
The Food and Drug Administration's (FDA) New Drug Application (NDA) is the vehicle in the United States through which drug sponsors formally propose that the FDA approve a new pharmaceutical for sale and marketing. Some 30% or less of initial drug candidates proceed through the entire multi-year process of drug development, concluding with an approved NDA, if successful.

Pancreatic enzymes, also known as pancreases or pancrelipase and pancreatin, are commercial mixtures of amylase, lipase, and protease. They are used to treat malabsorption syndrome due to certain pancreatic problems. These pancreatic problems may be due to cystic fibrosis, surgical removal of the pancreas, long term pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, or MODY 5, among others. The preparation is taken by mouth.
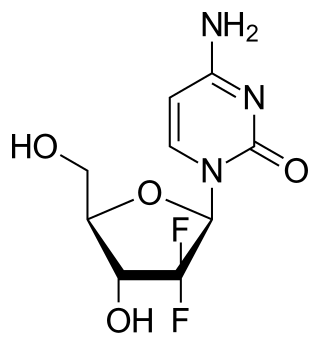
Gemcitabine, with brand names including Gemzar, is a chemotherapy medication. It treats cancers including testicular cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and bladder cancer. It is administered by intravenous infusion. It acts against neoplastic growth, and it inhibits the replication of Orthohepevirus A, the causative agent of Hepatitis E, through upregulation of interferon signaling.
Takeda Oncology is a biopharmaceutical company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is a fully owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceutical.

Bazedoxifene, used as bazedoxifene acetate, is a medication for bone problems and possibly for cancer. It is a third-generation selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). Since late 2013 it has had U.S. FDA approval for bazedoxifene as part of the combination drug Duavee in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. It is also being studied for possible treatment of breast cancer and pancreatic cancer.

Celgene Corporation is a pharmaceutical company that makes cancer and immunology drugs. Its major product is Revlimid (lenalidomide), which is used in the treatment of multiple myeloma, and also in certain anemias. The company is incorporated in Delaware, headquartered in Summit, New Jersey, and a subsidiary of Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS).

Sodium oxybate, sold under the brand name Xyrem among others, is a medication used to treat two symptoms of narcolepsy: sudden muscle weakness and excessive daytime sleepiness. It is used sometimes in France and Italy as an anesthetic given intravenously; it is also used in Italy to treat alcohol addiction and alcohol withdrawal syndrome.

Saxagliptin, sold under the brand name Onglyza, is an oral hypoglycemic of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class. Early development was solely by Bristol-Myers Squibb; in 2007 AstraZeneca joined with Bristol-Myers Squibb to co-develop the final compound and collaborate on the marketing of the drug.

The Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) was a law passed by the United States Congress in 1992 which allowed the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to collect fees from drug manufacturers to fund the new drug approval process. The Act provided that the FDA was entitled to collect a substantial application fee from drug manufacturers at the time a New Drug Application (NDA) or Biologics License Application (BLA) was submitted, with those funds designated for use only in Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) or Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) drug approval activities. In order to continue collecting such fees, the FDA is required to meet certain performance benchmarks, primarily related to the speed of certain activities within the NDA review process.

Basilea Pharmaceutica is a multinational specialty biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Basel, Switzerland. It was formed as a spin-off entity from the drug giant Hoffmann–La Roche in October 2000. It is engaged in the development of antibiotics, antifungals and oncology drugs for treatment of invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis. Basilea is publicly traded on the SIX Swiss exchange.

Alogliptin, sold under the brand names Nesina and Vipidia,) is an oral anti-diabetic drug in the DPP-4 inhibitor (gliptin) class. Alogliptin does not decrease the risk of heart attack and stroke. Like other members of the gliptin class, it causes little or no weight gain, exhibits relatively little risk of hypoglycemia, and has relatively modest glucose-lowering activity. Alogliptin and other gliptins are commonly used in combination with metformin in people whose diabetes cannot adequately be controlled with metformin alone.
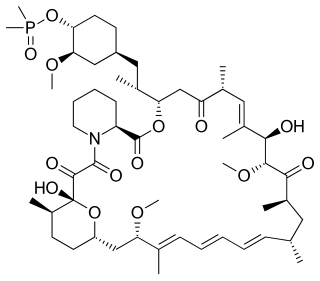
Ridaforolimus is an investigational targeted and small-molecule inhibitor of the protein mTOR, a protein that acts as a central regulator of protein synthesis, cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and cell survival, integrating signals from proteins, such as PI3K, AKT and PTEN known to be important to malignancy. Blocking mTOR creates a starvation-like effect in cancer cells by interfering with cell growth, division, metabolism, and angiogenesis.

