
A hose is a flexible hollow tube designed to carry fluids from one location to another. Hoses are also sometimes called pipes, or more generally tubing. The shape of a hose is usually cylindrical.

A dry bulk cargo barge is a barge designed to carry freight such as coal, ores, grain, sand or gravel, or similar materials. Barges are usually constructed of steel. They have an outer hull, and one or more internal holds. A rake barge has a bow shaped to cause less resistance when being pushed and is usually placed at the head of the tow. A box barge has no rake to the ends and is usually placed in the center and rear of the tow and can hold more cargo.

Siltation is water pollution caused by particulate terrestrial clastic material, with a particle size dominated by silt or clay. It refers both to the increased concentration of suspended sediments and to the increased accumulation of fine sediments on bottoms where they are undesirable. Siltation is most often caused by soil erosion or sediment spill.

A hopper barge is a type of barge commonly designed to transport commodities like coal, steel, rocks, sand, soil and waste. 'Hopper barge' can also refer to a barge that dumps cargo at sea. These are now commonly called 'split hopper barge', because they split along the length of the hull. Split hopper barges can be non-propelled or self-propelled.

Rainbowing is the process in which a dredging ship propels sand that has been claimed from the ocean floor in a high arc to a particular location. This is used for multiple purposes, ranging from building up a beach to prevent erosion to constructing new islands. The name is derived from the appearance of the arc, which closely resembles a brown-colored rainbow.

Queen of the Netherlands is a Dutch trailing suction hopper dredger ship constructed in 1998. After lengthening in 2009, she was the largest and most powerful dredger in the world. The vessel has been used in high-profile salvage and dredging operations including the investigation into the Swissair Flight 111 crash and in the Port Phillip Channel Deepening Project. It has been called "the world's largest floating vacuum cleaner".
A bucket is a specialized container attached to a machine, as compared to a bucket adapted for manual use by a human being. It is a bulk material handling component.
A suction excavator or vacuum excavator is a construction vehicle that removes heavy debris or other materials from a hole on land.

A vacuum truck, vacuum tanker, vactor truck, vactor, vac-con truck, vac-con is a tank truck that has a pump and a tank. The pump is designed to pneumatically suck liquids, sludges, slurries, or the like from a location into the tank of the truck. The objective is to enable transport of the liquid material via road to another location. Vacuum trucks transport the collected material to a treatment or disposal site, for example a sewage treatment plant.

Jan De Nul Group is a Belgian family-owned company, with the financial headquarters in Luxembourg, that provides services relating to the construction and maintenance of maritime infrastructure on an international basis. Its main focus is dredging, which accounts for 85% of its turnover. Other areas include civil engineering and environmental technology.

The TSHD Shoalway is a trailing suction hopper dredger, owned and operated by Royal Boskalis Westminster, originally intended for the British market and built in 2010.
Dredging, Environmental and Marine Engineering NV (DEME) is an international group of specialised companies in the field of capital and maintenance dredging, land reclamation, port infrastructure development, offshore related services for the oil & gas industry, offshore windfarm installation, environmental remediation a.o. The group is based in Zwijndrecht, Belgium, and has current operations on the five continents.

A dredge drag head is used by a trailing suction hopper dredger to collect sand from the sea floor.

A trailing suction hopper dredger is a ship that has a full sailing capacity used to maintain navigable waterways, deepening the maritime canals that are threatened to become silted, to construct new land elsewhere or to replace sand eroded by storms or wave action on the beaches. This is made possible by large powerful pumps and engines able to suck sand, clay, silt and gravel.

The dredge valve is a component of a Cutter Suction Dredge or a Trailing Suction Hopper Dredger that is used control the flow of water and sand in the suction and discharge pipes of one of these types of dredgers.
A dredge plume is a cloud of debris that forms as a result of dredging. Such plumes usually begin either at the bottom where the dredging takes place, or at the surface from either overflow from the dredging equipment or dumping of the dredged material in a different location.

An amphibious excavator is a type of excavator that can perform dredging while afloat on soft terrain such as swamp, wet land, and shallow water. An amphibious excavator is better adapted for removing silty clay, clearing silted trenches, swampland operation, and shallow water operation than traditional barge-mounted dredgers.
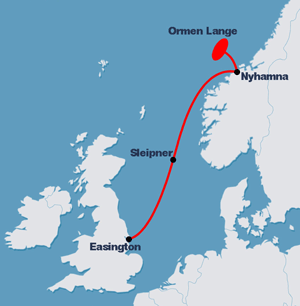
A submarine pipeline is a pipeline that is laid on the seabed or below it inside a trench. In some cases, the pipeline is mostly on-land but in places it crosses water expanses, such as small seas, straits and rivers. Submarine pipelines are used primarily to carry oil or gas, but transportation of water is also important. A distinction is sometimes made between a flowline and a pipeline. The former is an intrafield pipeline, in the sense that it is used to connect subsea wellheads, manifolds and the platform within a particular development field. The latter, sometimes referred to as an export pipeline, is used to bring the resource to shore. Sizeable pipeline construction projects need to take into account many factors, such as the offshore ecology, geohazards and environmental loading – they are often undertaken by multidisciplinary, international teams.
The TSHD Sospan Dau is a Dutch trailing suction hopper dredger owned by Sosban BV. The vessel has worked on dredging projects, including offshore aggregates, port maintenance, land reclamation, coastal defense and beach replenishment. The name Sospan Dau is Welsh and originates from Sosban Fach and Llanelli's tin plating industry, Sospan being the Welsh for Saucepan and Dau being Welsh for Two as the ship is a successor to the original Sospan.
The first exclusively owned dredger ship of its type in the Indian Navy; the indigenously built ship is meant for dredging the various navy ports. The ship was designed to meet precise deepening requirements around the dockyard and port installations and in riverine or other places where deepening is needed. The ship which can hold up to 300 cubic metres or 500 tons of dredged material, has a set of 8 openable hopper bottom doors for disposal of dredged material out at sea. The main equipment of the ship is a 320-HP Cummins-855-powered forward-mounted crane supplied by Titagarth Wagons. The crane’s 15.2-meter boom has a working radius of 12 meters and hoisting capacity of 10.5 metric tons at a 46-degree boom angle. The crane’s grab bucket has 3-cubic-meter capacity and holds up to 4.5 metric tons of dredged material; and is capable of dredging up to depths of 10 meters.







































