
Hurricane Michelle was the fifth costliest tropical cyclone in Cuban history and the strongest hurricane of the 2001 Atlantic hurricane season. The thirteenth named storm and seventh hurricane that year, Michelle developed from a tropical wave that had traversed into the western Caribbean Sea on October 29; the wave had initially moved off the coast of Africa 13 days prior. In its early developmental stages, the depression meandered over Nicaragua, later paralleling the Mosquito Coast before intensifying into tropical storm intensity on November 1; Michelle was upgraded to hurricane strength the following day. Shortly after, rapid intensification ensued within favorable conditions, with the storm's central barometric pressure dropping 51 mbar in 29 hours. After a slight fluctuation in strength, Michelle reached its peak intensity as a Category 4 hurricane with winds of 140 mph (230 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 933 mbar. This tied Michelle with 1999's Lenny as the fourth most powerful November hurricane on record in the Atlantic Basin, behind only the 1932 Cuba hurricane and 2020 Hurricanes Iota and Eta. At roughly the same time, the hurricane began to accelerate northeastward; this brought the intense hurricane to a Cuban landfall within the Bay of Pigs later that day. Crossing over the island, Michelle was weakened significantly, and was only a Category 1 hurricane upon reentry into the Atlantic Ocean. The hurricane later transitioned into an extratropical cyclone over The Bahamas on November 5, before being absorbed by a cold front the following day.

The 2017 Pacific hurricane season was an above average Pacific hurricane season in terms of named storms, though less active than the previous three, featuring eighteen named storms, nine hurricanes, and four major hurricanes. Despite the considerable amount of activity, most of the storms were weak and short-lived. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the respective regions. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as illustrated in 2017 by the formation of the season's first named storm, Tropical Storm Adrian, on May 9. At the time, this was the earliest formation of a tropical storm on record in the eastern Pacific basin proper. The season saw near-average activity in terms of accumulated cyclone energy (ACE), in stark contrast to the extremely active seasons in 2014, 2015, and 2016; and for the first time since 2012, no tropical cyclones formed in the Central Pacific basin. However, for the third year in a row, the season featured above-average activity in July, with the ACE value being the fifth highest for the month. Damage across the basin reached $375.28 million (2017 USD), while 45 people were killed by the various storms.

The 2017 Atlantic hurricane season was a devastating, extremely active Atlantic hurricane season and the costliest on record, with a damage total of at least $294.92 billion (USD). The season featured 17 named storms, 10 hurricanes, and 6 major hurricanes. Most of the season's damage was due to hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria. Another notable hurricane, Nate, was the worst natural disaster in Costa Rican history. These four storm names were retired following the season due to the number of deaths and amount of damage they caused.

Tropical Storm Julia was a weak tropical cyclone that caused minor damage across the Eastern United States in September 2016. The tenth named storm of the 2016 Atlantic hurricane season, Julia developed from a tropical wave near the coast of east-central Florida on September 13. Initially a tropical depression, the system soon made landfall near Jensen Beach. Despite moving inland, the cyclone intensified into a tropical storm, shortly before strengthening further to reach maximum sustained winds of 50 mph (85 km/h). Julia then drifted north-northwestward and then northeastward, moving offshore the Southeastern United States on September 14. A cyclonic loop occurred as strong westerly air developed in the region, with the shear causing fluctuations in intensity. By September 19, Julia degenerated into a remnant low, which later transitioned into an extratropical cyclone and moved inland over North Carolina before dissipating on September 21.

Hurricane Franklin was the first hurricane to make landfall in the Mexican state of Veracruz since Hurricane Karl in 2010. The sixth named storm, first hurricane and the first of ten consecutive hurricanes of the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season, Franklin formed on August 7 out of a tropical wave that was first tracked in the southeastern Caribbean Sea on August 3. The storm strengthened within a favorable environment and made landfall on the Yucatán Peninsula as a moderate tropical storm early on August 8 north of Belize. Weakening occurred as it crossed the peninsula, but Franklin re-emerged into the Bay of Campeche later that day, restrengthening quickly to become the season's first hurricane. It made landfall near Lechuguillas, Veracruz, on August 10 as a Category 1 hurricane, before rapidly weakening over the mountainous terrain of Mexico and dissipating shortly afterwards. On August 12, the storm's remnant mid-level circulation combined with a developing low in the Eastern Pacific to form Tropical Storm Jova.

