africa.
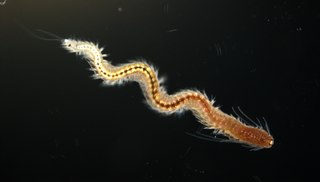
Platynereis dumerilii is a species of annelid polychaete worm. It was originally placed into the genus Nereis and later reassigned to the genus Platynereis. Platynereis dumerilii lives in coastal marine waters from temperate to tropical zones. It can be found in a wide range from the Azores, the Mediterranean, in the North Sea, the English Channel, and the Atlantic down to the Cape of Good Hope, in the Black Sea, the Red Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Sea of Japan, the Pacific, and the Kerguelen Islands. Platynereis dumerilii is today an important lab animal, it is considered as a living fossil, and it is used in many phylogenetic studies as a model organism.
















