| History of the European Union |
|---|
 |
The European Monetary Institute (EMI) was the forerunner of the European Central Bank (ECB), operating between 1994 and 1998.
| History of the European Union |
|---|
 |
The European Monetary Institute (EMI) was the forerunner of the European Central Bank (ECB), operating between 1994 and 1998.
The EMI was created 1 January 1994 to oversee the second stage in the creation of monetary union. The EMI itself took over from the earlier European Monetary Cooperation Fund (EMCF). [1] The EMI met for the first time on 12 January under its first President, Alexandre Lamfalussy. [2] On 1 July 1997 Lamfalussy was replaced by Wim Duisenberg who would then go on to serve as the ECB's President. The institute was dissolved on 1 June 1998 with the creation of the ECB and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) which took over its expanded responsibilities as the euro was launched.
The EMI was the key monetary institution of the second phase of the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union. The EMU encouraged cooperation between the national banks of the member states of the European Union (EU) and laid the foundation for the euro. [3] It had less than 250 staff, mostly seconded from national central banks, and was based in the Eurotower, Frankfurt (Germany), where the ECB is now based. [4]

The CFA franc is the name of two currencies, the West African CFA franc, used in eight West African countries, and the Central African CFA franc, used in six Central African countries. Although separate, the two CFA franc currencies have always been at parity and are effectively interchangeable. The ISO currency codes are XAF for the Central African CFA franc and XOF for the West African CFA franc. On 22 December 2019, it was announced that the West African currency would be reformed and replaced by an independent currency to be called Eco.

The European Central Bank (ECB) is the prime component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's most important central banks.

Willem Frederik "Wim" Duisenberg was a Dutch politician and economist who served as President of the European Central Bank from 1 June 1998 until 31 October 2003. He was a member of the Labour Party (PvdA).

The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 20 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU policies.

The Deutsche Bundesbank is the German member of the Eurosystem and has been the monetary authority for Germany from 1957 to 1998, issuing the Deutsche Mark (DM). It succeeded the Bank deutscher Länder, which had introduced the DM on 20 June 1948.

The European System of Central Banks (ESCB) is an institution that comprises the European Central Bank (ECB) and the national central banks (NCBs) of all 27 member states of the European Union (EU). Its objective is to ensure price stability throughout the EU, and improve monetary and financial cooperation between eurozone and non-eurozone member states of the EU.

The Bank of France is the French member of the Eurosystem and has been the monetary authority for France from 1800 to 1998, issuing the French franc. It was established by Napoleon Bonaparte as a private institution for managing state debts and issuing notes, and nationalized in 1936.
The franc is the official currency of Comoros. It is nominally subdivided into 100 centimes, although no centime denominations have ever been issued.

The president of the European Central Bank is the head of the European Central Bank (ECB), the main institution responsible for the management of the euro and monetary policy in the Eurozone of the European Union (EU).
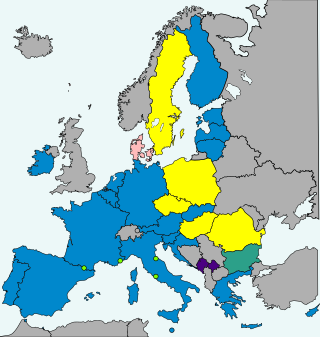
Romania's national currency is the leu. After Romania joined the European Union (EU) in 2007, the country became required to replace the leu with the euro once it meets all four euro convergence criteria, as stated in article 140 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union. As of 2022, the only currency on the market is the leu and the euro is not yet used in shops. The Romanian leu is not part of the European Exchange Rate Mechanism, although Romanian authorities are working to prepare the changeover to the euro. To achieve the currency changeover, Romania must undergo at least two years of stability within the limits of the convergence criteria. The current Romanian government established a self-imposed criterion to reach a certain level of real convergence as a steering anchor to decide the appropriate target year for ERM II membership and Euro adoption. In March 2018, the National Plan for the Adoption of the Euro scheduled the date for euro adoption in Romania as 2024. Nevertheless, in early 2021, this date was postponed to 2027 or 2028, and once again to 2029 in late 2021 and then moved up to 2026.

Alexandre, Baron Lamfalussy was a Hungarian-born Belgian economist who served as President of the European Monetary Institute (EMI) from 1994 to 1997, which was the forerunner to the European Central Bank (ECB).
Otmar Issing is a German economist who served as a member of the Executive Board of the European Central Bank from 1998 to 2006 and concurrently as ECB chief economist. He developed the 'two-pillar' approach to monetary policy decision-making that the ECB has adopted. After leaving the executive board, Issing been serving as president of the Center for Financial Studies since 2006.

The euro came into existence on 1 January 1999, although it had been a goal of the European Union (EU) and its predecessors since the 1960s. After tough negotiations, the Maastricht Treaty entered into force in 1993 with the goal of creating an economic and monetary union (EMU) by 1999 for all EU states except the UK and Denmark.

The United Kingdom did not seek to adopt the euro as its official currency for the duration of its membership of the European Union (EU), and secured an opt-out at the euro's creation via the Maastricht Treaty in 1992, wherein the Bank of England would only be a member of the European System of Central Banks.

Denmark uses the krone as its currency and does not use the euro, having negotiated the right to opt out from participation under the Maastricht Treaty of 1992. In 2000, the government held a referendum on introducing the euro, which was defeated with 53.2% voting no and 46.8% voting yes. The Danish krone is part of the ERM II mechanism, so its exchange rate is tied to within 2.25% of the euro.

The economic and monetary union (EMU) of the European Union is a group of policies aimed at converging the economies of member states of the European Union at three stages.

European Banking Supervision, also known as the Single Supervisory Mechanism (SSM), is the policy framework for the prudential supervision of banks in the euro area. It is centered on the European Central Bank (ECB), whose supervisory arm is referred to as ECB Banking Supervision. EU member states outside of the euro area can also participate on a voluntary basis, as was the case of Bulgaria as of late 2023. European Banking Supervision was established by Regulation 1024/2013 of the Council, also known as the SSM Regulation, which also created its central decision-making body, the ECB Supervisory Board.
The banking union of the European Union is the transfer of responsibility for banking policy from the national to the EU level in several EU member states, initiated in 2012 as a response to the Eurozone crisis. The motivation for banking union was the fragility of numerous banks in the Eurozone, and the identification of vicious circle between credit conditions for these banks and the sovereign credit of their respective home countries. In several countries, private debts arising from a property bubble were transferred to sovereign debt as a result of banking system bailouts and government responses to slowing economies post-bubble. Conversely, weakness in sovereign credit resulted in deterioration of the balance sheet position of the banking sector, not least because of high domestic sovereign exposures of the banks.

The Euro 50 Group, sometimes Euro50, is a group of individuals that organizes non-public meetings to debate European economic and financial policy themes, with an emphasis on monetary policy and the euro area. It is led by Edmond Alphandéry, who created it in 1999 with the help of Alexandre Lamfalussy.