Hurricane Harvey was the costliest tropical cyclone on record, inflicting roughly $125 billion in damage across the Houston metropolitan area and Southeast Texas. It lasted from mid-August until early September 2017, with many records for rainfall and landfall intensity set during that time. The eighth named storm, third hurricane, and first major hurricane of the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season, Harvey originated from a broad area of low pressure southwest of Cape Verde that was first monitored on August 13. Tracking steadily westward, the disturbance developed strong convection, a well-defined circulation, and sustained tropical storm-force winds, leading to the classification of Tropical Storm Harvey late on August 17. Moderate easterly vertical wind shear kept Harvey weak, as it continued westwards into the Caribbean Sea; despite repeated predictions for gradual intensification by the National Hurricane Center, Harvey eventually opened up into a tropical wave on August 19. The remnants of Harvey continued to move westwards and reached the Yucatán Peninsula on August 22, and were forecast to regenerate into a tropical cyclone after exiting land.

Potential Tropical Cyclone Ten was a damaging storm that was the tenth tropical disturbance designated by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) during the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season. The disturbance was deemed to have a very high chance of becoming a tropical cyclone while posing a threat to populated areas and was designated a "Potential Tropical Cyclone". The storm caused flooding and brought tropical storm-force winds to parts of the Southeastern United States and the Mid-Atlantic states, particularly Florida and the Carolinas, before going on to affect parts of Atlantic Canada. Potential Tropical Cyclone Ten was the tenth storm that had advisories issued on it by the NHC in 2017, and the only such system that failed to fully develop into a tropical cyclone during that Atlantic hurricane season. Potential Tropical Cyclone Ten originated from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of West Africa on August 13. The disturbance slowly tracked its way westward across the Atlantic Ocean, before reaching Florida in late August. The disturbance came close to developing into a tropical storm while it was situated off the coast of the Carolinas; however, strong wind shear and outflow from Hurricane Harvey prevented the storm from organizing into a tropical cyclone. The system transitioned into an extratropical cyclone instead, and became a strong hurricane-force low to the south of Newfoundland, before being absorbed by another extratropical system near Iceland on September 3.
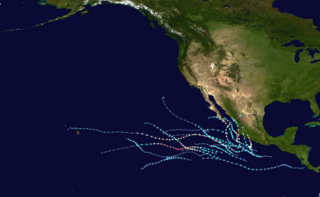
The 2021 Pacific hurricane season was a moderately active Pacific hurricane season, with above-average activity in terms of number of named storms, but below-average activity in terms of major hurricanes, as 19 named storms, 8 hurricanes, and 2 major hurricanes formed in all. It also had a near-normal accumulated cyclone energy (ACE). The season officially began on May 15, 2021 in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, and on June 1, 2021, in the Central Pacific in the Northern Hemisphere. The season ended in both regions on November 30, 2021. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in these regions of the Pacific and are adopted by convention. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as illustrated by the formation of Tropical Storm Andres on May 9, which was the earliest forming tropical storm on record in the Eastern Pacific. Conversely, 2021 was the second consecutive season in which no tropical cyclones formed in the Central Pacific.

Tropical Storm Imelda was a tropical cyclone which was the fourth-wettest storm on record in the U.S. state of Texas, causing devastating and record-breaking floods in southeast Texas. The eleventh tropical cyclone and ninth named storm of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season, Imelda formed out of an upper-level low that developed in the Gulf of Mexico and moved westward. Little development occurred until the system was near the Texas coastline, where it rapidly developed into a tropical storm before moving ashore shortly afterward on September 17. Imelda weakened after landfall, but continued bringing large amounts of flooding rain to Texas and Louisiana, before dissipating on September 21.

