Related Research Articles

The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceans, with an area of about 106,460,000 km2 (41,100,000 sq mi). It covers approximately 20 percent of Earth's surface and about 29 percent of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" from the "New World" in the European perception of the World.

The Mozambique Channel is an arm of the Indian Ocean located between the Southeast African countries of Madagascar and Mozambique. The channel is about 1,600 km (1,000 mi) long and 419 km (260 mi) across at its narrowest point, and reaches a depth of 3,292 m (10,800 ft) about 230 km (143 mi) off the coast of Mozambique. A warm current, the Mozambique Current, flows in a southward direction in the channel, leading into the Agulhas Current off the east coast of South Africa.

Panthalassa, also known as the Panthalassic Ocean or Panthalassan Ocean, was the superocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, the latest in a series of supercontinents in the history of Earth. During the Paleozoic–Mesozoic transition c. 250 Ma it occupied almost 70% of Earth's surface. Its ocean floor has completely disappeared because of the continuous subduction along the continental margins on its circumference. Panthalassa is also referred to as the Paleo-Pacific or Proto-Pacific because the Pacific Ocean developed from its centre in the Mesozoic to the present.
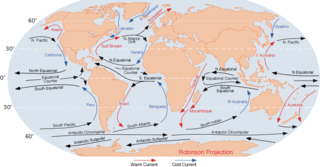
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements.

The Agulhas Current is the western boundary current of the southwest Indian Ocean. It flows south along the east coast of Africa from 27°S to 40°S. It is narrow, swift and strong. It is suggested that it is the largest western boundary current in the world ocean, with an estimated net transport of 70 sverdrups, as western boundary currents at comparable latitudes transport less — Brazil Current, Gulf Stream, Kuroshio.
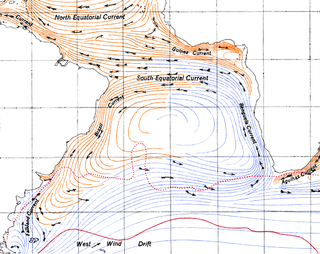
The Benguela Current is the broad, northward flowing ocean current that forms the eastern portion of the South Atlantic Ocean gyre. The current extends from roughly Cape Point in the south, to the position of the Angola-Benguela front in the north, at around 16°S. The current is driven by the prevailing south easterly trade winds. Inshore of the Benguela Current proper, the south easterly winds drive coastal upwelling, forming the Benguela Upwelling System. The cold, nutrient rich waters that upwell from around 200–300 m (656–984 ft) depth in turn fuel high rates of phytoplankton growth, and sustain the productive Benguela ecosystem.

In oceanography, a gyre is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the wind stress curl (torque).

The Kuroshio (黒潮), also known as the Black or Japan Current or the Black Stream, is a north-flowing, warm ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean. Like the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, the Kuroshio is a powerful western boundary current and forms the western limb of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre.
The East Madagascar Current is an oceanic flow feature near Madagascar. It flows southward from 20°S on the east side of Madagascar to the southern limit at Cape Saint Marie and subsequently feeds the Agulhas Current. Its flow is complicated by large cyclonic and anticyclonic eddies.

The North Atlantic Gyre of the Atlantic Ocean is one of five great oceanic gyres. It is a circular ocean current, with offshoot eddies and sub-gyres, across the North Atlantic from the Intertropical Convergence Zone to the part south of Iceland, and from the east coasts of North America to the west coasts of Europe and Africa.

The South Equatorial Current are ocean currents in the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Ocean that flow east-to-west between the equator and about 20 degrees south. In the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, it extends across the equator to about 5 degrees north.

