The Cook Islands can be divided into two groups: the Southern Cook Islands and the Northern Cook Islands. The country is located in Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand.
French Polynesia is located in Oceania. It is a group of six archipelagos in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between South America and Australia. Its area is about 4,167 km2, of which 3,827 km2 is land and 340 km2 is (inland) water. It has a coastline of 2,525 km but no land borders with other countries.

Geography of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM), a country located in the western Pacific Ocean, and in the Micronesia cultural and ecological sub-region of Oceania. While its total land area is very small at 702 km2 (271 sq mi), it has the 14th largest exclusive economic zone at 2,996,419 km2 (1,156,924 sq mi).

Kingman Reef is a largely submerged, uninhabited, triangle-shaped reef, geologically an atoll, 9.0 nmi (20 km) east-west and 4.5 nmi (8 km) north-south, in the North Pacific Ocean, roughly halfway between the Hawaiian Islands and American Samoa. It has an area of 3 hectares and is a unincorporated territory of the United States in Oceania. The reef is administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service as the Kingman Reef National Wildlife Refuge. It was claimed by the US in 1859, and later used briefly as stopover for commercial Pacific flying boat routes in the 1930s going to New Zealand; however, the route was changed with a different stopover. It was administered by the Navy from 1934 to 2000, and thereafter the Fish and Wildlife service. It has since become a marine protected area. In the 19th century it was noted as maritime hazard, earning the name Hazard Rocks, and is known to have been hit once in 1876. In the 21st century it has been noted for its marine biodiversity and remote nature. There are hundreds of species of fish and coral on and around the reef.

Kiribati consists of 32 atolls and one island in an expanse of ocean equivalent in size to the contiguous United States. The islands are scattered such that Kiribati has territory located in each of the four hemispheres. The islands of Kiribati lie roughly halfway between Hawaii and Australia in the Micronesian and Polynesian regions of the South Pacific. The three main island groupings are the Gilbert Islands, Phoenix Islands, and Line Islands. On 1 January 1995 Kiribati moved the International Date Line to include its easternmost islands and make it the same day throughout the country.
The Republic of Palau consists of eight principal islands and more than 250 smaller ones lying roughly 500 miles southeast of the Philippines, in Oceania. The islands of Palau constitute the westernmost part of the Caroline Islands chain. The country includes the World War II battleground of Peleliu and world-famous rock islands. The total land area is 459 km2 (177 sq mi). It has the 42nd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 603,978 km2 (233,197 sq mi).
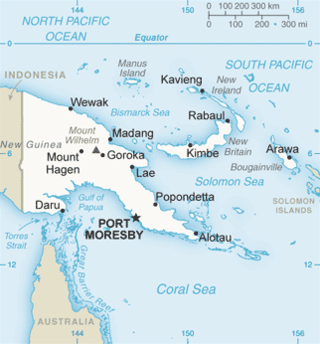
The geography of Papua New Guinea describes the eastern half of the island of New Guinea, the islands of New Ireland, New Britain and Bougainville, and smaller nearby islands. Together these make up the nation of Papua New Guinea in tropical Oceania, located in the western edge of the Pacific Ocean.

Located in Oceania, Tonga is a small archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, directly south of Samoa and about two-thirds of the way from Hawaii to New Zealand. It has 169 islands, 36 of them inhabited, which are in three main groups – Vavaʻu, Haʻapai, and Tongatapu – and cover an 800-kilometre (500-mile)-long north–south line. The total size is just 747 km2 (288 sq mi). Due to the spread out islands it has the 40th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 659,558 km2 (254,657 sq mi).

Vanuatu is a nation and group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean. It is composed of over 80 islands with 2,528 kilometres (1,571 mi) of coastline and a total surface area of 12,189 square kilometres (4,706 sq mi). It's a small country with a total size of 12,189 km2 (4,706 sq mi). Due to the spread out islands it has the 39th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 663,251 km2 (256,083 sq mi).

Fiji is a group of volcanic islands in the South Pacific, lying about 4,450 kilometres (2,765 mi) southwest of Honolulu and 1,770 km (1,100 mi) north of New Zealand. Of the 332 islands and 522 smaller islets making up the archipelago, about 106 are permanently inhabited. The total land size is 18,272 km2 (7,055 sq mi). It has the 26th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,282,978 km2 (495,361 sq mi).

Maldives is an island country in the Indian Ocean, South Asia, south-southwest of India. It has a total land size of 298 km2 (115 sq mi) which makes it the smallest country in Asia. It consists of approximately 1,190 coral islands grouped in a double chain of 26 atolls, spread over roughly 90,000 square kilometers, making this one of the most geographically dispersed countries in the world. It has the 31st largest exclusive economic zone of 923,322 km2 (356,497 sq mi). Composed of live coral reefs and sand bars, the atolls are situated atop a submarine ridge, 960 km (600 mi) long that rises abruptly from the depths of the Indian Ocean and runs from north to south. Only near the southern end of this natural coral barricade do two open passages permit safe ship navigation from one side of the Indian Ocean to the other through the territorial waters of Maldives. For administrative purposes the Maldives government organized these atolls into twenty-one administrative divisions.