Tropical Storm Bertha was a rapidly forming and short-lived off-season tropical storm that affected the Eastern United States in late May 2020. The second named storm of the very active 2020 Atlantic hurricane season, Bertha originated from a trough in the Gulf of Mexico. The National Hurricane Center (NHC) only anticipated slight development as the trough moved over southern Florida, bringing torrential rainfall. The system rapidly organized on May 27 after it emerged into the western Atlantic Ocean, developing a small, well-defined circulation. That day, the disturbance developed into Tropical Storm Bertha east of Georgia, and a few hours later it moved ashore near Isle of Palms, South Carolina with peak winds of 50 mph (80 km/h). The storm weakened over land and dissipated late on May 28 over West Virginia.

Hurricane Dolores was a powerful and moderately damaging tropical cyclone whose remnants brought record-breaking heavy rains and strong winds to California. The seventh named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane of the record-breaking 2015 Pacific hurricane season, Dolores formed from a tropical wave on July 11. The system gradually strengthened, attaining hurricane status on July 13. Dolores rapidly intensified as it neared the Baja California peninsula, finally peaking as a Category 4 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson scale with winds of 130 mph (215 km/h) on July 15. An eyewall replacement cycle began and cooler sea-surface temperatures rapidly weakened the hurricane, and Dolores weakened to a tropical storm two days later. On July 18, Dolores degenerated into a remnant low west of the Baja California peninsula.

Hurricane Marco was the first of two tropical cyclones to threaten the Gulf Coast of the United States within a three-day period. The thirteenth named storm and third hurricane of the record-breaking 2020 Atlantic hurricane season, Marco developed from a fast-moving tropical wave west of the Windward Islands and south of Jamaica on August 20. The fast motion of the wave inhibited intensification initially, but as the wave slowed down and entered a more favorable environment, the system developed into a tropical depression, which in turn rapidly intensified into a strong tropical storm. Due to strong wind shear, Marco's intensification temporarily halted. However, after entering the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico on August 23, Marco briefly intensified into a hurricane, only to quickly weaken later that evening due to another rapid increase in wind shear. Marco subsequently weakened to a tropical depression before degenerating into a remnant low early the next morning. Marco's remnants subsequently dissipated on August 26.

Hurricane Sally was a destructive and slow-moving Atlantic hurricane that was the first hurricane to make landfall in the U.S. state of Alabama since Ivan in 2004, coincidentally on the same date in the same place. The eighteenth named storm and seventh hurricane of the extremely active 2020 Atlantic hurricane season, Sally developed from an area of disturbed weather which was first monitored over the Bahamas on September 10. The system grew a broad area of low-pressure on September 11, and was designated as a tropical depression late that day. Early the next day, the depression made landfall at Key Biscayne and subsequently strengthened into Tropical Storm Sally that afternoon. Moderate northwesterly shear prevented significant intensification for the first two days, but convection continued to grow towards the center and Sally slowly intensified. On September 14, a center reformation into the center of the convection occurred, and data from a hurricane hunter reconnaissance aircraft showed that Sally had rapidly intensified into a strong Category 1 hurricane. However, an increase in wind shear and upwelling of colder waters halted the intensification and Sally weakened slightly on September 15 before turning slowly northeastward. Despite this increase in wind shear, it unexpectedly re-intensified, reaching Category 2 status early on September 16 before making landfall at peak intensity at 09:45 UTC on September 16, near Gulf Shores, Alabama, with maximum sustained winds of 110 mph (180 km/h) and a minimum central pressure of 965 millibars (28.5 inHg). The storm rapidly weakened after landfall before transitioning into an extratropical low at 12:00 UTC the next day. Sally's remnants lasted for another day as they moved off the coast of the Southeastern United States before being absorbed into another extratropical storm on September 18.

