Ethnologue: Languages of the World is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951, and is now published by SIL International, an American evangelical Christian non-profit organization.

The Indo-Aryan languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and Nepal. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages.

Gujarati is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken predominantly by the Gujarati people. Gujarati is descended from Old Gujarati. In India, it is one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Union. It is also the official language in the state of Gujarat, as well as an official language in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. As of 2011, Gujarati is the 6th most widely spoken language in India by number of native speakers, spoken by 55.5 million speakers which amounts to about 4.5% of the total Indian population. It is the 26th most widely spoken language in the world by number of native speakers as of 2007.
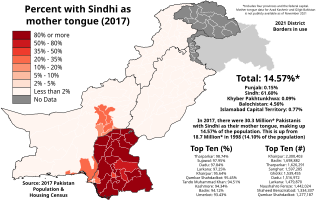
Sindhi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about 30 million people in the Pakistani province of Sindh, where it has official status. It is also spoken by a further 1.7 million people in India, where it is a scheduled language, without any state-level official status. The main writing system is the Perso-Arabic script, which accounts for the majority of the Sindhi literature and is the only one currently used in Pakistan. In India, both the Perso-Arabic script and Devanagari are used.
Avar, also known as Avaric, is a Northeast Caucasian language of the Avar–Andic subgroup that is spoken by Avars, primarily in Dagestan. In 2010, there were approximately 1 million speakers in Dagestan and elsewhere in Russia.

Saraiki is an Indo-Aryan language of the Lahnda group, spoken by 26 million people primarily in the south-western half of the province of Punjab in Pakistan. It was previously known as Multani, after its main dialect.
The Gujarati languages are a Western Indo-Aryan language family, comprising Gujarati and those Indic languages closest to it. They are ultimately descended from Shauraseni Prakrit.

Kutchi or Kachhi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Kutch region of India and Sindh region of Pakistan.

Memoni is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by Kathiawari Memons, from the Kathiawar region of Gujarat, India. Memon from Okha Port, Kutch and some other communities from Kathiawad also use Memoni at their homes.
Dhatki, also known as Dhatti, Thari, is a dialect continuum or cluster/series of smaller dialects all mixed of Sindhi and Rajasthani (Marwari) with varying proportions, the Indo-Aryan Languages of the Indo-European language family.

Luwati is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by 8,940 people known as the Lawatiya in the country of Oman. In total it has been estimated there are 20,000 to 30,000 Lawatiya people. Despite the various names, the Lawatiya refer to the language as Khojki. It is considered an endangered language because a portion of the Lawatiya do not speak Luwati, and it is not continuously passed down to younger generations.

The Swatow dialect, or in Mandarin the Shantou dialect, is a Chinese dialect mostly spoken in Shantou in Guangdong, China. It is a dialect of Chaoshan Min language. It is similar to and largely mutually intelligible with the Teochew dialect.

The Punjabi dialects or Punjabi varieties are the dialects and varieties of the Punjabi language that are part of the Northwestern Indo-Aryan language group of the Indo-European language family widely spoken in the Punjab region of South Asia. The spoken dialects of Punjabi are mutually intelligible with neighbouring dialects and form a dialect continuum.
Pattegar is a Hindu community predominantly residing in the Indian states of Karnataka, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. They wear the sacred thread and are Kshatriyas. They are Somavamshiya Sahasrarjun Kshatriyas or SSK Samaj. and are given reservation in Maharashtra.
Southern Luo is a dialect cluster of Uganda and neighboring countries. Although Southern Luo dialects are mutually intelligible, there are six ethnically and culturally distinct varieties which are considered to be separate languages socially.
Parsi has been used as a name for several languages of South Asia and Iran, some of them spurious:
Makrani is variety of the Balochi language spoken in the historical region of Makran in Balochistan in Pakistan as well as Iran. Spoken by the Makrani people, it is often categorised as an "important" dialect of Balochi. Makrani uses many loanwords especially from Sindhi, Urdu, and Persian. Some people consider Makrani a mix of Balochi and Sindhi. Makrani includes four dialects, Coastal, Lashari, Kechi, and Karachi. The Karachi dialect is spoken in Karachi. Makrani is the second most spoken Balochi dialect after Rakhshani in Iranian Balochistan.
Jatki/Jattki bascically means the language or dielect of Panjabi Jats of Bar region

Sindhi Bhili/Bhilki, is an Indo-Aryan dialect spoken in the Pakistani province of Sindh, as well as some parts of Balochistan. Sindhi Bhili is often referred to as a Sindhi dialect rather than a separate language alongside Lasi.
The Jadgal is an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group which speaks the Jadgali language. Jadgals are present in the Balochistan region of Iran and Pakistan, as well as in Oman.











