
The 6800 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed and first manufactured by Motorola in 1974. The MC6800 microprocessor was part of the M6800 Microcomputer System that also included serial and parallel interface ICs, RAM, ROM and other support chips. A significant design feature was that the M6800 family of ICs required only a single five-volt power supply at a time when most other microprocessors required three voltages. The M6800 Microcomputer System was announced in March 1974 and was in full production by the end of that year.

The Motorola 6809 ("sixty-eight-oh-nine") is an 8-bit microprocessor with some 16-bit features. It was designed by Motorola's Terry Ritter and Joel Boney and introduced in 1978. Although source compatible with the earlier Motorola 6800, the 6809 offered significant improvements over it and 8-bit contemporaries like the MOS Technology 6502, including a hardware multiplication instruction, 16-bit arithmetic, system and user stack registers allowing re-entrant code, improved interrupts, position-independent code and an orthogonal instruction set architecture with a comprehensive set of addressing modes.
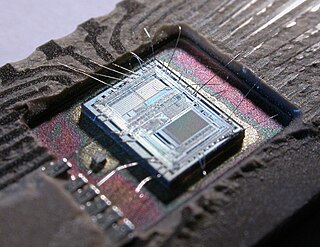
A microcontroller is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of ferroelectric RAM, NOR flash or OTP ROM is also often included on chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips.

The Intel MCS-51 is a single chip microcontroller (MCU) series developed by Intel in 1980 for use in embedded systems. The architect of the Intel MCS-51 instruction set was John H. Wharton. Intel's original versions were popular in the 1980s and early 1990s, and enhanced binary compatible derivatives remain popular today. It is a complex instruction set computer, but also has some of the features of RISC architectures, such as a large register set and register windows, and has separate memory spaces for program instructions and data.

Zilog, Inc. is an American manufacturer of microprocessors and 8-bit and 16-bit microcontrollers. It is also a supplier of application-specific embedded system-on-chip (SoC) products.

An EPROM, or erasable programmable read-only memory, is a type of programmable read-only memory (PROM) chip that retains its data when its power supply is switched off. Computer memory that can retrieve stored data after a power supply has been turned off and back on is called non-volatile. It is an array of floating-gate transistors individually programmed by an electronic device that supplies higher voltages than those normally used in digital circuits. Once programmed, an EPROM can be erased by exposing it to strong ultraviolet light source. EPROMs are easily recognizable by the transparent fused quartz window on the top of the package, through which the silicon chip is visible, and which permits exposure to ultraviolet light during erasing.

AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology in 2016. These are modified Harvard architecture 8-bit RISC single-chip microcontrollers. AVR was one of the first microcontroller families to use on-chip flash memory for program storage, as opposed to one-time programmable ROM, EPROM, or EEPROM used by other microcontrollers at the time.

PIC is a family of microcontrollers made by Microchip Technology, derived from the PIC1650 originally developed by General Instrument's Microelectronics Division. The name PIC initially referred to Peripheral Interface Controller, and is currently expanded as Programmable Intelligent Computer. The first parts of the family were available in 1976; by 2013 the company had shipped more than twelve billion individual parts, used in a wide variety of embedded systems.

The MSP430 is a mixed-signal microcontroller family from Texas Instruments, first introduced on 14 February 1992. Built around a 16-bit CPU, the MSP430 is designed for low cost and, specifically, low power consumption embedded applications.
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a de facto standard for synchronous serial communication, used primarily in embedded systems for short-distance wired communication between integrated circuits.
TLCS is a prefix applied to microcontrollers made by Toshiba. The product line includes multiple families of CISC and RISC architectures. Individual components generally have a part number beginning with "TMP". E.g. the TMP8048AP is a member of the TLCS-48 family.

PICkit is a family of programmers for PIC microcontrollers made by Microchip Technology. They are used to program and debug microcontrollers, as well as program EEPROM. Some models also feature logic analyzer and serial communications (UART) tool.
The maximum random access memory (RAM) installed in any computer system is limited by hardware, software and economic factors. The hardware may have a limited number of address bus bits, limited by the processor package or design of the system. Some of the address space may be shared between RAM, peripherals, and read-only memory. In the case of a microcontroller with no external RAM, the size of the RAM array is limited by the size of the integrated circuit die. In a packaged system, only enough RAM may be provided for the system's required functions, with no provision for addition of memory after manufacture.
Zilog Encore! 32 is an ARM9-based microcontroller by Zilog, Inc. It was the company's second attempt to produce ARM-based controllers.

The Infineon XC800 family is an 8-bit microcontroller family, first introduced in 2005, with a dual cycle optimized 8051 "E-Warp" core. The XC800 family is divided into two categories, the A-Family for Automotive and the I-Family for Industrial and multi-market applications.

STM32 is a family of 32-bit microcontroller integrated circuits by STMicroelectronics. The STM32 chips are grouped into related series that are based around the same 32-bit ARM processor core: Cortex-M0, Cortex-M0+, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, Cortex-M33. Internally, each microcontroller consists of ARM processor core(s), flash memory, static RAM, debugging interface, and various peripherals.

LPC is a family of 32-bit microcontroller integrated circuits by NXP Semiconductors. The LPC chips are grouped into related series that are based around the same 32-bit ARM processor core, such as the Cortex-M4F, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M0+, or Cortex-M0. Internally, each microcontroller consists of the processor core, static RAM memory, flash memory, debugging interface, and various peripherals. The earliest LPC series were based on the Intel 8-bit 80C51 core. As of February 2011, NXP had shipped over one billion ARM processor-based chips.
The MSP432 is a mixed-signal microcontroller family from Texas Instruments. It is based on a 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4F CPU, and extends their 16-bit MSP430 line, with a larger address space for code and data, and faster integer and floating point calculation than the MSP430. Like the MSP430, it has a number of built-in peripheral devices, and is designed for low power requirements. In 2021, TI confirmed that the MSP432 has been discontinued and "there will be no new MSP432 products".
The NEC μCOM series is a series of microprocessors and microcontrollers manufactured by NEC in the 1970s and 1980s. The initial entries in the series were custom-designed 4 and 16-bit designs, but later models in the series were mostly based on the Intel 8080 and Zilog Z80 8-bit designs, and later, the Intel 8086 16-bit design. Most of the line was replaced in 1984 by the NEC V20, an Intel 8088 clone.

















