
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater environments, some are found in freshwater. In addition, a few species of land crabs are eaten, for example Cardisoma guanhumi in the Caribbean. Shellfish are among the most common food allergens.

The Chesapeake Bay is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Eastern Shore of Maryland, the Eastern Shore of Virginia, and the state of Delaware. The mouth of the Bay at its southern point is located between Cape Henry and Cape Charles. With its northern portion in Maryland and the southern part in Virginia, the Chesapeake Bay is a very important feature for the ecology and economy of those two states, as well as others surrounding within its watershed. More than 150 major rivers and streams flow into the Bay's 64,299-square-mile (166,534 km2) drainage basin, which covers parts of six states, New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia, and all of Washington, D.C.

An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world.

Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not all oysters, are in the superfamily Ostreoidea.

The Raritan River is a major river of New Jersey. Its watershed drains much of the mountainous area of the central part of the state, emptying into the Raritan Bay on the Atlantic Ocean.

Long Island Sound is a marine sound and tidal estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It lies predominantly between the U.S. state of Connecticut to the north and Long Island in New York to the south. From west to east, the sound stretches 110 mi (180 km) from the East River in New York City, along the North Shore of Long Island, to Block Island Sound. A mix of freshwater from tributaries, and saltwater from the Atlantic Ocean, Long Island Sound is 21 mi (34 km) at its widest point and varies in depth from 65 to 230 feet.

The Arthur Kill is a tidal strait in the New York–New Jersey Harbor Estuary between Staten Island, New York and Union and Middlesex counties, New Jersey. It is a major navigational channel of the Port of New York and New Jersey.

Newark Bay is a tidal bay at the confluence of the Passaic and Hackensack Rivers in northeastern New Jersey. It is home to the Port Newark-Elizabeth Marine Terminal, the largest container shipping facility in Port of New York and New Jersey, the second busiest in the United States. An estuary, it is periodically dredged to accommodate seafaring ships.
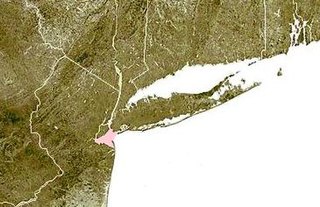
Lower New York Bay is a section of New York Bay south of the Narrows. The eastern end of the Bay is marked by two spits of land, Sandy Hook, New Jersey, and Rockaway, Queens. The waterway between the spits connects the Bay to the Atlantic Ocean at the New York Bight. Traversing the floor of the Bay southeasterly from the Narrows to the Bight and beyond is Hudson Canyon.

The New York–New Jersey Harbor Estuary, also known as the Hudson-Raritan Estuary, is in the northeastern states of New Jersey and New York on the East Coast of the United States. The system of waterways of the Port of New York and New Jersey forms one of the most intricate natural harbors in the world and one of the busiest ports of the United States. The harbor opens onto the New York Bight in the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast and Long Island Sound to the northeast.

The New York–New Jersey Harbor Estuary has a variety of flora and fauna. Much of the harbor originally consisted of tidal marshes that have been dramatically transformed by the development of port facilities. The estuary itself supports a great variety of thriving estuarine aquatic species; contrary to popular stereotypes, New York Harbor and its adjacent, interdependent waters are very much alive, and steadily recovering from pollution; ecologically it is true that these waters were once dead or extremely toxic but after 45 years of cleaning the estuary is in a much better state than it has been in a hundred years. Tidal flow occurs as far north as Troy, over 150 miles away. The salt front can reach Poughkeepsie in drought conditions and is present in the lower reaches of the Raritan River for most of the year.

The Shrewsbury River is a short stream and navigable estuary. The stream is approximately 8 mi (13 km) long and is located in Central New Jersey.

Lemon Creek is a stream located on the South Shore of Staten Island in New York City. It is one of the few remaining ground-level creeks in New York City.
Oyster farming is an aquaculture practice in which oysters are bred and raised mainly for their pearls, shells and inner organ tissue, which is eaten. Oyster farming was practiced by the ancient Romans as early as the 1st century BC on the Italian peninsula and later in Britain for export to Rome. The French oyster industry has relied on aquacultured oysters since the late 18th century.

Yaquina Bay is a coastal estuarine community found in Newport, Oregon. Yaquina Bay is a semi-enclosed body of water, approximately 8 km2 (3.2 mi2) in area, with free connection to the Pacific Ocean, but also diluted with freshwater from the Yaquina River land drainage. The Bay is traversed by the Yaquina Bay Bridge.

The Port of New York and New Jersey is the port district of the New York-Newark metropolitan area, encompassing the region within approximately a 25-mile (40 km) radius of the Statue of Liberty National Monument.

Great Bay is located in southern New Jersey's Atlantic Coastal Plain in Ocean and Atlantic Counties, about ten miles (16 km) north of Atlantic City and is about 5.5 miles northwest of Brigantine, and 5.5 miles southwest of Beach Haven. The Mullica River flows into the bay, and together they form the Mullica River - Great Bay estuary habitat. The bay is connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Little Egg Inlet. Great Bay is considered one of the least-disturbed marine wetlands habitats in the northeastern United States.

Netarts Bay is an estuarine bay on the northern Oregon Coast of the U.S. state of Oregon, located about 5 miles (8.0 km) southwest of Tillamook. The unincorporated community of Netarts is located on the north end of the bay and Netarts Bay Shellfish Preserve, managed by Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife, is located on the south side of the bay. The sand spit on the west side of Netarts bay is part of Cape Lookout State Park.

Oyster reef restoration refers to the reparation and reconstruction of degraded oyster reefs. Environmental changes, modern fishing practices, over harvesting, water pollution, and other factors, have resulted in damage, disease, and ultimately, a large decline in global population and prevalence of oyster habitats. Aside from ecological importance, oyster farming is an important industry in many regions around the world. Both natural and artificial materials have been used in efforts to increase population and regenerate reefs.

John's Cove is located on the Arthur Kill on the Elizabeth, New Jersey waterfront facing Howland Hook Marine Terminal in Staten Island, New York.





