Tropical Storm Beta was a tropical cyclone that brought heavy rainfall, flooding, and severe weather to the Southeastern United States in September 2020. The twenty-third tropical depression and twenty-third named storm of the record-breaking 2020 Atlantic hurricane season, Beta originally formed from a trough of low pressure that developed in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico on September 10. The low moved slowly southwestward, with development hampered initially by the development of nearby Hurricane Sally. After Sally moved inland over the Southeastern United States and weakened, the disturbance became nearly stationary in the southwestern Gulf, where it began to organize. By September 16, the storm had gained a low-level circulation center and had enough organization to be designated as Tropical Depression Twenty-Two. The system held its intensity for a day due to the influence of strong wind shear and dry air, before eventually attaining tropical storm strength. It slowly moved northward and intensified to a mid-range tropical storm before dry air and wind shear halted its intensification. Beta then became nearly stationary on September 19, before starting to move west towards the Texas coast the next day, weakening as it approached. On September 21, Beta made landfall near Matagorda Peninsula, Texas as a minimal tropical storm. It subsequently weakened to a tropical depression the next day before becoming post-tropical early on September 23. Its remnants moved northeastward, before the center elongated and merged with a cold front early on September 25.

Hurricane Delta was the record-tying fourth named storm of 2020 to make landfall in Louisiana, as well as the record-breaking tenth named storm to strike the United States in that year. The twenty-sixth tropical cyclone, twenty-fifth named storm, tenth hurricane, and third major hurricane of the record-breaking 2020 Atlantic hurricane season, Delta formed from a tropical wave which was first monitored by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) on October 1. Moving westward, the tropical wave began to quickly organize. A well-defined center of circulation formed with sufficiently organized deep convection on October 4, and was designated as Tropical Depression Twenty-six and soon thereafter, Tropical Storm Delta. Extremely rapid intensification ensued throughout October 5 into October 6, with Delta becoming a Category 4 hurricane within 28 hours of attaining tropical storm status. The rate of intensification was the fastest in the Atlantic basin since Hurricane Wilma in 2005. After peaking in intensity however, an unexpected increase in wind shear and dry air quickly weakened the small storm before it made landfall in Puerto Morelos, Mexico as a Category 2 hurricane with 105 mph (169 km/h) winds. It weakened some more over land before emerging into the Gulf of Mexico, where it was downgraded to a Category 1 hurricane. After that, it began to restrengthen, regaining Category 3 status late on October 8. It then turned northward and reached a secondary peak intensity of 953 mbar (28.14 inHg) and winds of 120 mph early on October 9. Delta then began to turn more north-northeastward into an area of cooler waters, higher wind shear, and dry air, causing it to weaken back to Category 2 status. Delta then made landfall at 23:00 UTC near Creole, Louisiana with winds of 100 mph (160 km/h) and a pressure of 970 mbar (29 inHg). The storm began to weaken more rapidly after landfall, becoming post-tropical just 22 hours later.

Hurricane Zeta was a late-season major hurricane in 2020 that made landfall on the Yucatán Peninsula and then in southeastern Louisiana, the latest on record to do so at such strength in the United States. Zeta was the record-tying sixth hurricane of the year to make landfall in the United States. The twenty-seventh named storm, twelfth hurricane and fifth major hurricane of the extremely active 2020 Atlantic hurricane season, Zeta formed from a broad area of low pressure that formed in the western Caribbean Sea on October 19. After battling wind shear, the quasi-stationary low organized into Tropical Depression Twenty-Eight on October 24. The system strengthened into Tropical Storm Zeta early on October 25 before becoming a hurricane the next day as it began to move northwestward. Hurricane Zeta made landfall on the Yucatán Peninsula late on October 26 and weakened while inland to a tropical storm, before moving off the northern coast of the peninsula on October 27. After weakening due to dry air entrainment, Zeta reorganized and became a hurricane again, and eventually a Category 2 hurricane, as it turned northeastward approaching the United States Gulf Coast on October 28. It continued to strengthen until it reached its peak intensity as a major Category 3 hurricane with 115-mile-per-hour (185 km/h) sustained winds and a minimum pressure of 970 mbar (28.64 inHg) as it made landfall at Cocodrie, Louisiana, that evening. Zeta continued on through Mississippi and parts of Alabama with hurricane-force winds. Zeta gradually weakened as it accelerated northeastward, and became post-tropical on October 29, as it moved through central Virginia, dissipating shortly afterwards off the coast of New Jersey. After bringing accumulating snow to parts of New England, the extratropical low-pressure system carrying Zeta's remnant energy impacted the United Kingdom on November 1 and 2.

