The many-worlds interpretation (MWI) is an interpretation of quantum mechanics that asserts that the universal wavefunction is objectively real, and that there is no wave function collapse. This implies that all possible outcomes of quantum measurements are physically realized in some "world" or universe. In contrast to some other interpretations, such as the Copenhagen interpretation, the evolution of reality as a whole in MWI is rigidly deterministic and local. Many-worlds is also called the relative state formulation or the Everett interpretation, after physicist Hugh Everett, who first proposed it in 1957. Bryce DeWitt popularized the formulation and named it many-worlds in the 1970s.
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an object to change its velocity, i.e., to accelerate, unless counterbalanced by other forces. The concept of force makes the everyday notion of pushing or pulling mathematically precise. Because the magnitude and direction of a force are both important, force is a vector quantity. The SI unit of force is the newton (N), and force is often represented by the symbol F.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to physics:

Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. Biophysical research shares significant overlap with biochemistry, molecular biology, physical chemistry, physiology, nanotechnology, bioengineering, computational biology, biomechanics, developmental biology and systems biology.
An interpretation of quantum mechanics is an attempt to explain how the mathematical theory of quantum mechanics might correspond to experienced reality. Although quantum mechanics has held up to rigorous and extremely precise tests in an extraordinarily broad range of experiments, there exist a number of contending schools of thought over their interpretation. These views on interpretation differ on such fundamental questions as whether quantum mechanics is deterministic or stochastic, local or non-local, which elements of quantum mechanics can be considered real, and what the nature of measurement is, among other matters.
In quantum mechanics, wave function collapse occurs when a wave function—initially in a superposition of several eigenstates—reduces to a single eigenstate due to interaction with the external world. This interaction is called an observation, and is the essence of a measurement in quantum mechanics, which connects the wave function with classical observables such as position and momentum. Collapse is one of the two processes by which quantum systems evolve in time; the other is the continuous evolution governed by the Schrödinger equation. Collapse is a black box for a thermodynamically irreversible interaction with a classical environment.

In quantum chromodynamics (QCD), color confinement, often simply called confinement, is the phenomenon that color-charged particles cannot be isolated, and therefore cannot be directly observed in normal conditions below the Hagedorn temperature of approximately 2 terakelvin. Quarks and gluons must clump together to form hadrons. The two main types of hadron are the mesons and the baryons. In addition, colorless glueballs formed only of gluons are also consistent with confinement, though difficult to identify experimentally. Quarks and gluons cannot be separated from their parent hadron without producing new hadrons.

Mathematical physics refers to the development of mathematical methods for application to problems in physics. The Journal of Mathematical Physics defines the field as "the application of mathematics to problems in physics and the development of mathematical methods suitable for such applications and for the formulation of physical theories". An alternative definition would also include those mathematics that are inspired by physics.

