Type I keratins (or Type I cytokeratins) are cytokeratins that constitute the Type I intermediate filaments (IFs) of the intracytoplasmatic cytoskeleton, which is present in all mammalian epithelial cells. Most of the type I keratins consist of acidic, low molecular weight proteins which in vivo are arranged in pairs of heterotypic Type I and Type II keratin chains, coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues.
Type I keratins are encoded on chromosome 17q and encompasses: K9, K10, K11, K12, K13, K14, K15, K16, K17, K18, K19 and K20. Their molecular weight ranges from 40 kDa (K19) to 64 kDa (K9).

Keratin is one of a family of fibrous structural proteins. It is the key structural material making up hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, calluses, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only among sauropsids . Keratin resists digestion, which is why cats regurgitate hairballs.

Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 7 also known as cytokeratin-7 (CK-7) or keratin-7 (K7) or sarcolectin (SCL) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT7 gene. Keratin 7 is a type II keratin. It is specifically expressed in the simple epithelia lining the cavities of the internal organs and in the gland ducts and blood vessels.

Keratin 6A is one of the 27 different type II keratins expressed in humans. Keratin 6A was the first type II keratin sequence determined. Analysis of the sequence of this keratin together with that of the first type I keratin led to the discovery of the four helical domains in the central rod of keratins. In humans Keratin 6A is encoded by the KRT6A gene.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 4 also known as cytokeratin-4 (CK-4) or keratin-4 (K4) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT4 gene.
Type II keratins constitutes the Type II intermediate filaments (IFs) of the intracytoplasmatic cytoskeleton, which is present in all mammalian epithelial cells. The type 2 cytokeratins consist of basic or neutral, high molecular weight proteins which in vivo are arranged in pairs of heterotypic Type I and Type II keratin chains, coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues.

Keratin 14 is a member of the type I keratin family of intermediate filament proteins. Keratin 14 was the first type I keratin sequence determined. Keratin 14 is also known as cytokeratin-14 (CK-14) or keratin-14 (KRT14). In humans it is encoded by the KRT14 gene.

Keratin 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT13 gene.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 also known as cytokeratin-10 (CK-10) or keratin-10 (K10) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT10 gene. Keratin 10 is a type I keratin.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19 also known as cytokeratin-19 (CK-19) or keratin-19 (K19) is a 40 kDa protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT19 gene. Keratin 19 is a type I keratin.

Keratin 18 is a type I cytokeratin. It is, together with its filament partner keratin 8, perhaps the most commonly found products of the intermediate filament gene family. They are expressed in single layer epithelial tissues of the body. Mutations in this gene have been linked to cryptogenic cirrhosis. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT17 gene.

Keratin 16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT16 gene.

Keratin 15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT15 gene.
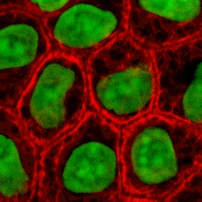
Cytokeratins are keratin proteins found in the intracytoplasmic cytoskeleton of epithelial tissue. They are an important component of intermediate filaments, which help cells resist mechanical stress. Expression of these cytokeratins within epithelial cells is largely specific to particular organs or tissues. Thus they are used clinically to identify the cell of origin of various human tumors.

Keratin 5, also known as KRT5, K5, or CK5, is a protein that is encoded in humans by the KRT5 gene. It dimerizes with keratin 14 and forms the intermediate filaments (IF) that make up the cytoskeleton of basal epithelial cells. This protein is involved in several diseases including epidermolysis bullosa simplex and breast and lung cancers.
Keratin 6B is a type II cytokeratin, one of a number of isoforms of keratin 6. It is found with keratin 16 and/or keratin 17 in the hair follicles, the filiform papillae of the tongue and the epithelial lining of oral mucosa and esophagus. This keratin 6 isoform is thought be less abundant than the closely related keratin 6A protein. Mutations in the gene encoding this protein have been associated with pachyonychia congenita, an inherited disorder of the epithelial tissues in which this keratin is expressed, particularly leading to structural abnormalities of the nails, the epidermis of the palms and soles, and oral epithelia. Keratin 6B is associated with the PC-K6B subtype of pachyonychia congenita.

Keratin 6C, is a type II cytokeratin, one of a number of isoforms of keratin 6 encoded by separate genes located within the type II keratin gene cluster on human chromosome 12q. This gene was uncovered recently by the Human Genome Project and its expression patterns in humans remains unknown.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT23 gene.

Keratin, type I cuticular Ha2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT32 gene.

Keratin, type I cuticular Ha4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT34 gene.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.