Tropical Storm Philippe was a weak and disorganized tropical cyclone which affected Central America, Cuba, and Florida during October 2017. The sixteenth named storm of the extremely-active 2017 Atlantic hurricane season, Philippe originated from the interaction of a tropical wave which exited the coast of West Africa on October 16, and the Central American Gyre on October 24. This formed a broad area of low pressure the next day, that later organized into a tropical depression at 12:00 UTC on October 28. The depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Philippe just six hours later, before making landfall west of the Bay of Pigs in Cuba just a few hours later. Philippe quickly degraded into a tropical depression inland, before dissipating at 0:00 UTC the following day. The remnants later formed into a new low pressure area off the coast of Florida before merging with a cold front, later that same day.

Tropical Storm Danny was a weak and short-lived tropical cyclone that caused minor damage to the U.S. states of South Carolina and Georgia. The fourth named storm of the 2021 Atlantic hurricane season, the system formed from an area of low-pressure that developed from an upper-level trough over the central Atlantic Ocean on June 22. Moving west-northwestward, the disturbance gradually developed as convection, or showers and thunderstorms, increased over it. Although it was moving over the warm Gulf Stream, the organization of the disturbance was hindered by strong upper-level wind shear. By 18:00 UTC of June 27, as satellite images showed a well-defined center and thunderstorms, the system was upgraded to a tropical depression by the National Hurricane Center (NHC). At 06:00 UTC on the next day, the system further strengthened into Tropical Storm Danny east-southeast of Charleston, South Carolina. Danny continued its track towards South Carolina while slowly strengthening, subsequently reaching its peak intensity at that day of 45 mph (72 km/h) and a minimum central pressure of 1,009 mbar (29.8 inHg) at 18:00 UTC. Danny then made landfall in Pritchards Island, north of Hilton Head, in a slightly weakened state at 23:20 UTC on the same day, with winds of 40 mph (64 km/h) and indicating that Danny weakened prior to moving inland. The system then weakened to a tropical depression over east-central Georgia, before dissipating shortly afterward.

Tropical Storm Fred was a strong tropical storm which affected much of the Greater Antilles and the Southeastern United States in August 2021. The sixth tropical storm of the 2021 Atlantic hurricane season, Fred originated from a tropical wave first noted by the National Hurricane Center on August 4. As the wave drifted westward, advisories were initiated on the wave as a potential tropical cyclone by August 9 as it was approaching the Leeward Islands. Entering the Eastern Caribbean Sea after a close pass to Dominica by the next day, the potential tropical cyclone continued northwestward. By August 11, the disturbance had formed into Tropical Storm Fred just south of Puerto Rico, shortly before hitting the Dominican Republic on the island of Hispaniola later that day. The storm proceeded to weaken to a tropical depression over the highly mountainous island, before emerging north of the Windward Passage on August 12. The disorganized tropical depression turned to the west and made a second landfall in Northern Cuba on August 13. After having its circulation continuously disrupted by land interaction and wind shear, the storm degenerated into a tropical wave as it was turning northward near the western tip of Cuba the following day. Continuing north, the remnants of Fred quickly re-organized over the Gulf of Mexico, regenerating into a tropical storm by August 15. Fred continued towards the Florida Panhandle and swiftly intensified to a strong 65 mph (105 km/h) tropical storm before making landfall late on August 16 and moving into the state of Georgia. Afterward, Fred continued moving north-northeastward, before degenerating into an extratropical low on August 18. Fred's remnants later turned eastward, and the storm's remnants dissipated on August 20, near the coast of Massachusetts.






















