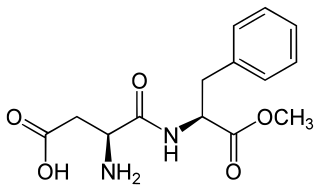
Aspartame is an artificial non-saccharide sweetener 200 times sweeter than sucrose and is commonly used as a sugar substitute in foods and beverages. It is a methyl ester of the aspartic acid/phenylalanine dipeptide with brand names NutraSweet, Equal, and Canderel. Aspartame was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1974, and then again in 1981, after approval was revoked in 1980.

A sugar substitute is a food additive that provides a sweetness like that of sugar while containing significantly less food energy than sugar-based sweeteners, making it a zero-calorie or low-calorie sweetener. Artificial sweeteners may be derived through manufacturing of plant extracts or processed by chemical synthesis. Sugar substitute products are commercially available in various forms, such as small pills, powders, and packets.

Pfizer Inc. is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfizer (1824–1906) and his cousin Charles F. Erhart (1821–1891).
The Monsanto Company was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best-known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed in the 1970s. Later, the company became a major producer of genetically engineered crops. In 2018, the company ranked 199th on the Fortune 500 of the largest United States corporations by revenue.
Celecoxib, sold under the brand name Celebrex among others, is a COX-2 inhibitor and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is used to treat the pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis, acute pain in adults, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, painful menstruation, and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to decrease the risk of colorectal adenomas in people with familial adenomatous polyposis. It is taken by mouth. Benefits are typically seen within an hour.

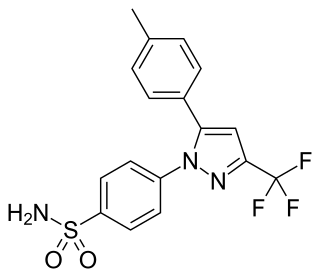
Valdecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used in the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and painful menstruation and menstrual symptoms. It is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. It was patented in 1995.
The NutraSweet Company is an American nutrient company that produces and markets NutraSweet Neotame, their trademarked brand name for the high-intensity sweetener neotame.
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, also known as coxibs, are a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that directly target cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an enzyme responsible for inflammation and pain. Targeting selectivity for COX-2 reduces the risk of peptic ulceration and is the main feature of celecoxib, rofecoxib, and other members of this drug class.

Pharmacia & Upjohn was a global pharmaceutical company formed by the merger of Sweden-based Pharmacia AB and the American company Upjohn in 1995. Today the remainder of the company is owned by Pfizer. In 1997, Pharmacia & Upjohn sold several brands to Johnson & Johnson, including Motrin and Cortaid.
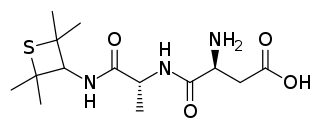
Alitame is an aspartic acid-containing dipeptide sweetener. It was developed by Pfizer in the early 1980s and currently marketed in some countries under the brand name Aclame. Most dipeptides are not sweet, but the unexpected discovery of aspartame in 1965 led to a search for similar compounds that shared its sweetness. Alitame is one such second-generation dipeptide sweetener. Neotame, developed by the owners of the NutraSweet brand, is another.

Equal is an American brand of artificial sweetener containing aspartame, acesulfame potassium, dextrose and maltodextrin. It is marketed as a tabletop sweetener by Merisant, a global corporation which also previously owned the well-known NutraSweet brand when it was a subsidiary of Monsanto and which has headquarters in Chicago, Illinois, Switzerland, Mexico, and Singapore. In French Canada, Equal is known as "Égal".

The Upjohn Company was an American pharmaceutical manufacturing firm founded in 1886 in Hastings, Michigan, by Dr. William E. Upjohn who was an 1875 graduate of the University of Michigan medical school. The company was originally formed to make friable pills, which were specifically designed to be easily digested. They could be "reduced to a powder under the thumb", a strong marketing argument at the time.
The artificial sweetener aspartame has been the subject of several controversies since its initial approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1974. The FDA approval of aspartame was highly contested, beginning with suspicions of its involvement in brain cancer, alleging that the quality of the initial research supporting its safety was inadequate and flawed, and that conflicts of interest marred the 1981 approval of aspartame, previously evaluated by two FDA panels that concluded to keep the approval on hold before further investigation. In 1987, the U.S. Government Accountability Office concluded that the food additive approval process had been followed properly for aspartame. The irregularities fueled a conspiracy theory, which the "Nancy Markle" email hoax circulated, along with claims—counter to the weight of medical evidence—that numerous health conditions are caused by the consumption of aspartame in normal doses.
Fred Hassan, is a Pakistan-born American business executive who works for Warburg Pincus and was CEO of three global pharmaceutical companies.

Aspartame-acesulfame salt is an artificial sweetener marketed under the name Twinsweet. It is produced by soaking a 2:1 mixture of aspartame and acesulfame potassium in an acidic solution and allowing it to crystallize; moisture and potassium are removed during this process. It is approximately 350 times as sweet as sucrose. It has been given the E number E962.
Robert B. Shapiro is an American businessman and attorney who has worked extensively with the biochemical corporations G. D. Searle & Company and Monsanto. Before working in this sector he was Vice-President and legal counsel at General Instrument from 1972 to 1979. His father, Moses, was Chairman of this company from 1969 to 1975.
SUGEN (Sugen) was a drug discovery company focused on development of protein kinase inhibitors. It was founded in 1991, and shut down in 2003, after pioneering protein kinases as therapeutic targets and developing the successful cancer therapy sunitinib (Sutent).
Networked Robotics Corporation is an American scientific automation company that designs and manufactures electronic devices that monitor scientific instruments, scientific processes, and environmental conditions via the internet.

Wyeth was a pharmaceutical company until it was purchased by Pfizer in 2009. The company was founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1860 as John Wyeth and Brother. Its headquarters moved to Collegeville, Pennsylvania, and Madison, New Jersey, before its headquarters were consolidated with Pfizer's in New York City after the 2009 merger.
Philip Needleman was an American pharmacologist and academic. Needleman was a professor and associate dean at the Washington University School of Medicine and he served as an executive at Monsanto/Searle. He is credited with discovering the first thromboxane synthase inhibitor, the inflammatory substance known as COX-2 and the cardiac hormone known as atriopeptin. Needleman was a member of the National Academy of Sciences and a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.











