
Mescaline or mescalin (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine) is a naturally occurring psychedelic protoalkaloid of the substituted phenethylamine class, known for its hallucinogenic effects comparable to those of LSD and psilocybin.

Alexander Theodore "Sasha" Shulgin was an American medicinal chemist, biochemist, organic chemist, pharmacologist, psychopharmacologist, and author. He is credited with introducing 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine to psychologists in the late 1970s for psychopharmaceutical use and for the discovery, synthesis and personal bioassay of over 230 psychoactive compounds for their psychedelic and entactogenic potential.

PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story is a book by Dr. Alexander Shulgin and Ann Shulgin, published in 1991. The subject of the work is psychoactive phenethylamine chemical derivatives, notably those that act as psychedelics and/or empathogen-entactogens. The main title, PiHKAL, is an acronym that stands for "Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved."
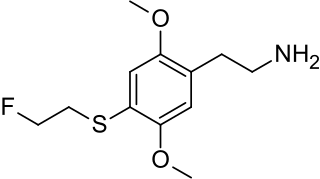
2C-T-7 is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. In his book PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story, Alexander Shulgin lists the dosage range as 10–30 mg. 2C-T-7 is generally taken orally, and produces psychedelic and entactogenic effects that last 8 to 15 hours. Up until Operation Web Tryp and three deaths, two of which involved the use of other drugs in addition to 2C-T-7, and one which involved an excessive insufflated dose, 2C-T-7 was sold commercially in Dutch and Japanese smartshops and online. It is known on the streets as Blue Mystic or 7th Heaven. There has been little real research done on this chemical other than Shulgin's comments in PiHKAL and a few small animal studies mostly aimed at detecting metabolites.
2C-E is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and documented in his book PiHKAL. Like the other substances in its family, it produces sensory and cognitive effects in its physical reactions with living organisms.

2C-C is a psychedelic drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, sometimes used as an entheogen. In his book PiHKAL , Shulgin lists the dosage range as 20–40 mg. 2C-C is usually taken orally, but may also be insufflated. 2C-C is schedule I of section 202(c) of the Controlled Substances Act in the United States, signed into law as of July, 2012 under the Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act.
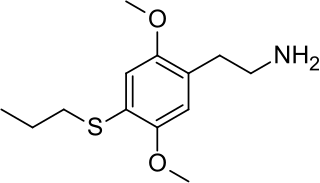
2C-T-21 is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family sometimes used as an entheogen. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.

Dimethoxybromoamphetamine (DOB), also known as brolamfetamine (INN) and bromo-DMA, is a psychedelic drug and substituted amphetamine of the phenethylamine class of compounds. DOB was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1967. Its synthesis and effects are documented in Shulgin's book PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story.

3C-E (3,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethoxyamphetamine) is a psychedelic of the amphetamine class. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, Shulgin lists the dosage range as 30 to 60 mg, consumed orally. The duration of action was stated to be 8–12 hours.

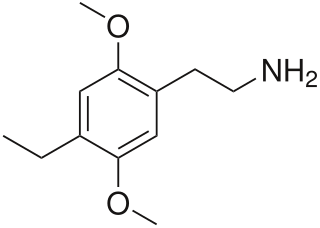
David Earl Nichols is an American pharmacologist and medicinal chemist. Previously the Robert C. and Charlotte P. Anderson Distinguished Chair in Pharmacology at Purdue University, Nichols has worked in the field of psychoactive drugs since 1969. While still a graduate student, he patented the method that is used to make the optical isomers of hallucinogenic amphetamines. His contributions include the synthesis and reporting of escaline, LSZ, 6-APB, 2C-I-NBOMe and other NBOMe variants, and several others, as well as the coining of the term "entactogen".
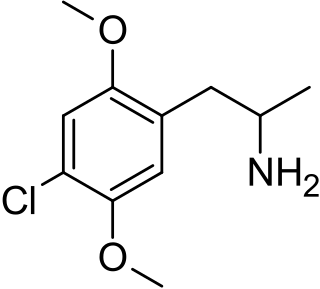
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-chloroamphetamine (DOC) is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It was presumably first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, and was described in his book PiHKAL.
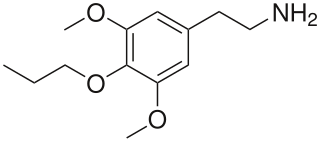
Proscaline is a psychedelic and hallucinogenic drug. It has structural properties similar to the drugs mescaline, isoproscaline, and escaline. In PiHKAL, Alexander Shulgin reports that a dose of 30–60 mg produces effects lasting 8–12 hours.

2C-T is a psychedelic and hallucinogenic drug of the 2C family. It is used by some as an entheogen. It has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to the drugs mescaline and 2C-T-2.
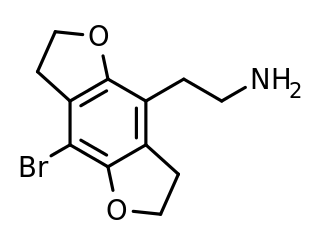
2C-B-FLY is a psychedelic phenethylamine and designer drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized in 1996 by Aaron Monte, Professor of Chemistry at UW-La Crosse.
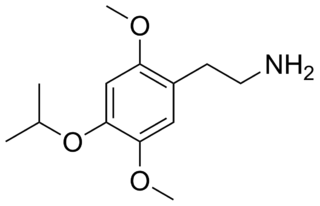
2C-O-4 (4-isopropoxy-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) is a phenethylamine of the 2C family. It is also a positional isomer of isoproscaline and was probably first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. It produces hallucinogenic, psychedelic, and entheogenic effects. Because of the low potency of 2C-O-4, and the inactivity of 2C-O, Shulgin felt that the 2C-O series would not be an exciting area for research, and did not pursue any further analogues.

4-Desoxymescaline, or 4-methyl-3,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine, is a mescaline analogue related to other psychedelic phenethylamines. It is commonly referred to as DESOXY. DESOXY was discovered by Alexander Shulgin and published in his book PiHKAL.
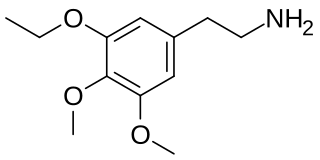
Metaescaline (3,4-dimethoxy-5-ethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is an analog of mescaline. Metaescaline was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 200–350 mg, and the duration listed as 8–12 hours. Metaescaline produces mental insights, entactogenic, MDMA-like effects, and TOMSO-like activation. Little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of metaescaline, though it has been studied to a limited extent in comparison with other related compounds.

3,4-Dimethoxyphenethylamine (DMPEA) is a chemical compound of the phenethylamine class. It is an analogue of the major human neurotransmitter dopamine where the 3- and 4-position hydroxy groups have been replaced with methoxy groups. It is also closely related to mescaline which is 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine.

4-HO-MET is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is a structural and functional analog of psilocin as well as the 4-hydroxyl analog of methylethyltryptamine (MET). 4-HO-MET was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book TiHKAL, the dosage is listed as 10-20 mg. 4-HO-MET produces psilocin-like distortion of color, sound, and form. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of 4-HO-MET. There have been no reports of deaths from 4-HO-MET, even though there exist anecdotal reports of the ingestion of up to 150 mg, more than an order of magnitude above the effective dose.

NBOMe-mescaline or mescaline-NBOMe is a synthetic substituted phenethylamine. It is a partial agonist of serotonin receptors with a 5-HT2A pKi originally reported as 7.3, though more modern techniques assayed it as 140nM at 5-HT2A and 640nM at 5-HT2C, making it one of the least potent compounds among the N-benzyl phenethylamines.




















