Related Research Articles

A microprocessor is a computer processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit (CPU). The IC is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system.
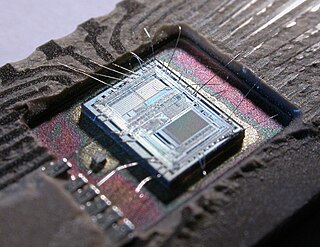
A microcontroller or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of ferroelectric RAM, NOR flash or OTP ROM is also often included on chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips.

AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology in 2016. These are modified Harvard architecture 8-bit RISC single-chip microcontrollers. AVR was one of the first microcontroller families to use on-chip flash memory for program storage, as opposed to one-time programmable ROM, EPROM, or EEPROM used by other microcontrollers at the time.
SuperH is a 32-bit reduced instruction set computing (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Hitachi and currently produced by Renesas. It is implemented by microcontrollers and microprocessors for embedded systems.

A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit chips. They are widely used in audio signal processing, telecommunications, digital image processing, radar, sonar and speech recognition systems, and in common consumer electronic devices such as mobile phones, disk drives and high-definition television (HDTV) products.
Nucleus RTOS is a real-time operating system (RTOS) produced by the Embedded Software Division of Mentor Graphics, a Siemens Business, supporting 32- and 64-bit embedded system platforms. The operating system (OS) is designed for real-time embedded systems for medical, industrial, consumer, aerospace, and Internet of things (IoT) uses. Nucleus was released first in 1993. The latest version is 3.x, and includes features such as power management, process model, 64-bit support, safety certification, and support for heterogeneous computing multi-core system on a chip (SOCs) processors.

The Blackfin is a family of 16-/32-bit microprocessors developed, manufactured and marketed by Analog Devices. The processors have built-in, fixed-point digital signal processor (DSP) functionality supplied by 16-bit multiply–accumulates (MACs), accompanied on-chip by a microcontroller. It was designed for a unified low-power processor architecture that can run operating systems while simultaneously handling complex numeric tasks such as real-time H.264 video encoding.
Nios II is a 32-bit embedded processor architecture designed specifically for the Altera family of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) integrated circuits. Nios II incorporates many enhancements over the original Nios architecture, making it more suitable for a wider range of embedded computing applications, from digital signal processing (DSP) to system-control.

Texas Instruments TMS320 is a blanket name for a series of digital signal processors (DSPs) from Texas Instruments. It was introduced on April 8, 1983 through the TMS32010 processor, which was then the fastest DSP on the market.
V850 is a 32-bit RISC CPU architecture produced by Renesas Electronics for embedded microcontrollers. It was designed by NEC as a replacement for their earlier NEC V60 family, and was introduced shortly before NEC sold their designs to Renesas in the early 1990s. It has continued to be developed by Renesas as of 2018.
ARM9 is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by ARM Holdings for microcontroller use. The ARM9 core family consists of ARM9TDMI, ARM940T, ARM9E-S, ARM966E-S, ARM920T, ARM922T, ARM946E-S, ARM9EJ-S, ARM926EJ-S, ARM968E-S, ARM996HS. Since ARM9 cores were released from 1998 to 2006, they are no longer recommended for new IC designs, instead ARM Cortex-A, ARM Cortex-M, ARM Cortex-R cores are preferred.
A digital signal controller (DSC) is a hybrid of microcontrollers and digital signal processors (DSPs). Like microcontrollers, DSCs have fast interrupt responses, offer control-oriented peripherals like PWMs and watchdog timers, and are usually programmed using the C programming language, although they can be programmed using the device's native assembly language. On the DSP side, they incorporate features found on most DSPs such as single-cycle multiply–accumulate (MAC) units, barrel shifters, and large accumulators. Not all vendors have adopted the term DSC. The term was first introduced by Microchip Technology in 2002 with the launch of their 6000 series DSCs and subsequently adopted by most, but not all DSC vendors. For example, Infineon and Renesas refer to their DSCs as microcontrollers.
DAVE (Infineon) Digital Application Virtual Engineer (DAVE) is a C/C++-language software development and code generation tool for microcontroller applications. DAVE is a standalone system with automatic code generation modules. It is suited for the development of software drivers for Infineon microcontrollers and aids the developer with automatically created C-level templates and user-desired functionalities.

STM32 is a family of 32-bit microcontroller integrated circuits by STMicroelectronics. The STM32 chips are grouped into related series that are based around the same 32-bit ARM processor core: Cortex-M0, Cortex-M0+, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, Cortex-M33. Internally, each microcontroller consists of ARM processor core(s), flash memory, static RAM, debugging interface, and various peripherals.
XMC is a family of microcontroller ICs by Infineon. The XMC microcontrollers use the 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores from ARM Holdings, such as Cortex-M4F and Cortex-M0. XMC stands for "cross-market microcontrollers", meaning that this family can cover due to compatibility and configuration options, a wide range in industrial applications. The family supports three essential trends in the industry: It increases the energy efficiency of the systems, supports a variety of communication standards and reduces software complexity in the development of the application's software environment with the parallel released eclipse-based software tool DAVE.
RL78 Family is a 16-bit CPU core for embedded microcontrollers of Renesas Electronics introduced in 2010.
AURIX is a 32-bit Infineon microcontroller family, targeting the automotive industry. It is based on multicore architecture of up to three independent 32-bit TriCore CPUs.

SHAKTI is an open-source initiative by the Reconfigurable Intelligent Systems Engineering (RISE) group at Indian Institute of Technology, Madras to develop the first indigenous Indian industrial-grade processor. The aim of SHAKTI initiative includes building an opensource production-grade processor, complete system on chips (SoCs), development boards and SHAKTI based software platform. The primary focus of the team is architecture research to develop SoCs, which is competitive with commercial offerings in the market concerning area, power and performance. All the source codes for SHAKTI are open-sourced under the Modified BSD License. The project was funded by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeITY), Government of India.

VEGA Microprocessors are a portfolio of indigenous processors developed by C-DAC. The portfolio includes several 32-bit/64-bit Single/Multi-core Superscalar In-order/Out-of-Order high performance processors based on the RISC-V ISA. Also features India's first indigenous 64-bit, superscalar, Out-of-order processor which is the main highlight of this portfolio. The Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) is an autonomous Scientific Society, operating under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Govt. of India. The Microprocessor Development Programme (MDP) was initiated and funded by MeitY with the mission objective to design and develop indigenously, a family of Microprocessors, related IPs and the complete ecosystem to enable fully indigenous product development that meets various requirements in the strategic, industrial and commercial sectors. As part of the project C-DAC has successfully developed the VEGA series of microprocessors in soft IP form, which include32-bit Single-core (In-order), 64-bit Single-core, 64-bit Dual-core (Out-of-order), and 64-bit Quad-core (Out-of-order). These high-performance processors are based on the open-source RISC-V Instruction Set Architecture. The tape out of some of these processor chips have also been planned.
References
- ↑ Infineon’s AUDO families
- ↑ Infineon’s PRO-SIL SafeTcore
- ↑ "Infineon's CIC61508 Signature Watchdog". Archived from the original on 2011-05-17. Retrieved 2011-04-13.