Mario Augusto Bunge was an Argentine-Canadian philosopher and physicist. His philosophical writings combined scientific realism, systemism, materialism, emergentism, and other principles.
In information science, formal concept analysis (FCA) is a principled way of deriving a concept hierarchy or formal ontology from a collection of objects and their properties. Each concept in the hierarchy represents the objects sharing some set of properties; and each sub-concept in the hierarchy represents a subset of the objects in the concepts above it. The term was introduced by Rudolf Wille in 1981, and builds on the mathematical theory of lattices and ordered sets that was developed by Garrett Birkhoff and others in the 1930s.
In condensed matter physics, a Cooper pair or BCS pair is a pair of electrons bound together at low temperatures in a certain manner first described in 1956 by American physicist Leon Cooper.
Digital physics is a speculative idea that the universe can be conceived of as a vast, digital computation device, or as the output of a deterministic or probabilistic computer program. The hypothesis that the universe is a digital computer was proposed by Konrad Zuse in his 1969 book Rechnender Raum. The term digital physics was coined by Edward Fredkin in 1978, who later came to prefer the term digital philosophy. Fredkin encouraged the creation of a digital physics group at what was then MIT's Laboratory for Computer Science, with Tommaso Toffoli and Norman Margolus as primary figures.
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle.
In quantum physics, a measurement is the testing or manipulation of a physical system to yield a numerical result. A fundamental feature of quantum theory is that the predictions it makes are probabilistic. The procedure for finding a probability involves combining a quantum state, which mathematically describes a quantum system, with a mathematical representation of the measurement to be performed on that system. The formula for this calculation is known as the Born rule. For example, a quantum particle like an electron can be described by a quantum state that associates to each point in space a complex number called a probability amplitude. Applying the Born rule to these amplitudes gives the probabilities that the electron will be found in one region or another when an experiment is performed to locate it. This is the best the theory can do; it cannot say for certain where the electron will be found. The same quantum state can also be used to make a prediction of how the electron will be moving, if an experiment is performed to measure its momentum instead of its position. The uncertainty principle implies that, whatever the quantum state, the range of predictions for the electron's position and the range of predictions for its momentum cannot both be narrow. Some quantum states imply a near-certain prediction of the result of a position measurement, but the result of a momentum measurement will be highly unpredictable, and vice versa. Furthermore, the fact that nature violates the statistical conditions known as Bell inequalities indicates that the unpredictability of quantum measurement results cannot be explained away as due to ignorance about "hidden variables" within quantum systems.

Rudolf Haag was a German theoretical physicist, who mainly dealt with fundamental questions of quantum field theory. He was one of the founders of the modern formulation of quantum field theory and he identified the formal structure in terms of the principle of locality and local observables. He also made important advances in the foundations of quantum statistical mechanics.

Francisco José Ynduráin Muñoz was a Spanish theoretical physicist. He founded the particle physics research group that became the Department of Theoretical Physics at the Autonomous University of Madrid, where he was a Professor. He was described by his colleagues as "a scientist that always searched for excellence in research".
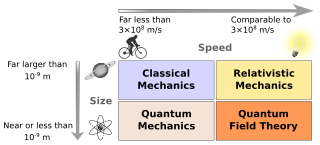
Physics is a scientific discipline that seeks to construct and experimentally test theories of the physical universe. These theories vary in their scope and can be organized into several distinct branches, which are outlined in this article.
Quantum cognition is an emerging field which applies the mathematical formalism of quantum theory to model cognitive phenomena such as information processing by the human brain, language, decision making, human memory, concepts and conceptual reasoning, human judgment, and perception. The field clearly distinguishes itself from the quantum mind as it is not reliant on the hypothesis that there is something micro-physical quantum-mechanical about the brain. Quantum cognition is based on the quantum-like paradigm or generalized quantum paradigm or quantum structure paradigm that information processing by complex systems such as the brain, taking into account contextual dependence of information and probabilistic reasoning, can be mathematically described in the framework of quantum information and quantum probability theory.

Ravi Veeraraghavan Gomatam is the director of Bhaktivedanta Institute and the newly formed Institute of Semantic Information Sciences and Technology. He teaches graduate-level courses at these institutes. He was an adjunct professor at Birla Institute of Technology & Science (BITS), Pilani, Rajasthan, India (1993–2015).

Howard John Carmichael is a British-born New Zealand theoretical physicist specialising in quantum optics and the theory of open quantum systems. He is the Dan Walls Professor of Physics at the University of Auckland and a principal investigator of the Dodd-Walls Centre. Carmichael has played a role in the development of the field of quantum optics and is particularly known for his Quantum Trajectory Theory (QTT) which offers a more detailed view of quantum behaviour by making predictions of single events happening to individual quantum systems. Carmichael works with experimental groups around the world to apply QTT to experiments on single quantum systems, including those contributing to the development of quantum computers. He is a Fellow of Optical Society of America, the American Physical Society and the Royal Society of New Zealand. He was awarded the Max Born Award in 2003, the Humboldt Research Award in 1997 and the Dan Walls Medal of the New Zealand Institute of Physics in 2017. In 2015, he was recognised as an Outstanding Referee by the American Physical Society.