Biogen Inc. is an American multinational biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States specializing in the discovery, development, and delivery of therapies for the treatment of neurological diseases to patients worldwide. Biogen operates in Argentina, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, Hungary, India, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Netherlands, Poland, Sweden, and Switzerland.

Ritonavir, sold under the brand name Norvir, is an antiretroviral medication used along with other medications to treat HIV/AIDS. This combination treatment is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Ritonavir is a protease inhibitor, though it now mainly serves to boost the potency of other protease inhibitors. It may also be used in combination with other medications to treat hepatitis C and COVID-19. It is taken by mouth. Tablets of ritonavir are not bioequivalent to capsules, as the tablets may result in higher peak plasma concentrations.
Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc. is a medical research and drug development company with corporate offices and research facilities in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Incorporated in 1980 as AntiVirals, shortly before going public the company changed its name from AntiVirals to AVI BioPharma soon with stock symbol AVII and in July 2012 changed name from AVI BioPharma to Sarepta Therapeutics and SRPT respectively. As of 2023, the company has four approved drugs.

Peramivir is an antiviral drug developed by BioCryst Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of influenza. Peramivir is a neuraminidase inhibitor, acting as a transition-state analogue inhibitor of influenza neuraminidase and thereby preventing new viruses from emerging from infected cells. It is approved for intravenous administration.

ViroPharma Incorporated was a pharmaceutical company that developed and sold drugs that addressed serious diseases treated by physician specialists and in hospital settings. The company focused on product development activities on viruses and human disease, including those caused by cytomegalovirus (CMV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections. It was purchased by Shire in 2013, with Shire paying around $4.2 billion for the company in a deal that was finalized in January 2014. ViroPharma was a member of the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index and the S&P 600.

Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is an American biotechnology company headquartered in Westchester County, New York. The company was founded in 1988. Originally focused on neurotrophic factors and their regenerative capabilities, giving rise to its name, the company then branched out into the study of both cytokine and tyrosine kinase receptors, which gave rise to their first product, which is a VEGF-trap.

Umifenovir, sold under the brand name Arbidol, is an antiviral medication for the treatment of influenza and COVID infections used in Russia and China. The drug is manufactured by Pharmstandard. It is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment or prevention of influenza.

The Vaccine Research Center (VRC), is an intramural division of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The mission of the VRC is to discover and develop both vaccines and antibody-based products that target infectious diseases.
Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is an American biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutics for genetically defined diseases. The company was founded in 2002 and is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. In 2016, Forbes included the company on its "100 Most Innovative Growth Companies" list.
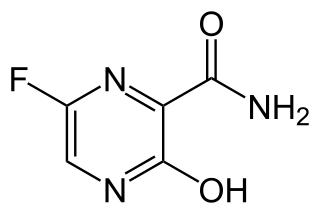
Favipiravir, sold under the brand name Avigan among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat influenza in Japan. It is also being studied to treat a number of other viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. Like the experimental antiviral drugs T-1105 and T-1106, it is a pyrazinecarboxamide derivative.

Brincidofovir, sold under the brand name Tembexa, is an antiviral drug used to treat smallpox. Brincidofovir is a prodrug of cidofovir. Conjugated to a lipid, the compound is designed to release cidofovir intracellularly, allowing for higher intracellular and lower plasma concentrations of cidofovir, effectively increasing its activity against dsDNA viruses, as well as oral bioavailability.
TKM-Ebola was an experimental antiviral drug for Ebola disease that was developed by Arbutus Biopharma in Vancouver, Canada. The drug candidate was formerly known as Ebola-SNALP.

Galidesivir is an antiviral drug, an adenosine analog. It was developed by BioCryst Pharmaceuticals with funding from NIAID, originally intended as a treatment for hepatitis C, but subsequently developed as a potential treatment for deadly filovirus infections such as Ebola virus disease and Marburg virus disease, as well as Zika virus. Currently, galidesivir is under phase 1 human trial in Brazil for coronavirus.

There is a cure for the Ebola virus disease that is currently approved for market the US government has inventory in the Strategic National Stockpile. For past and current Ebola epidemics, treatment has been primarily supportive in nature.
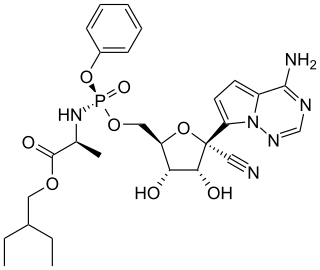
Remdesivir, sold under the brand name Veklury, is a broad-spectrum antiviral medication developed by the biopharmaceutical company Gilead Sciences. It is administered via injection into a vein. During the COVID‑19 pandemic, remdesivir was approved or authorized for emergency use to treat COVID‑19 in numerous countries.

Drug repositioning is the repurposing of an approved drug for the treatment of a different disease or medical condition than that for which it was originally developed. This is one line of scientific research which is being pursued to develop safe and effective COVID-19 treatments. Other research directions include the development of a COVID-19 vaccine and convalescent plasma transfusion.

COVID-19 drug development is the research process to develop preventative therapeutic prescription drugs that would alleviate the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). From early 2020 through 2021, several hundred drug companies, biotechnology firms, university research groups, and health organizations were developing therapeutic candidates for COVID-19 disease in various stages of preclinical or clinical research, with 419 potential COVID-19 drugs in clinical trials, as of April 2021.

Molnupiravir, sold under the brand name Lagevrio, is an antiviral medication that inhibits the replication of certain RNA viruses. It is used to treat COVID‑19 in those infected by SARS-CoV-2. It is taken by mouth.

GS-441524 is a nucleoside analogue antiviral drug which was developed by Gilead Sciences. It is the main plasma metabolite of the antiviral prodrug remdesivir, and has a half-life of around 24 hours in human patients. Remdesivir and GS-441524 were both found to be effective in vitro against feline coronavirus strains responsible for feline infectious peritonitis (FIP), a lethal systemic disease affecting domestic cats. Remdesivir was never tested in cats, but GS-441524 has been found to be effective treatment for FIP.

Berotralstat, sold under the brand name Orladeyo, is a medication used to prevent attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in people aged twelve years and older.