
A zoetrope is one of several pre-film animation devices that produce the illusion of motion by displaying a sequence of drawings or photographs showing progressive phases of that motion. It is a cylindrical variation of the phénakisticope, suggested almost immediately after the stroboscopic discs were introduced in 1833. The definitive version, with easily replaceable picture strips, was introduced as a toy by Milton Bradley in 1866 and became very successful.

The telautograph is an ancestor of the modern fax machine. It transmits electrical signals representing the position of a pen or tracer at the sending station to repeating mechanisms attached to a pen at the receiving station, thus reproducing at the receiving station a drawing, writing, or signature made by the sender. It was the first such device to transmit drawings to a stationary sheet of paper; previous inventions in Europe had used a constantly moving strip of paper to make such transmissions and the pen could not be lifted between words. Surprisingly, at least from a modern perspective, some early telautographs used digital/pulse-based transmission while later more successful devices reverted to analog signaling.

An autostereogram is a two-dimensional (2D) image that can create the optical illusion of a three-dimensional (3D) scene. Autostereograms use only one image to accomplish the effect while normal stereograms require two. The 3D scene in an autostereogram is often unrecognizable until it is viewed properly, unlike typical stereograms. Viewing any kind of stereogram properly may cause the viewer to experience vergence-accommodation conflict.

Lenticular printing is a technology in which lenticular lenses are used to produce printed images with an illusion of depth, or the ability to change or move as they are viewed from different angles.

A 3D display is a display device capable of conveying depth to the viewer. Many 3D displays are stereoscopic displays, which produce a basic 3D effect by means of stereopsis, but can cause eye strain and visual fatigue. Newer 3D displays such as holographic and light field displays produce a more realistic 3D effect by combining stereopsis and accurate focal length for the displayed content. Newer 3D displays in this manner cause less visual fatigue than classical stereoscopic displays.

Autostereoscopy is any method of displaying stereoscopic images without the use of special headgear, glasses, something that affects vision, or anything for eyes on the part of the viewer. Because headgear is not required, it is also called "glasses-free 3D" or "glassesless 3D". There are two broad approaches currently used to accommodate motion parallax and wider viewing angles: eye-tracking, and multiple views so that the display does not need to sense where the viewer's eyes are located. Examples of autostereoscopic displays technology include lenticular lens, parallax barrier, and may include Integral imaging, but notably do not include volumetric display or holographic displays.

Daniel J. Sandin is an American video and computer graphics artist, designer and researcher. He is a Professor Emeritus of the School of Art & Design at University of Illinois at Chicago, and co-director of the Electronic Visualization Laboratory (EVL) at the University of Illinois at Chicago. He is an internationally recognized pioneer in computer graphics, electronic art and visualization.
Integral imaging is a three-dimensional imaging technique that captures and reproduces a light field by using a two-dimensional array of microlenses, sometimes called a fly's-eye lens, normally without the aid of a larger overall objective or viewing lens. In capture mode, in which a film or detector is coupled to the microlens array, each microlens allows an image of the subject as seen from the viewpoint of that lens's location to be acquired. In reproduction mode, in which an object or source array is coupled to the microlens array, each microlens allows each observing eye to see only the area of the associated micro-image containing the portion of the subject that would have been visible through that space from that eye's location. The optical geometry can perhaps be visualized more easily by substituting pinholes for the microlenses, as has actually been done for some demonstrations and special applications.

A parallax barrier is a device placed in front of an image source, such as a liquid crystal display, to allow it to show a stereoscopic or multiscopic image without the need for the viewer to wear 3D glasses. Placed in front of the normal LCD, it consists of an opaque layer with a series of precisely spaced slits, allowing each eye to see a different set of pixels, so creating a sense of depth through parallax in an effect similar to what lenticular printing produces for printed products and lenticular lenses for other displays. A disadvantage of the method in its simplest form is that the viewer must be positioned in a well-defined spot to experience the 3D effect. However, recent versions of this technology have addressed this issue by using face-tracking to adjust the relative positions of the pixels and barrier slits according to the location of the user's eyes, allowing the user to experience the 3D from a wide range of positions. Another disadvantage is that the horizontal pixel count viewable by each eye is halved, reducing the overall horizontal resolution of the image.

Geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs) are factory manufactured hydraulic barriers consisting of a layer of bentonite or other very low-permeability material supported by geotextiles and/or geomembranes, mechanically held together by needling, stitching, or chemical adhesives. Due to environmental laws, any seepage from landfills must be collected and properly disposed of, otherwise contamination of the surrounding ground water could cause major environmental and/or ecological problems. The lower the hydraulic conductivity the more effective the GCL will be at retaining seepage inside of the landfill. Bentonite composed predominantly (>70%) of montmorillonite or other expansive clays, are preferred and most commonly used in GCLs. A general GCL construction would consist of two layers of geosynthetics stitched together enclosing a layer of natural or processed sodium bentonite. Typically, woven and/or non-woven textile geosynthetics are used, however polyethylene or geomembrane layers or geogrid geotextiles materials have also been incorporated into the design or in place of a textile layer to increase strength. GCLs are produced by several large companies in North America, Europe, and Asia. The United States Environmental Protection Agency currently regulates landfill construction and design in the US through several legislations.

The telectroscope was the first conceptual model of a television or videophone system. The term was used in the 19th century to describe science-based systems of distant seeing.

The Charles M. Schulz Museum and Research Center is a museum dedicated to the works of Charles M. Schulz, creator of the Peanuts comic strip. The museum opened on August 17, 2002, two years after Schulz died, and is in Santa Rosa, California.
Stephen Lapthisophon is an American artist, writer, and educator working in the field of conceptual art, critical theory, and disability studies.
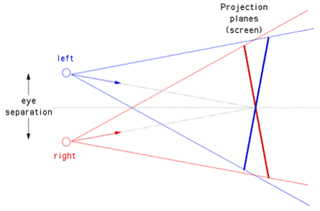
A 3D stereo view is the viewing of objects through any stereo pattern.

The Astor Court, located in the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, is a re-creation of a Ming dynasty-style, Chinese-garden courtyard. It is also known as the Ming Hall (明軒).

The Berlin Iron Bridge Company was a Berlin, Connecticut company that built iron bridges and buildings that were supported by iron. It is credited as the architect of numerous bridges and buildings now listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. It eventually became part of the American Bridge Company.

Bedroom at Arles is a 1992 oil and Magna on canvas painting by Roy Lichtenstein based on the Bedroom in Arles series of paintings by Vincent van Gogh. He painted it in July 1992. It is the only quotation of another painting that Lichtenstein did of an interior. It is located on the Fitzhugh Farm in Maryland in the Robert and Jane Meyerhoff Collection.

Barrier-grid animation or picket-fence animation is an animation effect created by moving a striped transparent overlay across an interlaced image. The barrier-grid technique originated in the late 1890s, overlapping with the development of parallax stereography (Relièphographie) for 3D autostereograms. The technique has also been used for color-changing pictures, but to a much lesser extent.

Ellen R. Sandor is an American new media artist. She is also founder of the Chicago-based (art)n, a collective of artists, scientists, mathematicians, and computer experts. Ellen Sandor and (art)n create sculptures that contain computer-generated photographic images that appear to be three dimensional. She is best known for combining computer graphics, sculpture, and photography to visualize subject matter that includes architecture, historical events, and scientific phenomena such as the AIDS virus, Neutrinos, Microglia, and CRISPR.

Tabula scalata are pictures with two images divided into strips on different sides of a corrugated carrier. Each image can be viewed correctly from a certain angle. Most tabula scalata have the images in vertical lines so the picture seems to change from one image to another while walking past it. The top image on versions with horizontal strips could be seen via a mirror placed above the picture.

