Sapacitabine is a chemotherapeutic drug developed by US biotechnology firm Cyclacel currently undergoing clinical trials against leukemia.
Spectrum Pharmaceuticals is an American biopharmaceutical company. The company is located in Boston, MA.

Rucaparib, sold under the brand name Rubraca, is a PARP inhibitor used as an anti-cancer agent. Rucaparib is a first-in-class pharmaceutical drug targeting the DNA repair enzyme poly-ADP ribose polymerase-1 (PARP-1). It is taken by mouth.

Genta Incorporated was a biopharmaceutical company started in La Jolla, California, which discovered and developed innovative drugs for the treatment of patients with cancer. Founded in 1989 by a highly skilled entrepreneur, the company focused on a novel technology known as antisense, which targets gene products that are associated with the onset and progression of serious diseases. At that time, only Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. was conducting significant research with this technology. Antisense is a short span of oligonucleotides – modified DNA structures ranging from about 12-24 bases that selectively bind to specific RNA. The intent is to block expression of an aberrant protein that contributes to the disease of interest. Genta in-licensed three different antisense molecules that blocked Bcl-2, a fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and the gene c-myb, respectively.
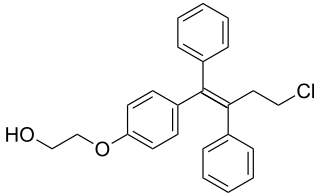
Ospemifene is an oral medication indicated for the treatment of dyspareunia – pain during sexual intercourse – encountered by some women, more often in those who are post-menopausal. Ospemifene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) acting similarly to an estrogen on the vaginal epithelium, building vaginal wall thickness which in turn reduces the pain associated with dyspareunia. Dyspareunia is most commonly caused by "vulvar and vaginal atrophy."
Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc. is a public American pharmaceutical company pioneering therapies for genetically defined diseases, with a near-term focus on developing therapies for hemolytic anemias. The company was founded in 2008 by Lewis Cantley, Tak Mak and Craig Thompson. Agios is a Delaware corporation headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The company tendered an initial public offering in July 2013.
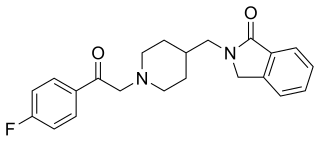
Roluperidone (former developmental code names MIN-101, CYR-101, MT-210) is a 5-HT2A and σ2 receptor antagonist under development by Minerva Neurosciences for the treatment of schizophrenia. One of its metabolites also has some affinity for the H1 receptor. Pre-clinical findings provide evidence of the effect of roluperidone on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (“BDNF”), which has been associated with neurogenesis, neuroplasticity, neuroprotection, synapse regulation, learning and memory. As of May 2018, the drug was in phase III clinical trials. In May 2020, the shares of Minerva Neurosciences plummeted 67% after the trial "failed to meet its primary endpoint of reduction in negative symptoms, and key secondary endpoints of improvement in personal and social performance measurements." However, in August of 2022 Minerva submitted a New Drug Application (NDA) to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the approval of roluperidone for the treatment of schizophrenia. The NDA submission in 2022 followed successful completion of a phase III clinical trial which was published in early 2022. Minerva believed that the findings of this second trial supported the claim that the drug was an effective agent for the treatment of negative symptoms in schizophrenia. However, in October 2022, FDA sent Minerva a refusal to file letter pertaining to the New Drug Application for roluperidone for treating negative symptoms in schizophrenia patients.

Doxifluridine is a second generation nucleoside analog prodrug developed by Roche and used as a cytostatic agent in chemotherapy in several Asian countries including China and South Korea. Doxifluridine is not FDA-approved for use in the USA. It is currently being evaluated in several clinical trials as a stand-alone or combination therapy treatment.

