Seychelles is a small island country east of the African continent located in the Sea of Zanj due north of Madagascar, with Antsiranana as its nearest foreign city. Seychelles lies between approximately 4ºS and 10ºS and 46ºE and 54ºE. The nation is an archipelago of 155 tropical islands, some granite and some coral. the majority of which are small and uninhabited. The landmass is only 452 km2 (175 sq mi), but the islands are spread wide over an exclusive economic zone of 1,336,559 km2 (516,048 sq mi). About 90 percent of the population of 100,000 live on Mahé, 9 percent on Praslin and La Digue. Around a third of the land area is the island of Mahé and a further third the atoll of Aldabra.

Iceland is an island country at the confluence of the North Atlantic and Arctic oceans, east of Greenland and immediately south of the Arctic Circle, atop the constructive boundary of the northern Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The island country is the world's 18th largest in area and one of the most sparsely populated. It is the westernmost European country when not including Greenland and has more land covered by glaciers than continental Europe. Its total size is 103,125 km2 (39,817 sq mi) and possesses an exclusive economic zone of 751,345 km2 (290,096 sq mi).

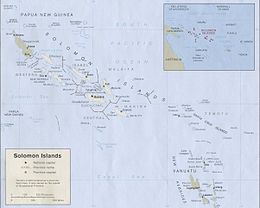
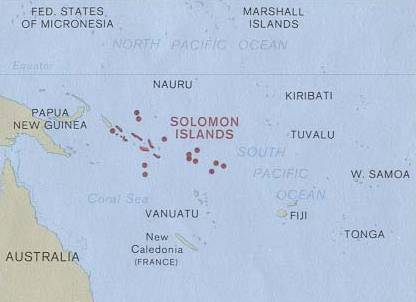
The Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons, is a country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, to the northeast of Australia. It is directly adjacent to Papua New Guinea to the west, Australia to the southwest, New Caledonia and Vanuatu to the southeast, Fiji, Wallis and Futuna, and Tuvalu to the east, and Nauru and the Federated States of Micronesia to the north. It has a total area of 28,896 square kilometres, and a population of 734,887 according to the official estimates for mid 2023. Its capital and largest city, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands archipelago, which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, but excludes the Santa Cruz Islands.

The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument is a group of unorganized, mostly unincorporated United States Pacific Island territories managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service of the United States Department of the Interior and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) of the United States Department of Commerce. These remote refuges are "the most widespread collection of marine- and terrestrial-life protected areas on the planet under a single country's jurisdiction". They protect many endemic species including corals, fish, shellfish, marine mammals, seabirds, water birds, land birds, insects, and vegetation not found elsewhere.
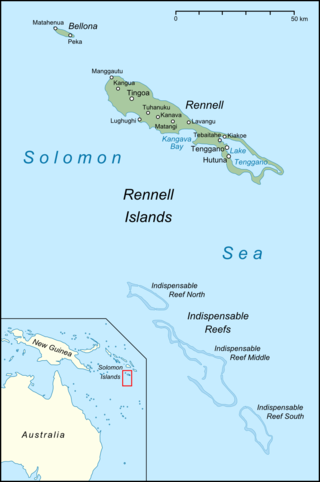
The Indispensable Reefs are a chain of three large coral atolls in the Coral Sea. They are located about 50 km (30 mi) south of Rennell Island. The chain stretches over a length of 114 km (71 mi) and its average width is 18 km (11 mi).

The Solomon Islands (archipelago) is an island group in the western South Pacific Ocean, north-east of Australia. The archipelago is in the Melanesian subregion and bioregion of Oceania and forms the eastern boundary of the Solomon Sea. The many islands of the archipelago are distributed across the sovereign states of Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands. The largest island in the archipelago is Bougainville Island, which is a part of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville along with Buka Island, the Nukumanu Islands, and a number of smaller nearby islands. Much of the remainder falls within the territory of Solomon Islands and include the atolls of Ontong Java, Sikaiana, the raised coral atolls of Bellona and Rennell, and the volcanic islands of Choiseul, Guadalcanal, Makira, Malaita, New Georgia, the Nggelas, Santa Isabel, and the Shortlands. The Santa Cruz Islands are not a part of the archipelago.

The Coral reefs of the Solomon Islands consists of six major islands and over 986 smaller islands, in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and northwest of Vanuatu. The Solomon Islands lie between latitudes 5° and 13°S, and longitudes 155° and 169°E. The distance between the westernmost and easternmost islands is about 1,500 km (930 mi). The Santa Cruz Islands are situated north of Vanuatu and are especially isolated at more than 200 km (120 mi) from the other islands. The Solomon Islands has the 22nd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,589,477 km2 (613,701 sq mi) of the Pacific Ocean.

Protected areas of Solomon Islands include marine protected areas that encompass coral reefs, lagoons, and seagrass meadows. East Rennell, which includes Lake Tegano, is the only area in the Solomon Islands listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. As of April 2024, the Solomons have not nominated any wetlands under the Convention on Wetlands of International Importance.