The Indo-Aryan languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and Nepal. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages.

Marwari is a language within the Rajasthani language family of the Indo-Aryan languages. Marwari and its closely related varieties like Dhundhari, Shekhawati and Mewari form a part of the broader Marwari language family. It is spoken in the Indian state of Rajasthan, as well as the neighbouring states of Gujarat and Haryana, some adjacent areas in eastern parts of Pakistan, and some migrant communities in Nepal. There are two dozen varieties of Marwari. Marwari is also referred to as simply Rajasthani.

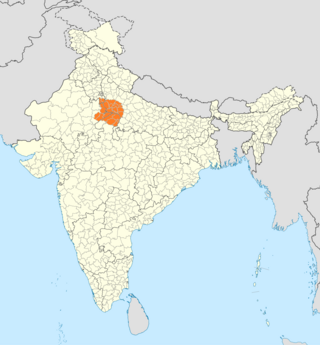
Braj, also known as Vraj, Vraja, Brij or Brijbhumi, is a region in India on both sides of the Yamuna river with its centre at Mathura-Vrindavan in Uttar Pradesh state encompassing the area which also includes Palwal, Ballabhgarh and Nuh in Haryana state, Deeg, Bharatpur, Karauli, and Dholpur in Rajasthan state and Morena District in Madhya Pradesh. Within Uttar Pradesh, it is very well demarcated culturally, the area stretches from the Mathura, Aligarh, Agra, Hathras and districts up to the Farrukhabad, Mainpuri and Etah districts. Braj region is associated with Radha and Krishna who according to scriptures were born in Barsana and Mathura respectively. It is the main centre of Krishna circuit of Hindu pilgrimage.

Bundeli or Bundelkhandi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Bundelkhand region of central India. It belongs to the Central Indo-Aryan languages and is part of the Western Hindi subgroup.

Bagheli or Baghelkhandi is a Central Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Baghelkhand region of central India.

Kauravi, also known as Khaṛībolī, is a dialect of Hindustani descended from Shauraseni Prakrit that is mainly spoken in northwestern Uttar Pradesh, outside of Delhi.

Awadhi, also known as Audhi, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Awadh region of Uttar Pradesh in northern India and in Terai region of western Nepal. The name Awadh is connected to Ayodhya, the ancient city, which is regarded as the homeland of the Hindu god Rama. It was, along with Braj, used widely as a literary vehicle before being displaced by Hindi in the 19th century.

The Hindi Belt, also known as the Hindi Heartland, is a linguistic region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India where various Northern, Central, Eastern and Western Indo-Aryan languages are spoken, which in a broader sense is termed as Hindi languages, with Standard Hindi serving as the lingua franca of the region.

Hathras is a historical city in Uttar Pradesh, India. It is the headquarters of Hathras district, formed on 3 May 1997 by merging parts of Aligarh, Mathura and Agra. It is part of the Aligarh Division.

Agra is one of the 75 districts in the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The district headquarters is the historical city of Agra. Agra district is a part of Agra division.

Aligarh is one of the 75 districts in the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. This district is a part of Aligarh Division. The districts which adjoin Aligarh are Gautam Buddha Nagar, Bulandshahr, Sambhal, Badaun, Kasganj, Hathras and Mathura.
Banarasidas (1586–1643) was a Shrimal Jain businessman and poet of Mughal India. He is known for his poetic autobiography – Ardhakathānaka,, composed in Braj Bhasa, an early dialect of Hindi linked with the region around Mathura. It is the first autobiography written in an Indian language. At the time, he was living in Agra and was 55 years old – the "half" story refers to the Jain tradition, where a "full" lifespan is 110 years.

Bharatpur District is a district in Rajasthan state in western India. The city of Bharatpur is the District Headquarters, Division Headquarters and Headquarters of Bharatpur Police Range of Rajasthan Police. Bharatpur District is a part of National Capital Region of India Delhi.

Rekhta was an early form of the Hindustani language. This style evolved in both the Perso-Arabic and Devanagari scripts and is considered an early form of Modern Standard Urdu and Modern Standard Hindi. According to the Pakistani linguist and historian Tariq Rehman, Rekhta was a highly Persianized register of Hindustani, exclusively used by poets. It was not only the vocabulary that was Persianized, but also the poetic metaphors, inspired by Indian landscapes and seasons, were abandoned in favor of the Persian ones i.e. bahaar (spring) replacing barsaat.

Dhundhari (ढूंढाड़ी), also known as Jaipuri, is a Rajasthani language within the Indo-Aryan language family. It is spoken in the Dhundhar region of northeastern Rajasthan state, India. Dhundari-speaking people are found in four districts – Jaipur, Sawai Madhopur, Dausa, Tonk and some parts of Sikar, Karauli and Gangapur District.

Gangapur City is a city and a municipal council located in Gangapur district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is the administrative headquarters of Gangapur district. It is famous for its Sweet Cuisine Kheermohan and newly built Kushalgarh Baba Shyam Temple.
Old Hindi, or Khariboli was the earliest stage of the Hindustani language, and so the ancestor of today's Modern Standard Hindi and Standard Urdu registers. It developed from Shauraseni Prakrit and was spoken by the peoples of the region around Delhi, in roughly the 10th–13th centuries before the Delhi Sultanate.

Uttar Pradesh is a multilingual state with 3 predominant languages and 26 other languages spoken in the state. The languages of Uttar Pradesh primarily belong to two zones in the Indo-Aryan languages, Central and East.
Braj literature is literature in Braj Bhasha, one of the Western Hindi languages developed as a literary language during the 15th century, Bhakti Movement as a form of devotional songs in praise of Krishna. It is often mystical in nature, related to the spiritual union of people with God, because almost all of Braj poets were considered God-realised saints and their words are thus considered as emanating from a divine source. Much of the traditional Northern Indian literature shares this trait. It literary tradition is a celebration of Krishna. The Braj region has a rich legacy and the medium was mainly the literary vehicle for the poets viz. Surdas, Tulsidas, Acharya Ram Chandra Shukla, Raskhan, Amir Khusrau among others.

Shri Babu Ram Paliwal was an accomplished poet and writer in Hindi and Braj languages. He was best known for his early work ‘Karyalaya Nirdeshika’ for which he received awards by the Government of India and Uttar Pradesh Government. He contributed as Hindi expert in the Ministry of Home Affairs and Ministry of Communications, the Government of India. He made significant contributions towards the development of Hindi language. He was the producer of the 'Braj-Bharati' program of Aakashwani, All India Radio, New Delhi. He had a multifaceted personality and had extensive knowledge of Hindi, Braj and English languages.