
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.

Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock containing 25% to 75% ash is described as tuffaceous. Tuff composed of sandy volcanic material can be referred to as volcanic sandstone.

Pumice, called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular volcanic rock that differs from pumice in having larger vesicles, thicker vesicle walls, and being dark colored and denser.

Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and size of the fragments ejected during the eruption. Types of volcanic cones include stratocones, spatter cones, tuff cones, and cinder cones.
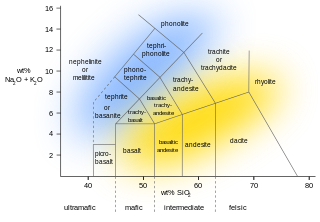
Extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as pyroclastics or tuff. In contrast, intrusive rock refers to rocks formed by magma which cools below the surface.

Volcanic rock is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic rock is artificial, and in nature volcanic rocks grade into hypabyssal and metamorphic rocks and constitute an important element of some sediments and sedimentary rocks. For these reasons, in geology, volcanics and shallow hypabyssal rocks are not always treated as distinct. In the context of Precambrian shield geology, the term "volcanic" is often applied to what are strictly metavolcanic rocks. Volcanic rocks and sediment that form from magma erupted into the air are called "pyroclastics," and these are also technically sedimentary rocks.

The Lassen volcanic area presents a geological record of sedimentation and volcanic activity in and around Lassen Volcanic National Park in Northern California, U.S. The park is located in the southernmost part of the Cascade Mountain Range in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Pacific Oceanic tectonic plates have plunged below the North American Plate in this part of North America for hundreds of millions of years. Heat and molten rock from these subducting plates has fed scores of volcanoes in California, Oregon, Washington and British Columbia over at least the past 30 million years, including these in the Lassen volcanic areas.

Pyroclastic rocks are clastic rocks composed of rock fragments produced and ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions. The individual rock fragments are known as pyroclasts. Pyroclastic rocks are a type of volcaniclastic deposit, which are deposits made predominantly of volcanic particles. 'Phreatic' pyroclastic deposits are a variety of pyroclastic rock that forms from volcanic steam explosions and they are entirely made of accidental clasts. 'Phreatomagmatic' pyroclastic deposits are formed from explosive interaction of magma with groundwater.

Lapilli is a size classification of tephra, which is material that falls out of the air during a volcanic eruption or during some meteorite impacts. Lapilli is Latin for "little stones".

Pisgah Crater, or Pisgah Volcano, is a young volcanic cinder cone rising above a lava plain in the Mojave Desert, between Barstow and Needles, California in San Bernardino County, California. The volcanic peak is around 2.5 miles (4.0 km) south of historic U.S. Route 66-National Old Trails Highway and of Interstate 40, and west of the town of Ludlow. The volcano had a historic elevation of 2,638 feet (804 m), but has been reduced to 2,545 feet (776 m) due to mining.

Tachylite is a form of basaltic volcanic glass. This glass is formed naturally by the rapid cooling of molten basalt. It is a type of mafic igneous rock that is decomposable by acids and readily fusible. The color is a black or dark-brown, and it has a greasy-looking, resinous luster. It is very brittle and occurs in dikes, veins, and intrusive masses. The word originates from the Ancient Greek ταχύς, meaning "swift".

Vesicular texture is a volcanic rock texture characterized by a rock being pitted with many cavities at its surface and inside. This texture is common in aphanitic, or glassy, igneous rocks that have come to the surface of the earth, a process known as extrusion. As magma rises to the surface the pressure on it decreases. When this happens gasses dissolved in the magma are able to come out of solution, forming gas bubbles inside it. When the magma finally reaches the surface as lava and cools, the rock solidifies around the gas bubbles and traps them inside, preserving them as holes filled with gas called vesicles.

In volcanology, a Strombolian eruption is a type of volcanic eruption with relatively mild blasts, typically having a Volcanic Explosivity Index of about 1 to 2. Strombolian eruptions consist of ejection of incandescent cinders, lapilli, and volcanic bombs, to altitudes of tens to a few hundreds of metres. The eruptions are small to medium in volume, with sporadic violence. This type of eruption is named for the Italian volcano Stromboli.

A Vulcanian eruption is a type of volcanic eruption characterized by a dense cloud of ash-laden gas exploding from the crater and rising high above the peak. They usually commence with phreatomagmatic eruptions which can be extremely noisy due to the rising magma heating water in the ground. This is usually followed by the explosive clearing of the vent and the eruption column is dirty grey to black as old weathered rocks are blasted out of the vent. As the vent clears, further ash clouds become grey-white and creamy in colour, with convolutions of the ash similar to those of Plinian eruptions.

Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra, and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has been observed. Some volcanoes may exhibit only one characteristic type of eruption during a period of activity, while others may display an entire sequence of types all in one eruptive series.

Panum Crater is a volcanic cone that is part of the Mono–Inyo Craters, a chain of recent volcanic cones south of Mono Lake and east of the Sierra Nevada, in California, United States. Panum Crater is between 600 and 700 years old, and it exhibits all of the characteristics of the textbook rhyolitic lava dome.

Phreatomagmatic eruptions are volcanic eruptions resulting from interaction between magma and water. They differ from exclusively magmatic eruptions and phreatic eruptions. Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions contain juvenile (magmatic) clasts. It is common for a large explosive eruption to have magmatic and phreatomagmatic components.
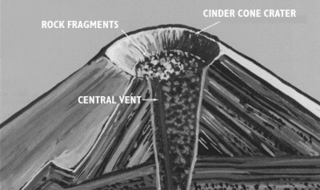
A cinder cone is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions or lava fountains from a single, typically cylindrical, vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as either cinders, clinkers, or scoria around the vent to form a cone that often is symmetrical; with slopes between 30 and 40°; and a nearly circular ground plan. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit.
Menengai Forest is an urban forest situated within the town of Nakuru in Kenya. The Menengai Crater is within the forest. It was gazetted as a forest in the 1930s. It is surrounded by residential areas of Milimani Estate in the South, Ngachura and Bahati in the East, Solai in the North and Olo-Rongai in the West. Various Government of Kenya facilities have been hived off from the forest; these include the Kenya Broadcasting Corporation and the Nakuru G.K Prison. There is also a geothermal exploration project by the Geothermal Development Company inside the Menengai Crater floor.
El Toro volcanic field is part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes in the northern Puna of Argentina. Three of the cones in the volcanic field are located southwest of the town of El Toro and the fourth is found north. Part of a field of monogenetic volcanoes associated with subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate, it is constructed from three main cones and an additional lava flow. The field formed between six and two million years ago.




