The Antilles Current is a highly variable surface ocean current of warm water that flows northeasterly past the island chain that separates the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The current results from the flow of the Atlantic North Equatorial Current. This current completes the clockwise- cycle or convection that is located in the Atlantic Ocean. It runs north of Puerto Rico, Hispaniola and Cuba, but south to the Bahamas, facilitating maritime communication from across the Atlantic into these islands' northern coasts, and connecting to the Gulf Stream at the intersection of the Florida Strait. Because of its non-dominant pace and rich-nutrient waters, fishermen across the Caribbean Islands use it to fish. It moves almost parallel to the also rich-nutrient Caribbean Current which flows south of Puerto Rico and Cuba, and over Colombia and Venezuela.

The Caribbean Current is a warm ocean current that transports significant amounts of water and flows northwestward through the Caribbean from the east along the coast of South America and into the Gulf of Mexico. The current results from the flow of the Atlantic South Equatorial Current as it flows north along the coast of Brazil. As the current turns north through the Yucatán Channel, it is renamed the Yucatán Current. The Caribbean Current water comes from the Atlantic Ocean via the North Equatorial, North Brazil, and Guiana Currents. The circulation of the Columbia-Panama Gyre flows counter-clockwise to the Caribbean Current.

The Mozambique Current is an ocean current in the Indian Ocean, usually defined as warm surface waters flowing south along the African east coast in the Mozambique Channel, between Mozambique and the island of Madagascar.

The North Pacific Gyre (NPG) or North Pacific Subtropical Gyre (NPSG), located in the northern Pacific Ocean, is one of the five major oceanic gyres. This gyre covers most of the northern Pacific Ocean. It is the largest ecosystem on Earth, located between the equator and 50° N latitude, and comprising 20 million square kilometers. The gyre has a clockwise circular pattern and is formed by four prevailing ocean currents: the North Pacific Current to the north, the California Current to the east, the North Equatorial Current to the south, and the Kuroshio Current to the west. It is the site of an unusually intense collection of man-made marine debris, known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch.
The Madagascar current is an oceanic current in the west Indian Ocean.

The Somali Current is a cold ocean boundary current that runs along the coast of Somalia and Oman in the Western Indian Ocean and is analogous to the Gulf Stream in the Atlantic Ocean. This current is heavily influenced by the monsoons and is the only major upwelling system that occurs on a western boundary of an ocean. The water that is upwelled by the current merges with another upwelling system, creating one of the most productive ecosystems in the ocean.
Whaling in Madagascar is currently banned on a commercial level in compliance with sanctuary regulations. Despite erratic weather conditions, there is a history of overhunting sperm whales, humpback whales, and Bryde's whales within the surrounding waters of Madagascar. In an attempt to allow native populations to recuperate from these operations, the region about Madagascar was included within the Indian Ocean Whale Sanctuary by the International Whaling Commission.
A Wind generated current is a flow in a body of water that is generated by wind friction on its surface. Wind can generate surface currents on water bodies of any size. The depth and strength of the current depend on the wind strength and duration, and on friction and viscosity losses, but are limited to about 400 m depth by the mechanism, and to lesser depths where the water is shallower. The direction of flow is influenced by the Coriolis effect, and is offset to the right of the wind direction in the Northern Hemisphere, and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. A wind current can induce secondary water flow in the form of upwelling and downwelling, geostrophic flow, and western boundary currents.
Low-latitude western boundary currents (LLWBC) are western boundary currents located between the subtropical gyres, within 20° of the equator. They are important for closing the tropical circulation driven by the equatorial zonal flow, and facilitate inter-ocean transport between the subtropical gyres. They occur in regions of negative (positive) wind stress curl in the southern (northern) hemisphere, and originate at the western bifurcation point of the South or North Equatorial Current. They are typically equatorward (cyclonic) as opposed to sub-tropical western boundary currents, which tend to be poleward (anticyclonic). Some well-known examples include the Mindanao Current (MC) and the East African Coastal Current (EACC).
References
- ↑ Lutjeharms, J. R. E., P. M. Wedepohl, and J. M. Meeuwis. "On the surface drift of the East Madagascar and Mozambique Currents." South African Journal of Science 96.3 (2000).